Abstract
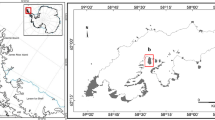
Mosses inhabiting alpine regions play a vital role in maintaining the stability of their environments. Despite their possible importance, the cultivatable endophytes of mosses in alpine regions have not been widely examined. The community structure of cultivatable endophytes from four species of mosses, Thuidium cymbifolium, Cirriphyllum cirrosum, Tortella tortuosa and Tortula reflexa, was assessed using 16S rRNA sequencing. The plant growth-promoting traits of all isolates were evaluated by measuring nitrogen fixation, phosphate solubilization, plant hormone (indoleacetic acid) production, and antifungal activity. Overall, 36 endophyte strains of bacteria were isolated from the 4 species of mosses from the Qilian Mountains in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, and were found to belong to 4 phyla, 11 genera, and 20 species. The dominant phyla were Proteobacteria (63.9%). Of the isolates, 53% belonged to Pseudomonas. The cultured bacteria from the mosses differed in their growth-promoting traits. This is the first report on the diversity of culturable endophytic bacteria in mosses from high-altitude cold regions. These plant growth-promoting bacteria might have applications in agriculture or be of value in strategies for environmental protection in alpine regions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abadias M, Altisent R, Usall J, Torres R, Oliveira M, Vinas I (2014) Biopreservation of fresh-cut melon using the strain Pseudomonas graminis CPA-7. Postharvest Biol Technol 96:69–77
Alegre I, Vinas I, Usall J, Anguera M, Altisent R, Abadias M (2013) Antagonistic effect of Pseudomonas graminis CPA-7 against foodborne pathogens in fresh-cut apples under simulated commercial conditions. Food Microbiol 33:139–148
Bach HJ, Jessen I, Schloter M, Munch JC (2003) A TaqMan-PCR protocol for quantification and differentiation of the phytopathogenic Clavibacter michiganensis subspecies. J Microbiol Methods 52:85–91
Bastian F, Cohen A, Luna V, Baraldi R, Bottini R (1998) Production of indole-3-acetic acid and gibberellins A1 and A3 by Acetobacter diazotrophicus and Herbaspirillum seropedicae in chemically-defined culture media. Plant Growth Regul 24:7–11
Bernard, G. and William, B. (2004) "Systematics of the Bryophyta (mosses): from molecules to a revised classification". Monographs in Systematic Botany Molecular Systematics of Bryophytes Missouri Botanical Garden Press 98, 205–239
Boddey RM, Knowles R (1987) Methods for quantification of nitrogen fixation associated with gramineae. Crit Rev Plant Sci 6:209–266
Bragina A, Berg C, Cardinale M, Shcherbakov A, Chebotar V (2012a) Sphagnum mosses harbour highly specific bacterial diversity during their whole lifecycle. International Society for Microbial Ecology 6:802–813
Bragina A, Maier S, Berg C, Mueller H, Chobot V, Hadacek F, Berg G (2012b) Similar diversity of Alphaproteobacteria and nitrogenase gene amplicons on two related Sphagnum mosses. Front Microbiol 2:275
Bragina A, Cardinale M, Berg C, Berg G (2013) Vertical transmission explains the specific Burkholderia pattern in Sphagnum mosses at multi-geographic scale. Front Microbiol 4:394
Bragina A, Oberauner-Wappis L, Zachow C, Halwachs B, Thallinger GG, Müller H, BERG G (2014) The Sphagnum microbiome supports greatly ecosystem functioning under extreme conditions. Mol Ecol 23:4498–44510
Bragina A, Müller CA, Berg G (2015a) The moss microbiome: new insights into the microbial world of plants and its biotechnological potential. Rostocker meeresbiologische Beiträge 26:25–33
Bragina A, Berg C, Berg G (2015b) The core microbiome bonds the Alpine bog vegetation to a transkingdom metacommunity. Mol Ecol 24:4794–4807
Burris RH (1972) Nitrogen fixation assay methods and techniques. Methods Enzymol 24:415–431
Cho KM, Hong SY, Lee SM, Kim YH, Kahng GG, Kim H, Yun HD (2006) A cel44C-man26A gene of endophytic Paenibacillus polymyxa GS01 has multi-glycosyl hydrolases in two catalytic domains. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73:618–630
