Abstract
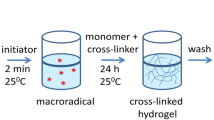
Since the management of infections becomes prior global healthcare issue, the “post antibiotic era” requires innovative and interdisciplinary approach. As an alternative to widespread and, nowdays mostly uneffective, antibiotic treatment of infections, the series of hydrogels were developed and further investigated as novel antibacterial biomaterials. The hydrogels based on 2-hydroxyethyl acrylate and itaconic acid were synthesized and used for silver(I) ions incorporation. The structural, thermal and swelling characteristics were examined by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, differential scanning calorimetry, and swelling study conducted in wide range of pHs at 37 °C. Results confirmed the expected structure, while the glass transition temperatures (Tg) of the hydrogels were detected in range of 10–37 °C. The in vitro release study revealed suitability of these pH sensitive hydrogels as the systems for topical delivery of silver(I) ions. Performed MTT test and Comet assay proved biocompatibility of the hydrogels, as well as the absence of acute genotoxic effect on human fibroblast cells (MRC-5). The hydrogels exhibited satisfying antibacterial activity against methicillin sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) and methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), indicating the capacity to treat the life-threatening infections.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Greenhalgh, N. C. Dempsey-Hibbert, and K. A. Whitehead, Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 136, 1 (2019).
A. Munoz-Bonilla and M. Fernández-García, Prog. Polym. Sci., 37, 281 (2012).
K. Vasilev, A. Cavallaro, and P. Zilm, Molecule., 23, 585 (2018).
K. R. Yang, Q. Han, B. Chen, Y. Zheng, K. Zhang, Q. Li, and J. C. Wang, Int. J. Nanomed., 13, 2217 (2018).
B. Li and T. J. Webster, J. Orthop. Res., 36, 22 (2018).
L. J. Bessa, P. Fazii, M. Di Giulio, and L. Cellini, Int. Wound J., 12, 47 (2015).
P. G. Bowler, B. I. Duerden, and D. G. Armstrong, Clin. Microbiol. Rev., 14, 244 (2001).
S. L. Percival, K. E. Hill, S. Malic, D. W. Thomas, and D. W. Williams, Wound Repair Regen., 19, 1 (2011).
H. Schöfer, R. Bruns, I. Effendy, M. Hartmann, U. Jappe, A. Plettenberg, H. Reimann, H. Seifert, P. Shah, C. Sunderkötter, T. Weberschock, T. A. Wichelhaus, and A. Nast, J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges., 9, 953 (2011).
K. S. Santos, A. M. Barbosa, L. P. da Costa, M. S. Pinheiro, M. B. Oliveira, F. Ferreira, and F. Padilha, Molecule., 21, 1 (2016).
B. A. Lipsky and C. Hoey, Clin. Inf. Dis., 49, 1541 (2009).
C. T. Spann, S. C. Taylor, and J. M. Weinberg, Clin. Dermatol., 21, 70 (2003).
P. Huira, J. K. Logan, S. Papadopoulos, and D. Whitney, Pharmacotherap., 32, 1006 (2012).
B. A. Lipsky, Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev., 32, 246 (2016).
A. J. Alanis, Arch. Med. Res., 36, 697 (2005).
G. Sussman, T. Swanson, J. Black, R. Cooper, G. Schultz, J. Fletcher, and D. Smith, Wounds Int., 5, 4 (2014).
J. B. Wright, K. Lam, and R. E. Burrell, Am. J. Infect. Control., 26, 572 (1998).
T. Bjarnsholt, K. Kirketerp-Møller, P. Ø. Jensen, K. G. Madsen, R. Phipps, K. Krogfelt, N. H øiby, and M. Givskov, Wound Repair. Regen., 16, 2 (2008).
C. Attinger and R. Wolcott, Adv. Wound Care (New Rochelle), 1, 127 (2012).
S. L. Percival, S. M. McCarty, and B. Lipsky, Adv. Wound Care (New Rochelle), 4, 373 (2015).
J. Fernebro, Drug Resist. Updat., 14, 125 (2011).
M. Zucca and D. Savoia, Int. J. Biomed. Sci., 6, 77 (2010).
Y. H. Lin, J. H. Lin, S. H. Wang, T. H. Ko, and G. C. Tseng, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part., 100, 2288 (2012).
