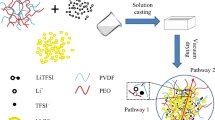
Abstract
Experimental and computational techniques have been applied to investigate the influence of Li0.5La0.5TiO3 nanoparticles on the ionic conductivity of the poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF)/LiClO4 nanocomposite solid polymer electrolyte. The theoretical evidence facilitated to suggest a plausible mechanism for Li-ion conduction across the PVDF/LiClO4/Li0.5La0.5TiO3 based solid polymer electrolytes. The solid composite polymer electrolyte with 30wt% of Li0.5La0.5TiO3 (LLTO) nanofiller exhibited an unprecedented ionic conductivity of 2.3687 × 10−3 S cm−1 at room temperature. The addition of LLTO nanoparticles to the polymer matrix enhanced its ionic conductivity by two orders of magnitude. The activation energy (Ea) and total transference number (t) were estimated to be 0.29 eV and 0.853, respectively. The interaction between the filler and polymer matrix has been inferred by the density functional theory (DFT)-IR analysis. The DFT calculations have been performed on the above system using the basis set of B3LYP-LANL2DZ. The calculated IR spectra were compared with the experimental FTIR data, which allowed us to propose accurate vibrational assignments and to clarify the complex IR vibration of the samples. All-solid-state Li2FeSiO4/CPVDF/LiClO4/LLTO graphite lithium cell has been fabricated using the highest Li-ion conducting PVDF/LiClO4/LLTO composite polymer electrolyte. The all-solid-state cell exhibits an excellent initial specific capacity of 87.13 and 73.24 mAh g−1 after 30 cycles, demonstrating higher capacity retention. The findings provide an avenue for exploring the simple all-solid-state lithium batteries, which are potential candidates for next-generation energy storage technology.

Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
07 April 2020
Figure 3 should be corrected as follows:
07 April 2020
Figure 3 should be corrected as follows:
07 April 2020
Figure 3 should be corrected as follows:
References
H. S. Min, J. M. Ko, and D. W. Kim, J. Power Sources., 119, 469 (2003).
B. Scrosati, F. Croe, and L. Pcrsi, J. Electrochem. Soc, 147, 1718 (2000).
H. S. Kim, J. H. Shin, S. I. Moon, and S. P. Kim, Electrochim. Acta, 48, 1573 (2003).
H. Lu, J. Du, C. Yu, X. Wang, Y. Gao, W. Xu, A. Liu, X. Lu, and Y. Chen, MacromoL Res., DOI: 10.1007/s13233-020-8073-5 (2020).
S. C. Ryu, J. Y. Kim, C. Cho, and W. N. Kim, MacromoL Res., 28, 118 (2020).
G. B. Appetecchi, F. Croce, L. Persi, F. Rond, and B. Scrosati, J. Electro-chem. Soc, 147, 4448 (2000).
L. M. Bronstein, R. L. Karlinsey, K. Ritter, C. G. Joo, B. Stein, and J. W. Zanziger, J. Mater. Chem., 14, 1812 (2004).
J. W. Kim, K. S. Ji, J. P. Lee, and J. W. Park, J. Power Sources, 119, 415 (2003).
A. M. Stephan and K. S. Nahm, Polymer, 47, 5952 (2006).
X. Qian, N. Gu, Z. Cheng, X. Yang, E. Wang and S. Dong, Electrochim. Acta, 46, 1829 (2001).
Y. J. Wang, Y. Pan, and D. Kim, J. Power Sources, 159, 690 (2006).
A. C. Balazs, T. Emrick, and T. P. Russell, Science, 314, 1107 (2006).
K. Malekshahinezhad, A. A. khaneghah, and H. Behniafar, MacromoL Res, DOI: 10.1007/sl3233-020-8067-3 (2019).
Inugama, C. Liquan, M. Itoh, T. Nakamura, T. Uchida, H. Ikuta, and M. Wakihar, Solid State Commun., 86, 689 (1993).
K. P. Abhilash, P. Christopher Selvin, B. Nalini, K. Somasundaram, P. Sivaraj, and A. Chandra Bose, J. Phys. Chem Solids, 91, 114 (2016).