Chung EJ, Park HH, Park TS, Ahn GW, Chung YR (2010) Production of a phytotoxic compound, 3-Phenylpropionic acid by a bacterial Endophyte, Arthrobacter humicola YC6002 isolated from the root of Zoysia japonica. The Plant Pathology Journal 26:245–252
Conard HS, Redfearn PL, Bamrick J (1980) How to know the mosses and liverworts, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Cowan ST, Steel KJ (1974) Cowan and Steel’s manual for the identification of medical Bacteria, 2nd edn. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press
Dedysh, S.N., Liesack,W., Khmelenina, V.N., Suzina, N.E., Trotsenko, Y.A., Semrau, J.D., Bares, A.M., Panikov,N.S. and Tiedje, J.M. (2000) Methylocella palustris gen. Nov., sp. nov., a new methaneoxidizing acidophilic bacterium from peat bogs, representing a novel subtype of serine-pathway methanotrophs. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50, 955–-969
Dedysh, S.N., Khmelenina, V.N., Suzina, N.E., Trotsenko, Y.A., Semrau, J.D., Liesack,W. and Tiedje, J.M. (2002) Methylocapsa acidophila gen. Nov., sp. nov., a novel methane-oxidizing and dinitrogen fixing acidophilic bacterium from Sphagnum bog. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52, 251–-261
Gaiero JR, McCall CA, Thompson KA, Day NJ, Best A, Dunfield KE (2013) Inside the root microbiome: bacterial root endophytes and plant growth promotion. Am J Bot 100:1738–1750
Goudjal Y, Toumatia O, Sabaou N, Barakate M, Mathieu F, Zitouni A (2013) Endophytic actinomycetes from spontaneous plants of Algerian Sahara: indole-3-acetic acid production and tomato plants growth promoting activity. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 29:1821–1829
Hardoim PR, Van Overbeek LS, Berg G, Pirttil AM, Compant S, Campisano A, Dring M, Sessitsch A (2015) The hidden world within plants: ecological and evolutionary considerations for defining functioning of microbial endophytes. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 79:293–320
Kim O-S, Cho Y-J, Lee K, Yoon S-H, Kim M, Na H, Park S-C, Jeon YS, Lee J-H, Yi H, Won S, Chun J (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNAgene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721
Kip N, Fritz C, Langelaan ES, Pan Y (2012) Methanotrophic activity and diversity in different Sphagnum magellanicum dominated habitats in the southernmost peat bogs of Patagonia. Biogeosciences 9:47–55
Kostka JE, Weston DJ, Glass JB, Lilleskov EA, Jonathan Shaw A, Turetsky M (2016) The Sphagnum microbiome: new insights from an ancient plant lineage. New Phytol 211:57–64
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874
Kukla M, Płociniczak T, Piotrowska-Seget Z (2014) Diversity of endophytic bacteria in Lolium perenne and their potential to degrade petroleum hydrocarbons and promote plant growth. Chemosphere 117:40–46
Kusari P, Kusari S, Spiteller M, Kayser O (2013) Endophytic fungi harbored in Cannabis sativa L.: diversity and potential as biocontrol agents against host plant-specific phytopathogens. Fungal Divers 60:137–151
Lane DJ (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. Wiley, Chichester, pp 115–175
Lebeis SL (2014) The potential for give and take in plant-microbiome relationships. Front Plant Sci 5:287
Liu M, Li YH, Liu Y, Zhu JN, Liu QF, Liu Y, Gu JG, Zhang XX, Li CL (2011) Flavobacterium phragmitis sp. nov., an endophyte of reed (Phragmites australis). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:2717–2721
Liu XL, Liu SL, Liu M, Kong BH, Liu L, Li YH (2014) A primary assessment of the endophytic bacterial community in a xerophilous moss (Grimmia montana) using molecular method and cultivated isolates. Braz J Microbiol 45:163–173
Lu, F.X., Sun, L.J., Lu, Z.X., Bie, X.M., Fang, Y.W. and Liu,S. (2007) Isolation and identification of an Endophytic strain EJS-3 producing novel Fibrinolytic enzymes. Curr Microbiol 54,435–439
Malcolm B, Malcolm N (2000) Mosses and bryophytes: an illustrated glossary. Timber Press/Micro-Optics Press, Portland, OR
Mathews D (1994) Cascade-Olympic natural history. Audubon Society of Portland/Raven Editions, Portland, Oregon
Mikicinski A, Sobiczewski P, Pulawska J, Malusa E (2016) Antagonistic potential of Pseudomonas graminis 49M against Erwinia amylovora, the causal agent of fire blight. Arch Microbiol 198:531–539
