Abstract
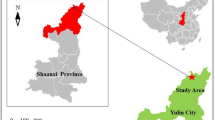
We investigated the concentration of heavy metals in the Fe–Mn nodules in soils derived from the carbonate rocks of typical karst areas in Guangxi, Southwest China. Compared with the soil background values in Guangxi, heavy metals are substantially enriched in the following order: Cd (268.13) > Pb (39.46) > Cr (11.80) > Zn (8.43) > Ni (6.16) > Cu (3.65). CaCl2 extraction results indicate that heavy metals in the nodules are substantially stable, while the proportions of the metals released to the surrounding environment are extremely low (≤ 0.003%). Moreover, pH-static leaching experiments indicate that heavy metals can hardly be dissolved into the surrounding soil environment under natural conditions (pH 6–8). However, once the soil environment is acidified, heavy metals incorporated in the nodules will gradually release into the surrounding environment, thereby causing potential ecological risks.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen H, Teng Y, Lu S, Wang Y, Wang J (2015) Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China. Sci Total Environ 512–513:143–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.01.025
China National Environmental Monitoring Centre (CNEMC) (1990) Elemental background values of soils in China. Environmental Science Press of China, Beijing
China Geological Survey (CGS) (2015) China cultivated land geochemistry survey report.
CEN/TS 14997 (2006) Characterization of waste-leaching behaviour tests-influence of pH on leaching with continuous pH-control. CEN, Brussels
Duan Q, Lee J, Liu Y, Chen H, Hu H (2016) Distribution of heavy metal pollution in surface soil samples in China: A graphical review. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 97(3):303–309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1857-9
Duan YR, Yang ZF, Yu T, Yang Q, Liu X, Ji WB, Jiang HY, Zhuo XX, Wu TS, Qin JX, Wang L (2020) Geogenic cadmium pollution in multi-medians caused by black shales in Luzhai, Guangxi. Environ Pollut 260:113905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113905
Ettler V, Tomášová Z, Komárek M, Mihaljevič M, Šebek O, Michálková Z (2015) The pH dependent long–term stability of amorphous manganese oxide in smelter–polluted soils: implication for chemical stabilization of metals and metalloids. J Hazard Mater 286:386–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.01.018
Ettler V, Chren M, Mihaljevič M, Drahota P, Kříbek B, Bohdan VF, Sracek O, Vaněk A, Penížek V, Komárek M, Mapani B, Kamona F (2017) Characterization of Fe–Mn concentric nodules from luvisol irrigated by mine water in a semi–arid agricultural area. Geoderma 299:32–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.03.022
Feng JL, Lin YC, Gao SP, Zhang JF (2012) Enrichment of trace elements in ferromanganese concretions from terra rossa and their potential desorption. Geochem J 46:151–161
Gao T, Ke S, Wang SJ, Li FB, Liu CS, Lei J, Liao CZ, Wu F (2018) Contrasting Mg isotopic compositions between Fe–Mn nodules and surrounding soils: accumulation of light Mg isotopes by Mg-depleted clay minerals and Fe oxides. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 237:205–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2018.06.028
Gasparatos D, Tarenidis D, Haidouti C, Oikonomou G (2005) Microscopic structure of soil Fe-Mn nodules: environmental implication. Environ Chem Lett 2(4):175–178. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-004-0092-5
Gasparatos D (2013) Sequestration of heavy metals from soil with Fe–Mn concretions and nodules. Environ Chem Lett 11(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-012-0386-y
Gu QB, Yang ZF, Yu T, Ji JF, Hou QY, Zhang QZ (2019) Application of ecogeochemical prediction model to safely exploit seleniferous soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 177:133–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.03.084
Houba VJG, Temminghoff EJM, Gaikhorst GA, Van Vark W (2000) Soil analysis procedures using 0.01 M calcium chloride as extraction reagent. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 31:1299–1396. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103620009370514
Jia ZY, Wang JX, Zhou XD, Zhou YJ, Li Y, Li BJ, Zhou SL (2019) Identification of the sources and influencing factors of potentially toxic elements accumulation in the soil from a typical karst region in Guangxi, Southwest China. Environ Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113505
Loganathan P, Vigneswaran S, Kandasamy J, Naidu R (2012) Cadmium sorption and desorption in soils: a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 42:489–533. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2010.520234
MNR (Ministry of Nature Resources of the Republic of China) and Ministry of Environmental Protection (MEP) (2014) A National Soil Pollution Survey Bulletin
