Abstract
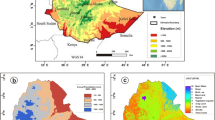
This study has evaluated Satellite Based Precipitation (SBP) products at key basins in Bolivia. Three basins of national interest were selected at different ecological steps: highlands, valleys and lowlands. GSMaP and CHIRPS products were tested showing promising detection abilities especially in regions with high elevation. At highlands the correlation coefficients of both SBP products showed values from 0.915 to 0.976. On the other hand, at lowlands, the coefficient values ranged from 0.895 to 0.926. Then, the combined products of GSMaP and CHIRPS with national rain gauge network were obtained using correction factors iteratively at sub-basin scale. The national sub-basins coding system of was used. These combined products so-called GS and CH showed a notorious improvement from 0.996 to 0.999 in relation to raw SBP products. At lowland regions results showed the largest improvement percentage in comparison with the other regions suggesting that higher intensities play a key role for correction scheme. The proposed scheme is feasible to implement with other SBP products and in other regions. The precipitation at sub-basins scale allows performing water balance, hydrological studies, biophysical assessments, water management planning among other applications.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, A.A.: Using lithologic modeling techniques for aquifer characterization and groundwater flow modeling of the Sohag area, Egypt. Hydrogeol. J. 17, 1189–1201 (2009)
Bielenki, C., Mendoça, F., Semensato, S., Mauad, F.: Alternative methodology to gap filling for generation of monthly rainfall series with GIS approach. Braz J Water Res. 23, (2018). https://doi.org/10.1590/2318-0331.231820170171
Blacutt, L.A., Herdies, D.L., de Goncalves, L.G., Vila, D.A., Andrade, M.: Precipitation comparison for the CFSR, MERRA, TRMM3B42 and Combined Scheme datasets in Bolivia. Atmos. Res. 163, 117–131 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2015.02.002
Climate Hazards Group. (n.d.). CHIRPS: Rainfall estimates from rain gauge and satellite observations. Retrieved from Climate Hazards Group: https://chc.ucsb.edu/data/chirps
Iriondo, M., Colombo, F., Kröhling, D.: The Pilcomayo Alluvial Fart, Chaco (Argentina - Bolivia - Paraguay): characteristics and sedimentary significance. Geogaceta. 28, 79–82 (2000)
Kim, K., Eom, D., Lee, D., Kuo, Y.: Diurnal variation of simulated 2007 summertime precipitation over South Korea in a real-time forecast model system. Asia-Pacific J Atmos Sci. 46, 505–512 (2010)
Kim, Y., Kim, H., Lee, G., & Min, K. (2019). A Modified Hybrid Gamma and Generalized Pareto Distribution for Precipitation Data. Asia-Pacific J Atmos Sci, 1-8.
Kubota, T., Okamoto, K., Shige, S., Ushio, T., Iguchi, T., Takahashi, N., . . . et al. (2007). The Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMaP) Project. The 7th International Planning Workshop. Tokyo.
Kwon, Y., Shin, H., Ban, H., Lee, Y., Park, K., Cho, J., et al.: A scattering-based over-land rainfall retrieval algorithm for South Korea using GCOM-W1/AMSR-2 data. Asia-Pacific J Atmos Sci. 53, 385–392 (2017)
Mahmund, M.R., Hashim, M., Reba, M.: How Effective is the New Generation of GPM Satellite Precipitation in Characterizing the Rainfall Variability over Malaysia? Asia-Pacific J Atmos Sci. 53, 375–384 (2017)
Ministerio de Medio Ambiente y Agua. (2011). Plan Nacional de Cuencas PNC. Retrieved from Biblioteca Virtual de la Cooperacion Alemana: https://www.bivica.org/files/cuencas-plan-nacional.pdf
Ministerio de Medio Ambiente y Agua. (2013). Marco Conceptual y Estratégico del Plan Director de la Cuenca del Río Grande. La Paz.
Molina, J., & Espinoza, D. (2005). Balance Hídrico Superficial de la Cuenca Alta del Río Pilcomayo. La Paz.
Redhum. (2016). Bolivia: Afectación y riesgo por sequía. Retrieved Abril 11, 2018, from ReliefWeb: https://reliefweb.int/sites/reliefweb.int/files/resources/Redhum-BO-Infografia_Sequia-20160602-AM-18551.pdf
Ryu, Y., Lim, Y., Ji, H., Park, H., Chang, E., Kim, B.: Applying a coupled hydrometeorological simulation system to flash flood forecasting over the Korean Peninsula. Asia-Pacific J Atmos Sci. 53, 421–430 (2017)
Tabios, G.Q., Salas, J.D.: A Comparative Analysis of Techniques for Spatial Interpolation of Precipitation. Water Resour. Bull. 21, 365–380 (1985)
Takido, K., Saavedra, O., Ryo, M., Tanuma, K., Ushio, T., Kubota, T.: Spatiotemporal Evaluation of the Gauge-Ajusted Satellite Mapping of Precipitation at the Basin Scale. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 94(2), 185–195 (2016)
Tian, Y., Peters-Lidard, C.D.: A global map of uncertainties in satellite-based precipitation measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 37 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1029/2010GL046008
Verdin, K., Verdin, J.: A topological system for delineation and codification of the Earth’s river basins. J. Hydrol. 218, 1–12 (1999)
World Meteorological Organization: Review of Requirements for Area-Averaged Precipitation Data, Surface-Based and Space-Based Estimation Techniques, Space and Time Sampling, Accuracy and Error; Data Exchange. Boulder, Colorado, U.S.A. Retrieved from World Meteorological Organization (1985) https://library.wmo.int/pmb_ged/wmo-td_115.pdf
Zhang, Y., Cassardo, C., Ye, C., Galli, M., Vela, N.: The role of the land surface processes in the rainfall generated by a landfall typhoon: A simulation of the typhoon Sepat (2007). Asia-Pacific J Atmos Sci. 47, 63–77 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Dong-Bin Shin.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ureña, J., Saavedra, O. Evaluation of Satellite Based Precipitation Products at Key Basins in Bolivia. Asia-Pacific J Atmos Sci 56, 641–655 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-020-00184-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-020-00184-4