Abstract
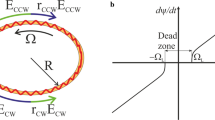
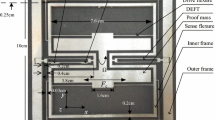
Generally, resonant optical gyroscopes (ROG) based on the Sagnac effect are very sensitive to the changes of temperature and optical power, which directly affects the output of the gyroscope. To improve the frequency lock-in accuracy and thermal stability of ROG system, the technology of laser frequency combination tuning and locking is proposed and experimentally demonstrated. Using the characteristics of voltage and temperature tuning wavelength of semiconductor laser, the output frequency range of laser is increased, the temperature control system of the resonant cavity can be removed and the gyro can never be unlocked in theory. In addition, the frequency lock-in accuracy under light power fluctuation is improved. Using this technique, a long-term (1-h) bias stability of 24.7 °/h is observed. Moreover, the weight and volume of the ROG are greatly reduced.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ROG:
-
Resonant optical gyroscope
- FRR:
-
Fiber ring resonator
- WRR:
-
Waveguide ring resonator
- FSR:
-
Free spectral range
- CW:
-
Clockwise
- CCW:
-
Counterclockwise
- FLRP:
-
Frequency lock reference point
- RIM:
-
Residual intensity modulation
- PD:
-
Photoelectric detector
- LIA:
-
Lock-in amplifier
- SG:
-
Signal generator
References
E.J. Post, Sagnac effect. Rev. Modern Phys. 39(2), 475–493 (1967)
G.A. Sanders, S.J. Sanders, L.K. Strandjord, T. Qiu, J. Wu, M. Smiciklas, D. Mead, S. Mosor, A. Arrizon, W. Ho, M. Salit, Fiber optic gyro development at Honeywell. Proc. SPIE. 9852, 985207 (2016)
H. Ma, J. Zhang, L. Wang, Z. Jin, Double closed-loop resonant micro optic gyro using hybrid digital phase modulation. Opt. Express. 23(12), 15088–15097 (2015)
W. Liang, V.S. Ilchenko, A.A. Savchenkov, E. Dale, D. Eliyahu, A.B. Matsko, L. Maleki, Resonant microphotonic gyroscope. Optica 4(1), 114–117 (2017)
Z.K. Ioannidis, P.M. Radmore, I.P. Giles, Dynamic response of an all-fiber ring resonator. Opt. Lett. 13(5), 422–424 (1988)
H. Cao, Y. Zhang, Z. Han, X. Shao, J. Gao, K. Huang, J. Liu, “Pole-zero-temperature compensation circuit design and experiment for dual-mass MEMS gyroscope bandwidth expansion,” IEEE/ASME Trans. Mech. (2019).
H. Cao, Y. Zhang, C. Shen, Y. Liu, X. Wang, “Temperature energy influence compensation for MEMS vibration gyroscope based on RBF NN-GA-KF method,” Shock Vibr. (2018).
P. Wang, G.S. Murugan, T. Lee, M. Ding, G. Brambilla, Y. Semenova, G. Farrell, High-Q bismuth silicate nonlinear glass microsphere resonators. IEEE Photon. J. 4(3), 1013–1020 (2012)
H. Guo, K. Qian, A. Cai, J. Tang, Jun Liu “Ordered gold nanoparticle arrays on the tip of silver wrinkled structures for single molecule detection,” Sens. Actuators, B. 300, 126846 (2019).
W. Gao, Z. Wang, G. Wang, W. Miao, Angular random walk improvement of resonator fiber optic gyro by optimizing modulation frequency. IEEE Photon. J. 11(4), 1–13 (2019)
H. Ma, J. Zhang, L. Wang, Y. Lu, D. Ying, Z. Jin, Resonant micro-optic gyro using a short and high-finesse fiber ring resonator. Opt. Lett. 40(24), 5862–5865 (2015)
K. Qian, J. Tang, H. Guo, W. Liu, J. Liu, C. Xue, C. Zhang, Under-coupling whispering gallery mode resonator applied to resonant micro-optic gyroscope. Sensors. 17(1), 100 (2017)
L. Wang, H. Li, J. Zhang, H. Ma, Z. Jin, Optimization of the sinusoidal phase modulation technique in resonant fiber optic gyro. Opt. Commun. 387, 18–23 (2017)
L. Maleki, W. Liang, D. Eliyahu, E. Dale, V. S. Ilchenko, A. A. Savchenkov, A. B. Matsko, “Sensitivity limitations of a resonant microphotonic gyroscope,” Proc. Avionics Veh. Fiber-Opt. Photon. Conf. pp. 343–344 (2016).
R. Zhang, C. Wang, H. Wang, X. Li, J. Li, and M. Kong, “Improving locking accuracy of resonant optical gyroscope by laser and acoustooptic frequency shifter jointed Pound-Drever-Hall technique,” Fiber Integr. Optics. pp. 1–11(2019).
H. Ma, X. Lu, Z. Jin, Reduction of reset pulse in resonant frequency servo loop for resonant fiber-optic gyro by an auto-controlled reset technique. Appl. Opt. 52(36), 8771–8778 (2013)
Z. Pan, C. Zhang, C. Xie, Y. Zheng, H. Li, J. Tang, J. Liu, Resonator integrated optic gyro based on multilevel laser frequency lock-in technique. Chin. Opt. Lett. 16(4), 040601 (2018)
G. A. Sanders, L. K. Strandjord, J. Wu, W. Williams, M. Smiciklas, M. Salit, T. Qiu, “Development of compact resonator fiber optic gyroscopes,” Proc. IEEE Int. Symp. Inertial Sensors Syst. pp 168–170 (2017).
D. Ying, J. Mao, Q. Li, Z. Jin, A miniaturized compact open-loop RFOG with demodulation signal compensation technique to suppress intensity modulation noise. Opt. Commun. 359, 364–371 (2016)
C. Zhang, Z. Pan, Y. Zheng, P. An, J. Tang, J. Liu, Suppression of residual intensity modulation noise in resonator integrated optic gyro. Opt. Commun. 430, 358–363 (2019)
E.A. Whittaker, M. Gehrtz, G.C. Bjorklund, Residual amplitude modulation in laser electro-optic phase modulation. JOSA B. 2(8), 1320–1326 (1985)
J.F. Diehl, C.E. Sunderman, J.M. Singley, V.J. Urick, K.J. Williams, Control of residual amplitude modulation in lithium niobate phase modulators. Opt. Express. 25(26), 32985–32994 (2017)
R. Duan, L. Feng, H. Jiao, X. Wang, Research on reducing the influence of laser frequency noise on resonator optical gyro. IEEE. Sens. J. 17(8), 2422–2427 (2017)
Funding
Natural National Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (No. 61803350,51635011 and 51727808); Science and Technology on Underwater Information and Control Laboratory (No. 6142218051810); Applied Basic Research Program in Shanxi Province (201901D211240, 201801D221202); Key Research and Development Program in Shanxi Province (201803D121067); Shanxi “1331 Project” Key Subjects Construction.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, S., Liu, W., Pan, Z. et al. Laser frequency combination tuning and locking technology in resonant optical gyro. Appl. Phys. B 126, 70 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-020-07421-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00340-020-07421-8