Abstract
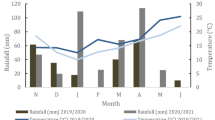
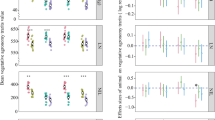
This study was purposely designed to evaluate the potential of faba bean (Vicia faba) residues as green manure in a maize-faba bean rotation system. Seed germination test and pot experiments were conducted to measure the effects of aqueous extract on maize seed germination and the effects of residues on crop growth and soil microbial activities. Litterbag experiment was conducted to analyze the decomposition patterns of faba bean residues during maize growing season in a regosol soil. The faba bean was separated into roots, stems, leaves, aboveground parts, and whole plants. Seed germination and the lengths of radicle and plumule were lower than those of the control, particularly with 1% aqueous extract concentrations. Aboveground biomass of maize at heading stages was negatively reduced by whole plant, aboveground part, and stem, whereas positively increased by leaf. Faba bean residues varied in their influences on the contents of soil microbial nitrogen and carbon as well as enzyme activities, mainly attributing to their differences in nutrient quality and allelophathy. Faba bean residues showed a quick decomposition rate during the first 5 weeks and slightly decomposed thereafter. The amount of nitrogen (N) released into soil ranged from 3.74 kg N ha−1 in root to 34.67 kg N ha−1 from leaf in the first 5 weeks. Compared with other plant parts, there were more remaining residues in root and stem residues. These results suggest that different management strategies should be taken to balance their negative and positive effects when using faba bean residues as green manure.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez-Iglesias L, Puig CG, Garabatos A, Reigosa MJ, Pedrol N (2014) Vicia faba aqueous extracts and plant material can suppress weeds and enhance crops. Allelopath J 34:299–313
Alvarez-Iglesias L, Puig CG, Revilla P, Reigosa MJ, Pedrol N (2018) Faba bean as green manure for field weed control in maize. Weed Res 58:437–449
Asaduzzaman M, Asao T (2012) Autotoxicity in beans and their allelochemicals. Sci Hortic-Amsterdam 134:26–31
Aschi A, Aubert M, Riah-Anglet W, Nelieu S, Dubois C, Akpa-Vinceslas M, Trinsoutrot-Gattin I (2017) Introduction of faba bean in crop rotation: impacts on soil chemical and biological characteristics. Appl Soil Ecol 120:219–228
Austin AT, Ballare CL (2010) Dual role of lignin in plant litter decomposition in terrestrial ecosystems. PNAS 107:4618–4622
Bao SD (2005) Agricultural chemical analysis of soil. China Agriculture Press, Beijing
Berg B, McClaugherty C (2003) Plant litter: decomposition, humus formation, Carbon sequestration. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Bergstrom L, Kirchmann H (2004) Leaching and crop uptake of nitrogen from nitrogen-15-labeled green manures and ammonium nitrate. J Environ Qual 33:1786–1792
Cao Y, Wu C, Wang L, Chen M, Zhao H, Bian X, Chen Y, Xia L (2017) Rotation of broad bean improves the soil quality of facility green house. Legum Res 40:710–715
Chaves B, De Neve S, Hofman G, Boeckx P, Van Cleemput O (2004) Nitrogen mineralization of vegetable root residues and green manures as related to their (bio) chemical composition. Eur J Agron 21:161–170
Chon SU, Kim JD (2002) Biological activity and quantification of suspected allelochemicals from alfalfa plant parts. J Agron Crop Sci 188:281–285
Deng WH, Chen BY, Zhang YQ, Zhang JQ, Qin SG, Wang R, Wang NN, Wu B, Shen YB (2014) Effects of extraction conditions on allelochemicals release from the Artemisia ordosica. Allelopath J 34:215–226
Erinle K, Marschner P (2019) Soil water availability influences P pools in the detritusphere of crop residues with different C/P ratios. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-019-00076-1
Etemadi F, Hashemi M, Shureshjani RA, Autio WR (2017) Application of data envelopment analysis to assess performance efficiency of eight faba bean varieties. Agron J 109:1225–1231
Havstad L, Aamlid T, Henriksen T (2010) Decomposition of straw from herbage seed production: Effects of species, nutrient amendment and straw placement on C and N net mineralization. Acta Agric Scand Sect B Soil Plant Sci 60:12
Javaid MM, Bhan M, Johnson JV, Rathinasabapathi B, Chase CA (2015) Biological and chemical characterizations of allelopathic potential of diverse accessions of the cover crop Sunn hemp. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 140:532–541
Jensen LS, Salo T, Palmason F, Breland TA, Henriksen TM, Stenberg B, Pedersen A, Lundstrom C, Esala M (2005) Influence of biochemical quality on C and N mineralisation from a broad variety of plant materials in soil. Plant Soil 273:307–326
Kadioglu I, Yanar Y, Asav U (2005) Allelopathic effects of weeds extracts against seed germination of some plants. J Environ Biol 26:169–173
Karkanis A, Ntatsi G, Lepse L, Fernandez JA, Vagen IM, Rewald B, Alsina I, Kronberga A, Balliu A, Olle M, Bodner G, Dubova L, Rosa E, Savvas D (2018) Faba bean cultivation—revealing novel managing practices for more sustainable and competitive. European cropping systems. Front Plant Sci 9:14