M. K. Rai, S. D. Deshmukh, A. P. Ingle, and A. K. Gade, J. Appl. Microbiol., 112, 841 (2012).
R. Singh and D. Singh, J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Med., 23, 2649 (2012).
S. L. Percival, W. Slone, S. Linton, T. Okel, L. Corum, and J. G. Thomas, Int. Wound J., 8, 237 (2011).
D. E. Marx and D. J. Barillo, Burn., 40, s9 (2014).
T. Maneerung, S. Tokura, and R. Rujiravanit, Carbohydr. Polym., 72, 43 (2008).
Z. Huang, P. Xu, G. Chen, G. Zeng, A. Chen, Z. Song, K. He, L. Yuan, H. Li, and L. Hu, Chemospher., 196, 575 (2018).
Z. Huang, Z. Zeng, A. Chen, G. Zeng, R. Xiao, P. Xu, K. He, Z. Song, L. Hu, M. Peng, T. Huang, and G. Chen, Chemospher., 203, 199 (2018).
Z. Huang, K. He, Z. Song, G. Zeng, A. Chen, L. Yuan, H. Li, L. Hu, Z. Guo, and G. Chen, Chemospher., 211, 573 (2018).
Z. Huang, G. Chen, G. Zeng, Z. Guo, K. He, L. Hu, J. Wu, L. Zhang, Y. Zhu, and Z. Song, J. Hazard. Mater., 321, 37 (2017).
J. Kopecek and J. Yang, Polym. Int., 56, 1078 (2007).
J. M. Rosiak, J. Control. Release., 31, 9 (1994).
B. Balakrishnan, M. Mohanty, P. R. Umashankar, and A. Jayakrishnan, Biomaterial., 26, 6335 (2005).
S. O. Rogero, S. M. Malmonge, A. B. Lugao, T. I. Ikeda, L. Miyamaru, and A. S. Cruz, Artif. Organ., 27, 424 (2003).
C. J. De Groot, M. J. A. Van Luyn, W. N. E. Van Dijk-Wolthuis, J. A. Cadee, J. A. Planting, W. Den Otter, and W. E. Hennink, Biomaterial., 22, 1197 (2001).
E. Karadag, D. Saraydin, S. Cetinkaya, and O. Guven, Biomaterial., 17, 67 (1996).
L. Ionov, Adv. Funct. Mater., 23, 4555 (2013).
M. C. Koetting, J. T. Peters, S. D. Steichen, and N. A. Peppas, Mater. Sci. Eng. R. Rep., 93, 1 (2015).
N. Ninan, A. Forget, V. P. Shastri, N. H. Voelcker, and A. Blencowe, ACS Appl. Mater. Interface., 8, 28511 (2016).
T. R. Dargaville, B. L. Farrugia, J. A. Broadbent, S. Pace, Z. Upton, and N. H. Voelcker, Biosens. Bioelectron., 41, 30 (2013).
E. M. Jones, C. A. Cochrane, and S. L. Percival, Adv. Wound Care (New Rochelle), 4, 431 (2015).
J. S. Vuković, M. M. Babić, K. M. Antić, J. M. Filipović, S. T. Stojanović, S. J. Najman, and S. Lj. Tomić, Mater. Chem. Phys., 175, 158 (2016).
J. S. Vuković, M. M. Babić, K. M. Antić, M. G. Miljković, A. A. Peric-Grujić, J. M. Filipović, and S. Lj. Tomić, Mater. Chem. Phys., 164, 51 (2015).
C. L. Bell and N. A. Peppas, J. Control. Releas., 37, 277 (1995).
P. L. Ritger and N. A. Peppas, J. Control. Releas., 5, 23 (1987).
A. R. Khare, N. A. Peppas, G. Massimo, and P. Colombo, J. Control. Releas., 22, 239 (1992).
H. J. Scott, Macromol. Sci. Phys. B, 31, 1 (1992).
Y. Yin, Y. Yang, and H. Xu, J. Pol. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys., 15, 3128 (2001).
N. A. Peppas and J. J. Sahlin, Int. J. Pharm., 57, 169 (1989).
K. Yamaoka, T. Nakagawa, and T. Uno, J. Pharmacokinet. Bioph., 6, 165 (1978).
T. Mosmann, J. Immunol. Method., 65, 55 (1983).
M. Ohno and T. Abe, J. Immunol. Method., 145, 199 (1991).
A. Dhawan, M. Bajpayee, and D. Parmar, Cell Biol. Toxicol., 25, 5 (2009).
A. S. Jaran, Eur. Sci. J., 13, 1 (2017).
G. Kronvall, I. Karlsson, M. Walder, M. Sörberg, and L. E. Nilsson, J. Antimicrob. Chemoth., 57, 498 (2006).
Y. Xiang and D. Chen, Eur. Polym. J., 43, 4178 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Acknowledgments: This work has been supported by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia (Grant Nos. 172062 and 172026).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vuković, J.S., Perić-Grujić, A.A., Mitić-Ćulafić, D.S. et al. Antibacterial Activity of pH-Sensitive Silver(I)/Poly(2-hydroxyethyl acrylate/itaconic acid) Hydrogels. Macromol. Res. 28, 382–389 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-020-8050-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-020-8050-z