Abstract
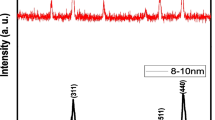
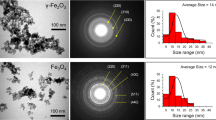
This study investigates (i) in planta uptake and transfer of magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) in the plant body and (ii) impact of MNPs on plant nutrition. For these purposes, barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) seedlings were subjected by varied MNP doses (125 to 1000 mg L−1 of CoNd0.2Fe1.8O4) for 3 weeks in a hydroponic system. Plant tissues (root and leaf) were analyzed by using vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) and inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer (ICP-OES) techniques to understand MNPs’ uptake and translocation in the plant body, and plant nutrition status as well. Elemental composition and magnetic behavior analyses of plant parts proved that MNPs, sized in 8.4 ± 0.05 nm, are uptaken by the plant roots and led to an increase in iron (Fe), neodymium (Nd), and cobalt (Co) contents of leaves (p < 0.005). However, compared with the untreated control, the amount of some macro- and micro-elements (K, Ca, Mg, Mn, and P) are declined in the leaf by increased MNP doses (p < 0.05). Root-to-leaf translocation index (%) of the elements were dramatically decreased, except the one for Fe which increased from 25 (control) to 55% in 1000 mg L−1 condition. Accordingly, MNPs are uptaken by the plant roots and transferred to the leaves. However, it suppresses the translocation of essential nutrients. This finding shows that MNPs used in this study is detrimental for plant mineral nutrition. Besides, the VSM technique coupled with ICP-OES enables to track MNPs in the plant body.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almessiere MA, Slimani Y, Korkmaz AD, Sertkol M, Baykal A, Ercan I, Özçelik B (2019) Sonochemical synthesis of CoFe2-xNdxO4 nanoparticles: structural, optical, and magnetic investigation. J Supercond Nov Magn:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-019-05147-z
Ancuceanu R, Dinu M, Hovaneţ M, Anghel A, Popescu C, Negreş S (2015) A survey of plant iron content—a semi-systematic review. Nutrients 7(12):10320–10351
Antisari LV, Carbone S, Gatti A, Vianello G, Nannipieri P (2015) Uptake and translocation of metals and nutrients in tomato grown in soil polluted with metal oxide (CeO2, Fe3O4, SnO2, TiO2) or metallic (Ag, Co, Ni) engineered nanoparticles. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(3):1841–1853
Aydin M, Tombuloglu G, Sakcali MS, Hakeem KR, Tombuloglu H (2019) Boron alleviates drought stress by enhancing gene expression and antioxidant enzyme activity. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 19:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-019-00053-8
Babitha N, Priya LS, Christy SR, Manikandan A, Dinesh A, Durka M, Arunadevi S (2019) Enhanced antibacterial activity and photo-catalytic properties of ZnO nanoparticles: Pedalium murex plant extract-assisted synthesis. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 19(5):2888–2894
Bostancioglu SM, Tombuloglu G, Tombuloglu H (2018) Genome-wide identification of barley MCs (metacaspases) and their possible roles in boron-induced programmed cell death. Mol Biol Rep 45(3):211–225
Cannata MG, Bertoli AC, Carvalho R, Bastos ARR, Freitas MP, Augusto AS (2014) Effects of cadmium on the content, accumulation, and translocation of nutrients in bean plant cultivated in nutritive solution. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 45(2):223–235
Carpenter D, Boutin C, Allison JE, Parsons JL, Ellis DM (2015) Uptake and effects of six rare earth elements (REEs) on selected native and crop species growing in contaminated soils. PLoS One 10(6):e0129936
Chichiriccò G, Poma A (2015) Penetration and toxicity of nanomaterials in higher plants. Nanomaterials 5(2):851–873
Corredor E, Testillano PS, Coronado MJ et al (2009) Nanoparticle penetration and transport in living pumpkin plants: in situ subcellular identification. BMC Plant Biol 9(1):45
Dhayalan M, Denison MIJ, Ayyar M, Gandhi NN, Krishnan K, Abdulhadi B (2018) Biogenic synthesis, characterization of gold and silver nanoparticles from Coleus forskohlii and their clinical importance. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 183:251–257
Ghafariyan MH, Malakouti MJ, Dadpour MR, Stroeve P, Mahmoudi M (2013) Effects of magnetite nanoparticles on soybean chlorophyll. Environ Sci Technol 47(18):10645–10652
Govea-Alcaide E, Masunaga SH, De Souza A, Fajardo-Rosabal L, Effenberger FB, Rossi LM, Jardim RF (2016) Tracking iron oxide nanoparticles in plant organs using magnetic measurements. J Nanopart Res 18:305
Hema E, Manikandan A, Gayathri M, Durka M, Antony SA, Venkatraman BR (2016) The role of Mn2 + -doping on structural, morphological, optical, magnetic and catalytic properties of spinel ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 16(6):5929–5943
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. Circular California agricultural experiment station 347(2nd edit).