Neaman A, Mouélé F, Trolard F, Bourrié G (2004) Improved methods for selective dissolution of Mn oxides: applications for studying trace element associations. Appl Geochem 19:973–979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2003.12.002
Palumbo B, Bellanca A, Neri R, Roe MJ (2001) Trace metal partitioning in Fe–Mn nodules from Sicilian soils, Italy. Chem Geol 173:257–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2541(00)00284-9
Quezada-Hinojosa RP, Föllmi KB, Verrecchia E, Adatte T, Matera V (2015) Speciation and multivariable analyses of geogenic cadmium in soils at Le Gurnigel, Swiss Jura Mountains. CATENA 125:10–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2014.10.003
Römkens PF, Guo HY, Chu CL, Liu TS, Chiang CF, Koopmans GF (2009) Characterization of soil heavy metal pools in paddy fields in Taiwan: chemical extraction and solid–solution partitioning. J Soils Sediments 9:216–228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-009-0075-z
Sun ZX, Jiang YY, Wang QB, Owens PR (2018) Fe-Mn nodules in a southern Indiana loess with a fragipan and their soil forming significance. Geoderma 313:92–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2017.10.025
Tan WF, Liu F, Feng XH, Huang QY, Li XY (2005) Adsorption and redox reactions of heavy metals on Fe–Mn nodules from chinese soils. J Colloid Interface Sci 284(2):600–605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.10.049
Tan WF, Liu F, Li YH, Hu HQ, Huang QY (2006) Elemental composition and geochemical characteristics of iron–manganese nodules in main soils of China. Pedosphere 16:72–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(06)60028-3
Temur S, Orhan H, Deli A (2009) Geochemistry of the limestone of Mortas Formation and related terra rossa, Seydisehir, Konya, Turkey. Geochem Int 47:67–93. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016702909010054
Wang P, Chen H, Kopittke PM, Zhao FJ (2019) Cadmium contamination in agricultural soils of China and the impact on food safety. Environ Pollut 249:1038–1048. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.03.063
Wen YB, Yang ZF, Zhuo XX, Guan DX, Song YX, Guo C, Ji JF (2019a) Evaluation of various approaches to predict cadmium bioavailability to rice grown in soils with high geochemical background in the karst region, Southwestern China. Environ Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113645
Wen YB, Li W, Yang ZF, Zhang QZ, Ji JF (2019b) Enrichment and source identification of Cd and other heavy metals in soils with high geochemical background in the karst region, Southwestern China. Chemosphere. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125620
Wei X, Ji HB, Wang SJ, Chu HS, Song CS (2014) The formation of representative lateritic weathering covers in south-central Guangxi (southern China). CATENA 118:55–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2014.01.019
Xie XJ, Ren TX, Sun H (2012) Geochemical atlas of China. Geological Publishing House, Beijing
Yamasaki SI, Takeda A, Nunohara K, Tsuchiya N (2013) Red soils derived from limestone contain higher amounts of trace elements than those derived from various other parent materials. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 59(5):692–699. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380768.2013.822301
Yang ZF, Yu T, Li M, Xi XH, Yun WJ, Ye JY, Liu RM, Cheng HX, Zhou GH, Cao SP, Bai RJ, Jin LX, Hou QY, Feng HY, Xia XQ, Yang Q, Zeng MZ (2016) DZ/T 0295-2016. Specification of land quality geochemical evaluation. Geological Publishing House, Beijing, China
Yu XL, Lu SG (2016) Micrometer-scale internal structure and element distribution of Fe-Mn nodules in Quaternary red earth of Eastern China. J Soils Sediments 16(2):621–633. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1212-5
Zhang MK, Liu ZY, Wang H (2010) Use of single extraction methods to predict bioavailability of heavy metals in polluted soils to rice. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 41(7):820–831. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103621003592341
Zhang S, Song J, Cheng Y, Lv M (2018) Proper management of lead–contaminated agricultural lands against the exceedance of lead in agricultural produce: derivation of local soil criteria. Sci Total Environ 634:321–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.337
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (Granted No. 2017YFD0800304), the ecological geochemical survey of heavy metals in typical soils of Guangxi and the research on the abnormal genesis and ecological effects of cadmium, selenium and germanium in soils of Guangxi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, W., Yang, Z., Yu, T. et al. Potential Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in the Fe–Mn Nodules in the Karst Area of Guangxi, Southwest China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 106, 51–56 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-020-02837-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-020-02837-6