Olsen SR, Sommers LE (1982) Phosphorus. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Dennis RK (eds) Methods of soil analysis. Madison, American Society of Agronomy, pp 403–430
Peix A, Rivas R, Mateos PF, Martinez-Molina E, Rodriguez-Barrueco C, Velazquez E (2003) Pseudomonas rhizosphaerae sp. nov., a novel species that actively solubilizes phosphate in vitro. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:2067–2072
Pikovskaya RI (1948) Mobilization of phosphorus in soil in connection with the vital activity of some microbial species. Mikrobiologiya. 7:362–370
Pojar J, MacKinnon A (2004) Plants of coastal British Columbia including Washington, Oregon & Alaska. Lone Pine, Vancouver, British Columbia
Raghoebarsing AA, Smolders AJP, Schmid MC, Rijpstra WC, Wolters-Art M, Derksen J, Jetten MSM, Schouten S, Sinninghe Damste JS, Lamers LPM, Roelofs JGM, Op den Camp HJM, Strous M (2005) Methanotrophic symbionts provide carbon for photo synthesis in peat bogs. Nature. 436:1153–1156
Raweekul W, Wuttitummaporn S, Sodchuen W, Kittiwongwattana C (2016) Plant growth promotion by Endophytic Bacteria Isolated from Rice. Thammasat International Journal of Science and Technology 21:6–17
Rosenblueth M, Martinez-Romero E (2006) Bacterial endophytes and their interactions with hosts. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 19:827–837
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method-a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Schmidt CS, Lovecka P, Mrnka L, Vychodilova A, Strejcek M, Fenclova M, Demnerova K (2018) Distinct communities of poplar Endophytes on an unpolluted and a risk element-polluted site and their plant growth-promoting potential in vitro. Microb Ecol 75:955–969
Schulz B, Boyle C (2005) The endophytic continuum. Mycol Res 109:661–686
Sharon JA, Hathwaik LT, Glenn GM, Imam SH, Lee CC (2016) Isolation of efficient phosphate solubilizing bacteria capable of enhancing tomato plant growth. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 16:525–536
Shcherbakov AV, Bragina AV, Kuzmina EY, Berg K, Muntyan AN, Malfanova NV, Cardinale M, Berg G, Chebotar VK, Tikhonovich IA (2013) Endophytic Bacteria of Sphagnum mosses as promising objects of agricultural microbiology. Microbiology. 82:306–315
Stępniewska Z, Goraj W, Kuźniar A (2014) Transformation of methane in peatland environments. For Res Pap 75:101–110
Sun HM, Wei YZ, Fang XM, Yu LN, Zhang YQ (2016) Diversity of endophytic bacteria isolated from Huperzia serrate. Acta Microbiol Sin 56:614–628
Sun GZ, Yao T, Feng CJ, Chen L, Li JH, Wang LD (2017) Identification and biocontrol potential of antagonistic bacteria strains against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and their growth-promoting effects on Brassica napus. Biol Control 104:35–43
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Wang Y, Yang CD, Yao YL, Wang YQ, Zhang ZF, Xue L (2016) The diversity and potential function of endophytic bacteria isolated from Kobreasia capillifolia at alpine grasslands on the Tibetan plateau. China Journal of Integrative Agriculture 15:2153–2162
Zenova GM, Stepanov AL, Likhacheva AA, Manucharova NA (2002) Praktikum po biologii pochv (practical course in soil biology). Mosk. Gos. Univ, Moscow
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by National Nature Science Foundation of China Grant No. 31660688 and Special funds for discipline construction of Gansu Agricultural University Grant No. GAU-XKJS-2018-007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
T.Y., X.J.L., and H.Z. designed the work. X.J.L., W.Q.D., and J.G.Z. performed experiments. D.R.H. analyzed data. X.J.L. wrote the paper with H.Z. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1535 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lan, X., Zhou, H., Yao, T. et al. Community structure and function of cultivable Endophytic Bacteria isolated from four Moss species in Qilian Mountain. Symbiosis 80, 257–267 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-020-00669-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-020-00669-w