Kong H, Song J, Jang J (2010) One-step fabrication of γ-Fe2O3/ polyrhodanine magnetic nanoparticles using in-situ chemical oxidation polymerization and their antibacterial properties (Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications). Chem Commun 46:6735–6737
Lee WM, An YJ, Yoon H, Kweon HS (2008) Toxicity and bioavailability of copper nanoparticles to the terrestrial plants mung bean (Phaseolus radiatus) and wheat (Triticum aestivum): plant agar test for water-insoluble nanoparticles. Environ Toxicol Chem 27:1915–1921
Li J, Hu J, Ma C, Wang Y, Wu C, Huang J, Xing B (2016) Uptake, translocation and physiological effects of magnetic iron oxide (γ-Fe2O3) nanoparticles in corn (Zea mays L.). Chemosphere 159:326–334
López-Moreno ML, Avilés LL, Pérez NG, Irizarry BÁ, Perales O, Cedeno-Mattei Y, Román F (2016) Effect of cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4) nanoparticles on the growth and development of Lycopersicon lycopersicum (tomato plants). Sci Total Environ 550:45–52
Manikandan A, Durka M, Amutha Selvi M, Arul Antony S (2016a) Sesamum indicum plant extracted microwave combustion synthesis and opto-magnetic properties of spinel Mn x Co1-x Al2O4 nano-catalysts. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 16(1):448–456
Manikandan A, Durka M, Amutha Selvi M, Arul Antony S (2016b) Aloe vera plant extracted green synthesis, structural and opto-magnetic characterizations of spinel Co x Zn1-x Al2O4 nano-catalysts. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 16(1):357–373
Pacheco I, Buzea C (2018) Nanoparticle uptake by plants: beneficial or detrimental? In Phytotoxicity of Nanoparticles (p 1-61) Springer, Cham
Paiva HN, Carvalho JG, Siqueira JO (2002) Índice de translocação de nutrientes em mudas de cedro (Cedrela fissilis Vell.) e de ipê-roxo (Tabebuia impetiginosa Mart Standl.) submetidas a doses crescentes de cádmio, níquel e chumbo. Revista Árvore 26:467–473
Peralta-Videa JR, Hernandez-Viezcas JA, Zhao L, Diaz BC, Ge Y, Priester JH, Holden PA, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2014) Cerium dioxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles alter the nutritional value of soil cultivated soybean plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 80:128–135
Prasad R, Bhattacharyya A, Nguyen QD (2017) Nanotechnology in sustainable agriculture: recent developments, challenges, and perspectives. Front Microbiol 8:1014
Santo Pereira ADE, Oliveira HC, Fraceto LF (2019) Polymeric nanoparticles as an alternative for application of gibberellic acid in sustainable agriculture: a field study. Sci Rep 9(1):7135
Tombuloglu H, Kekec G, Sakcali MS, Unver T (2013) Transcriptome-wide identification of R2R3-MYB transcription factors in barley with their boron responsive expression analysis. Mol Genet Genomics 288(3-4):141–155
Tombuloglu G, Tombuloglu H, Sakcali MS, Unver T (2015) High-throughput transcriptome analysis of barley (Hordeum vulgare) exposed to excessive boron. Gene 557(1):71–81
Tombuloglu H, Tombuloglu G, Slimani Y, Ercan I, Sozeri H, Baykal A (2018) Impact of manganese ferrite (MnFe2O4) nanoparticles on growth and magnetic character of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Environ Pollut 243:872–881
Tombuloglu H, Slimani Y, Tombuloglu G, Almessiere M, Baykal A (2019a) Uptake and translocation of magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles and its impact on photosynthetic genes in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Chemosphere 226:110–122
Tombuloglu H, Slimani Y, Tombuloglu G, Almessiere M, Baykal A, Ercan I, Sozeri H (2019b) Tracking of NiFe2O4 nanoparticles in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) and their impact on plant growth, biomass, pigmentation, catalase activity, and mineral uptake. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manage 11:100223
Tombuloglu H, Slimani Y, Güngüneş H, Tombuloglu G, Almessiere MA, Sozeri H, Ercan I (2019c) Tracking of SPIONs in Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) Plant Organs During its Growth. J Supercond Nov Magn:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-019-5059-7
Tombuloglu H, Slimani Y, Tombuloglu G, Demir-Korkmaz A, Baykal A, Almessiere M, Ercan I (2019d) Impact of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) and ionic iron on physiology of summer squash (Cucurbita pepo): a comparative study. Plant Physiol Biochem 139:56–65
USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) (1995) Method 3051: microwave assisted acid digestion of sediments, sludges, soils, and oils. Test methods for evaluating solid waste, 1-30
Valan MF, Manikandan A, Antony SA (2015) A novel synthesis and characterization studies of magnetic Co3O4 nanoparticles. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 15(6):4580–4586
Wang H, Kou X, Pei Z, Xiao JQ, Shan X, Xing B (2011) Physiological effects of magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles on perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) and pumpkin (Cucurbita mixta) plants. Nanotoxicol 5(1):30e42
Wang P, Lombi E, Zhao FJ, Kopittke PM (2016) Nanotechnology: a new opportunity in plant sciences. Trends Plant Sci 21(8):699–712
Yan A, Chen Z (2018) Detection methods of nanoparticles in plant tissues. In New Visions in Plant Science, IntechOpen
Zhu H, Han J, Xiao JQ (2008) Jin Y (2008) Uptake, translocation, and accumulation of manufactured iron oxide nanoparticles by pumpkin plants. J Environ Monit 10:713–717
Funding
The authors would like to the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR) fund of Imam Abdulrahman Bin Faisal University (IAU) with 2018-139-IRMC project number.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1080 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tombuloglu, H., Slimani, Y., Alshammari, T. et al. Magnetic Behavior and Nutrient Content Analyses of Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) Tissues upon CoNd0.2Fe1.8O4 Magnetic Nanoparticle Treatment. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 20, 357–366 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-019-00115-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-019-00115-x