Klotzbucher T, Kaiser K, Guggenberger G, Gatzek C, Kalbitz K (2011) A new conceptual model for the fate of lignin in decomposing plant litter. Ecology 92:1052–1062
Kraus E, Voeten M, Lambers H (2002) Allelopathic and autotoxic interactions in selected populations of Lolium perenne grown in monoculture and mixed culture. Functi Plant Bio 29:1465–1473
Lepse L, Dane S, Zeipina S, Dominguez-Perles R, Rosa EAS (2017) Evaluation of vegetable-faba bean (Vicia faba L) intercropping under Latvian agro-ecological conditions. J Sci Food Agric 97:4334–4342
Li J, He SY, Qin XD (2016) Allelopathic potential and volatile compounds of Manihot esculenta Crantz against weeds. Allelopath J 37:195–206
Lopez-Bellido FJ, Lopez-Bellido L, Lopez-Bellido RJ (2005) Competition, growth and yield of faba bean (Vicia faba L.). Eur J Agron 23:359–378
Lupwayi NZ, Soon YK (2015) Carbon and nitrogen release from legume crop residues for three subsequent crops. Soil Sci Soc Amer J 79:1650–1659
Magid J, Henriksen O, Thorup-Kristensen K, Mueller T (2001) Disproportionately high N-mineralisation rates from green manures at low temperatures—implications for modeling and management in cool temperate agro-ecosystems. Plant Soil 228:73–82
McKenna P, Cannon N, Conway J, Dooley J (2018) The use of red clover (Trifolium pratense) in soil fertility-building: a review. Field Crop Res 221:38–49
Miguez FE, Bollero GA (2005) Review of corn yield response under winter cover cropping systems using meta-analytic methods. Crop Sci 45:2318–2329
Nelson D, Sommers L (1982) Total carbon, organic carbon and organic matter. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keenay DR (eds) Methods of Soil Analysis. American Society of Agronomy and Soil Science Society of American, Madison, pp 101–129
Nicolardot B, Recous S, Mary B (2001) Simulation of C and N mineralisation during crop residue decomposition: a simple dynamic model based on the C : N ratio of the residues. Plant Soil 228:83–103
Puig CG, Revilla P, Esther Barreal M, Reigosa MJ, Pedrol N (2019) On the suitability of Eucalyptus globulus green manure for field weed control. Crop Prot 121:57–65
Rochester IJ, Peoples MB, Hulugalle NR, Gault RR, Constable GA (2001) Using legumes to enhance nitrogen fertility and improve soil condition in cotton cropping systems. Field Crop Res 70:27–41
Rubiales D (2010) Faba beans in sustainable agriculture Introduction. Field Crop Res 115:201–202
Santa-Regina I, Rapp M, Martin A, Gallardo JF (1997) Nutrient release dynamics in decomposing leaf litter in two Mediterranean deciduous oak species. Ann For Sci 54:747–760
Snapp S, Surapur S (2018) Rye cover crop retains nitrogen and doesn’t reduce corn yields. Soil Tillage Res 180:107–115
Stagnari F, Pisante M (2010) Managing faba bean residues to enhance the fruit quality of the melon (Cucumis melo L) crop. Sci Hortic 126:317–323
Surucu A, Ozyazici MA, Bayrakli B, Kizilkaya R (2014) Effects of green manuring on soil enzyme activity. Fresenius Environ Bull 23:2126–2132
Tefera T (2002) Allelopathic effects of Parthenium hysterophorus extracts on seed germination and seedling growth of Eragrostis tef. J Agron Crop Sci 188:306–310
Truong THA, Marschner P (2018) Addition of residues with different C/N ratio in soil over time individually or as mixes—effect on nutrient availability and microbial biomass depends on amendment rate and frequency. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 18:1157–1172
Turgut I, Bilgili U, Duman A, Acikgoz E (2005) Effect of green manuring on the yield of sweet corn. Agron Sustain Dev 25:433–438
Vandat E, Nourbakhsh F, Basiri M (2011) Lignin content of range plant residues controls N mineralization in soil. Eur J Soil Biol 47:243–246
Vyn TJ, Raimbault BA (1993) long term effect of five tillage systems on corn response and soil structure. Agron J 85:1074–1079
Yang ZP, Xu MG, Zheng SX, Nie J, Gao JS, Liao YL, Xie J (2012) Effects of long-term winter planted green manure on physical properties of reddish paddy soil under a double-rice cropping system. J Integr Agric 11:655–664
Yao ZY, Zhang DB, Yao PW, Zhao N, Li YY, Zhang SQ, Zhai BN, Huang DL, Ma AS, Zuo YJ, Cao WD, Gao YJ (2018) Optimizing the synthetic nitrogen rate to balance residual nitrate and crop yield in a leguminous green-manured wheat cropping system. Sci Total Environ 631-632:1234–1242
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express thanks to Miss Qing Yang from the College of Agronomy and Biotechnology of Southwest University (China) for her help during field sampling.
Funding
This study was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31670407), Science and Technology Innovation Project for Social Livelihood of Chongqing (cstc2016shmszx80107), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (XDJK2018B021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(JPG 245 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Z., Yao, L., Zhang, X. et al. Faba Bean Organs Differed in Their Effects on Maize Seed Germination Rate and Soil Microbial Activities as well as Their Decomposition Patterns in a Regosol Soil. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 20, 367–379 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-019-00117-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-019-00117-9