Abstract
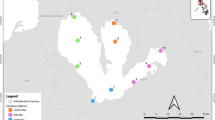
Organic pollutants are widespread environmental pollutants with high toxicity, persistence, and bioaccumulation. Our aim was to investigate the distribution of aromatic amines, phenols, chlorobenzenes, and naphthalenes in the surface sediment of the Dianchi Lake, China. Nineteen surface sediment samples were collected from the Dianchi Lake, and 40 types of organic pollutants were analyzed via gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. The total organic pollutant concentrations in the surface sediment of the Dianchi Lake varied from 27.4 to 1.62 × 103 ng/g. The concentrations of phenols were much higher than those in other water bodies but still within a controllable range, whereas the concentrations of the other organic pollutant classes were similar or even lower. The detection ratio of 3- or 4-methylphenol was the highest (100.00%) among the pollutants. The average total organic pollutant concentrations decreased in the following order: Caohai (540 ng/g)>the middle of Waihai (488 ng/g)>the edge of Waihai (351 ng/g)>Haigeng Dam (90.4 ng/g). Pearson analysis showed a strong correlation among 1-methylnaphthalene, 2-methylnaphthalene, 1,3-dinitronaphthalene, and 1,4-dinitronaphthalene (p<0.01). Caohai, the north lakeshore of Waihai and the south of Waihai showed higher risk because of high concentration; meanwhile, 1,4-dichlorobenzene, 3- or 4- methylphenol and 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene were more likely to cause risks.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cressie N (1990). The origins of kriging. Mathematical Geology, 22(3): 239–252
Department of Ecology of Washington State (2013). Sediment Management Standards. Chapter 173–204 WAC. D. C. Washington D.C.: Department of Ecology of Washington State
Ding W, Aldous K M, Briggs R G, Valente H, Hilker D R, Connor S, Eadon G A (1992). Application of multivariate statistical analysis to evaluate local sources of chlorobenzene congeners in soil samples. Chemosphere, 25(5): 675–690
Fan S, Liu H, Zheng G, Wang Y, Wang S, Liu Y, Liu X, Wan Y (2018). Differences in phytoaccumulation of organic pollutants in freshwater submerged and emergent plants. Environmental Pollution, 241: 247–253
Fan S, Wang B, Liu H, Gao S, Li T, Wang S, Liu Y, Liu X, Wan Y (2017). Trophodynamics of organic pollutants in pelagic and benthic food webs of Lake Dianchi: Importance of ingested sediment as uptake route. Environmental Science & Technology, 51(24): 14135–14143
Feng Y H, Lin Y S, Zhang X F, Xu Y G, Yu F, Xu J (2007). Organic contamination in river sediment and its distribution characteristics in southern Jiangsu. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 26(4): 1240–1244 (in Chinese)
Hu X Y, Gao B L, Chen T, Wang H T, Jin J, Rao Z, Zhu X Q, Wang X J, Wei B K, Zhan N (2019). Distribution of 16 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Dianchi Lake surface sediments after the integrated water environment control project. Environmental Sciences, 40(8): 3501–3508 (in Chinese)
Huang B, Wang B, Ren D, Jin W, Liu J, Peng J, Pan X (2013). Occurrence, removal and bioaccumulation of steroid estrogens in Dianchi Lake catchment, China. Environment International, 59(3): 262–273
Kan E, Koh C, Lee K, Kang J (2015). Decomposition of aqueous chlorinated contaminants by UV irradiation with H2O2. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 9(3): 429–435
Kang C, Bao S, Wang Y, Xiao K, Zhu L, Liu F, Tian T (2018). Comparison of the photoconversion of 1-chloronaphthalene and 2, 3- dichlornaphthalene in water. Water Science and Technology, 78(9): 1946–1955
Khairy M A (2013). Assessment of priority phenolic compounds in sediments from an extremely polluted coastal wetland (Lake Maryut, Egypt). Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185(1): 441–455
Li H, Qu R, Yan L, Guo W, Ma Y (2015). Field study on the uptake and translocation of PBDEs by wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in soils amended with sewage sludge. Chemosphere, 123: 87–92
Li Q, Xu X, Fang Y, Xiao R, Wang D, Zhong W (2018). The temporal changes of the concentration level of typical toxic organics in the river sediments around Beijing. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 12(6): 8
Li X, Janssen A B G, de Klein J J M, Kroeze C, Strokal M, Ma L, Zheng Y (2019). Modeling nutrients in Lake Dianchi (China) and its watershed. Agricultural Water Management, 212: 48–59
Lin P, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Chen C, Xie Y, Suffet I H (2015). The influence of chlorinated aromatics’ structure on their adsorption characteristics on activated carbon to tackle chemical spills in drinking water source. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 9(1): 138–146
Lu X, Chen C, Zhang S, Hou Z, Yang J (2013). Concentration levels and ecological risks of persistent organic pollutants in the surface sediments of Tianjin coastal area, China. The Scientific World Journal, 2013: 1–8