K. P. Abhilash, P. Sivaraj, P. Christopher Selvin, B. Nalini, and K. Somasundaram, Ceram Int., 41, 13823 (2015).
W. Liu, N. Liu, J. Sun, P. C. Hsu, Y. Li, H. W. Lee, and Y. Cui, Nano Lett., 15, 2740 (2015).
C. Wang, X. W. Zhang, and A. J. Appleby, J. Electrochem. Soc., 152, 205 (2005)
P. Sivaraj, B. Nalini, K. P. Abhilash, D. Lakshmi, P. Christopher Selvin, and P. Balraju, J. Alloys Compels., 740, 1116 (2018).
W. Kohn and L. Sham, J. Phys. Rev., 140, 1133 (1965).
R. G. Parr and W. Yang, Density-Functional Theory of Atoms and Mole-cules, Oxford University Press, Oxford, Clarendon, 1989.
A. D. Becke J. Chem. Phys, 98, 5648 (1993).
B. Miehlich, A. Savin, H. Stoll, and H. Preuss, Chem. Phys. Lett., 157, 200 (1989).
P. J. Hay and W. R. Wadt J. Chem. Phys., 82, 299 (1985).
C. Lee, W. Yang, and R. G. Parr, Phys. Rev B, 37, 785 (1988).
S. S. Chio, Y. S. Lee, C. W. Joo, S. G. Lee, J. K. Park, and K. S. Han, Electro-Electrochim. Acta., 50, 339 (2004).
D. T. Swamy, K. E. Babu, and V. Veeraiah, Bull. Mater. Set, 36, 1115 (2013).
C. L. Yang, Z. H. Li, W. J. Li, H. Y. Liu, Q. Z. Xiao, G. T. Lei, and Y. H. Ding, J. Membr. Set, 495, 341 (2015).
L. O. Faria and R. L. Moreira, J. Pofym. Sci. B: Pofym. Phys, 38, 34 (2000).
X. Zhen, L. Zhang, M. Shi, L. Li, L. Cheng, Z. Jiao, W. Yang, and Y. Ding, Macromoi. Res, 28, 266 (2020).
Y. Z. Zhangand, C. K. Chan, J. Phys. Chem. A, 107, 5956 (2003).
P. G. Pickup, Chem. Soc. Faraday. Trans., 86, 3631 (1990).
M. Sethupathy, V. Sethuraman, and P. Manisankar, Soft Nanoscience Lett., 3, 37 (2013).
M. Romero, R. Faccio, and A. W. Mombru, Mater. Lett., 172, 1 (2016).
L. Wang, W. Yang, X. D. Li, and G. Evans, Electrochem. Solid State Lett., 13, 7 (2010).
Z. X. Wang, X. J. Huang, and L. Q. Chen, Electrochem. Solid State Lett, 6, 40 (2003).
W. Wieczorek, Z. Florjanczyk, and J. R. Stevens, Electrochim. Acta, 40, 2251 (1995).
A. Dawar and A. Chandra, Phys. Lett A, 376, 3604 (2012).
S. Stramare, V. Thangadurai, and W. Weppner, Chem. Mater., 15, 3974 (2003).
L. Simon, L. Ruban, and A. Kumar, Mater. Res. Innov., 21, 249 (2017).
Y. Ding, P. Zhang, Z. Long, Y. Jiang, and F. Xu, J. Alloys Compds., 487, 507 (2009).
X. Wu, J. Huang, S. Yu, P. Ruan, R. Sun, and C.-P. Wong, MacromoL Res., DOI: 10.1007/sl3233-020-8049-5 (2019).
S. A. Hashmi and S. Chandra, J. Mater. Sci. Eng., 34, 18 (1995).
P. Sivaraj, K. P. Abhilash, B. Nalini, P. Christopher Selvin, S. Goel, and S. K. Yadav, J. Am. Ceram. Soc, 103, 1685 (2020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Acknowledgments: Mr. P. Sivaraj thanks to the Council of Scientific Industrial Research (CSIR), Govt. of India, New Delhi, for providing the necessary financial support through the Senior Research Fellowship (SRF) (File No:09/0472(181)-2018-EMR-I) for the present work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sivaraj, P., Abhilash, K.P., Nalini, B. et al. Performance Enhancement of PVDF/LiCIO4 Based Nanocomposite Solid Polymer Electrolytes via Incorporation of Li0.5La0.5TiO3 Nano Filler for All-Solid-State Batteries. Macromol. Res. 28, 739–750 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-020-8096-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-020-8096-y