Ma W, Pu C S, Luo J C (2013). Hydrodynamic characteristics of Dianchi Lake and its influence on accumulation of blue-green algae in Dianchi Lake. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 44(S1): 22–27 (in Chinese)
Mahmood A, Syed J H, Malik R N, Zheng Q, Cheng Z, Li J, Zhang G (2014). Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in air, soil, and cereal crops along the two tributaries of River Chenab, Pakistan: Concentrations, distribution, and screening level risk assessment. Science of the Total Environment, 481(2): 596–604
Oliver B G, Nicol K D (1982). Chlorobenzenes in sediments, water, and selected fish from Lakes Superior, Huron, Erie, and Ontario. Environmental Science & Technology, 16(8): 532–536
Wan X, Pan X, Wang B, Zhao S, Hu P, Li F, Boulanger B (2011). Distributions, historical trends, and source investigation of polychlorinated biphenyls in Dianchi Lake, China. Chemosphere, 85(3): 361–367
Wang J, Yang C, He L, Dao G, Du J, Han Y, Wu G, Wu Q, Hu H (2019). Meteorological factors and water quality changes of Plateau Lake Dianchi in China (1990–2015) and their joint influences on cyanobacterial blooms. Science of the Total Environment, 665: 406–418
Wang X, Hou X, Zhou Q, Liao C, Jiang G (2018). Synthetic phenolic antioxidants and their metabolites in sediments from the coastal area of northern China: spatial and vertical distributions. Environmental Science & Technology, 52(23): 13690–13697
Wu Q, Milliken C E, Meier G P, Watts J E M, Sowers K R, May H D (2002). Dechlorination of chlorobenzenes by a culture containing bacterium DF-1, a PCB dechlorinating microorganism. Environmental Science & Technology, 36(15): 3290–3294
Wu M, Wang L, Xu G, Liu N, Tang L, Zheng J, Bu T, Lei B (2013). Seasonal and spatial distribution of 4-tert-octylphenol, 4-nonylphenol and bisphenol A in the Huangpu River and its tributaries, Shanghai, China. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185 (4): 3149–3161
Yao J, Gao Q, Li X, Hu M, Miao M, Pan B (2014). Investigating river pollution flowing into Dianchi Lake using a combination of GC-MS analysis and toxicological tests. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 92(1): 67–70
Zhang J, Zhao W, Pan J, Qiu L, Zhu Y (2005). Tissue-dependent distribution and accumulation of chlorobenzenes by vegetables in urban area. Environment International, 31(6): 855–860
Zhao S M, Wang B, Wang D W, Li X M, Huang B, Hu P, Zhang L W, Pan X J (2014). Environmental behavior of PAHs in Dianchi Lake distributions, sources and risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments from Dianchi Lake, China. International Journal of Environmental of Research, 8(2): 317–328
Zhong W, Wang D, Wang Z (2018). Distribution and potential ecological risk of 50 phenolic compounds in three rivers in Tianjin, China. Environmental Pollution, 235: 121–128
Zhong Z, Xu J, Zhang Y, Li L, Guo C, He Y, Fan W, Zhang B (2013). Adsorption of sulfonamides on lake sediments. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 7(4): 518–525
Zhou L, Cao H, Descorme C, Xie Y (2018). Phenolic compounds removal by wet air oxidation based processes. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, 12(1): 1
Zhou M, Zhang J, Sun C (2017). Occurrence, ecological and human health risks, and seasonal variations of phenolic compounds in surface water and sediment of a potential polluted river basin in China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 14(10): 1140–1153
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate the financial support from the National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFC1903000), the Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities (2019QNYL23), and the Key Laboratory of Eco-geochemistry, Ministry of Natural Resources, China (CSJ2017012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Highlights
• The total organic pollutant concentrations in sediment were 27.4 – 1620 ng/g.
• The phenol concentrations were relatively high in the sediment of the Dianchi Lake.
• Average total concentrations decreased as follows: Caohai>Waihai>Haigeng Dam.
• 1,4-dichlorobenzene, 3- or 4-methylphenol, 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene might be risks.
Electronic Supplementary Material
11783_2020_1245_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Distribution of aromatic amines, phenols, chlorobenzenes, and naphthalenes in the surface sediment of the Dianchi Lake, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, X., Yang, T., Liu, C. et al. Distribution of aromatic amines, phenols, chlorobenzenes, and naphthalenes in the surface sediment of the Dianchi Lake, China. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 14, 66 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-020-1245-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-020-1245-x