Abstract
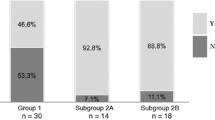
Brain donations are imperative for research; understanding possible barriers to entry is required to improve brain donation rates. While a few surveys have studied attitudes towards brain banking in patients with neurodegenerative disorders, none have surveyed patients with chronic neurological disorders but without neurodegeneration. This cross-sectional study was conducted on 187 participants, with both neurodegenerative (n = 122) and non-neurodegenerative disorders (n = 65), to compare their attitudes and preferences towards brain donation. Encouragingly, patients with non-neurodegenerative disorders were just as likely to consider brain donation as those with neurodegenerative diseases. Approximately half of each group were willing to consider brain donation, and majority of participants across both groups would not be offended if asked to participate in brain donation (71%). Across both groups, altruistic reasons such as desire to advance medical knowledge and benefit to other patients were the main motivating factors for brain donation, while perceived stress for family members, fears of body disfigurement and religious reasons were the main reasons against brain donation. Of note, nearly two-thirds of all participants were agreeable to allow their family to decide on their behalf. Overall, participants with non-neurodegenerative disorders appeared equally likely to consider brain donation as participants with neurodegenerative disorders. This is an important finding as they represent a significant population seen in specialist neurology clinics who may be overlooked in brain donor recruitment and awareness efforts. Healthcare professionals involved in brain banking should consider actively approaching these potential donors and involving their family members in these discussions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azizi L, Garrick TM, Harper CG (2006) Brain donation for research: strong support in Australia. J Clin Neurosci 13:449–452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2005.06.008
Boise L, Hinton L, Rosen HJ, Ruhl M (2017a) Will my soul go to heaven if they take my brain? Beliefs and worries about brain donation among four ethnic groups. Gerontologist 57:719–734. https://doi.org/10.1093/geront/gnv683
Boise L et al (2017b) Willingness to be a brain donor: a survey of research volunteers from 4 racial/ethnic groups. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 31:135–140. https://doi.org/10.1097/wad.0000000000000174
Carlos AF, Poloni TE, Medici V, Chikhladze M, Guaita A, Ceroni M (2019) From brain collections to modern brain banks: a historical perspective. Alzheimers Dement (N Y) 5:52–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trci.2018.12.002
Eatough V, Shaw K, Lees A (2012) Banking on brains: insights of brain donor relatives and friends from an experiential perspective. Psychol Health 27:1271–1290. https://doi.org/10.1080/08870446.2012.669480
Erkkinen MG, Kim MO, Geschwind MD (2018) Clinical neurology and epidemiology of the major neurodegenerative diseases. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a033118
Fonseca MK et al (2015) Assessing families’ and patients’ attitudes toward brain donation for research purposes in a Brazilian population sample. Cell Tissue Bank 16:287–294. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-014-9465-6
Francis PT, Hayes GM, Costello H, Whitfield DR (2019) Brains for dementia research: the importance of cohorts in brain banking. Neurosci Bull 35:289–294. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-018-0327-2
Garrick T, Azizi L, Merrick J, Harper C (2003) Brain donation for research, what do people say? Intern Med J 33:475
Garrick T, Howell S, Terwee P, Redenbach J, Blake H, Harper C (2006) Brain donation for research: who donates and why? J Clin Neurosci 13:524–528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2005.06.014
Garrick T, Sundqvist N, Dobbins T, Azizi L, Harper C (2009) Factors that influence decisions by families to donate brain tissue for medical research. Cell Tissue Bank 10:309–315. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-009-9136-1
Glaw XM, Garrick TM, Terwee PJ, Patching JR, Blake H, Harper C (2009) Brain donation: who and why? Cell Tissue Bank 10:241–246. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-009-9121-8
Harris C, Kiger A, Counsell C (2013) Attitudes to brain donation for Parkinson’s research and how to ask: a qualitative study with suggested guidelines for practice. J Adv Nurs 69:1096–1108. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2648.2012.06099.x
Hayes G, Costello H, Nurock S, Cornwall A, Francis P (2018) Ticking boxes or meaningful partnership—the experience of lay representation, participant and study partner involvement in brains for Dementia research. Dementia (London) 17:1023–1034. https://doi.org/10.1177/1471301218789308
Jefferson AL, Lambe S, Cook E, Pimontel M, Palmisano J, Chaisson C (2011) Factors associated with African American and white elders’ participation in a brain donation program. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 25:11–16. https://doi.org/10.1097/WAD.0b013e3181f3e059
Kaye JA, Dame A, Lehman S, Sexton G (1999) Factors associated with brain donation among optimally healthy elderly people. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 54:M560–M564. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/54.11.m560
Kretzschmar H (2009) Brain banking: opportunities, challenges and meaning for the future. Nat Rev Neurosci 10:70–78. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2535
Kuhta T, Zadikoff C, Simuni T, Martel A, Williams K, Videnovic A (2011) Brain donation–what do patients with movement disorders know and how do they feel about it? Parkinsonism Relat Disord 17:204–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2010.12.009
Lambe S, Cantwell N, Islam F, Horvath K, Jefferson AL (2011) Perceptions, knowledge, incentives, and barriers of brain donation among African American elders enrolled in an Alzheimer’s research program. Gerontologist 51:28–38. https://doi.org/10.1093/geront/gnq063
Le Bouc R et al (2016) Limiting factors of brain donation in neurodegenerative diseases: the example of French memory clinics. J Alzheimers Dis 49:1075–1083. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-150825
Patterson C, Lynch C, Bliss A, Lefevre M, Weidner W (2018) The state of the art of dementia research—World Alzheimer Report 2018. Alzheimer’s Disease International, London. https://www.alz.co.uk/research/WorldAlzheimerReport2018.pdf. Accessed 28 Aug 2019
Samarasekera N et al (2013) Brain banking for neurological disorders. Lancet Neurol 12:1096–1105. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70202-3
Schmitt FA, Wetherby MM, Wekstein DR, Dearth CM, Markesbery WR (2001) Brain donation in normal aging: procedures, motivations, and donor characteristics from the biologically resilient adults in neurological studies (BRAiNS) project. Gerontologist 41:716–722. https://doi.org/10.1093/geront/41.6.716
Schnieders T, Danner DD, McGuire C, Reynolds F, Abner E (2013) Incentives and barriers to research participation and brain donation among African Americans. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen 28:485–490. https://doi.org/10.1177/1533317513488922
Shepherd CE, Alvendia H, Halliday GM (2019) Brain banking for research into neurodegenerative disorders and ageing. Neurosci Bull 35:283–288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-018-0326-3
Stevens M (1998) Factors influencing decisions about donation of the brain for research purposes. Age Ageing 27:623–629. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/27.5.623
Striley CW, Milani SA, Kwiatkowski E, DeKosky ST, Cottler LB (2019) Community perceptions related to brain donation: evidence for intervention. Alzheimers Dement 15:267–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2018.09.005
Sundqvist N, Garrick T, Harding A (2012) Families’ reflections on the process of brain donation following coronial autopsy. Cell Tissue Bank 13:89–101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-010-9233-1
Tysnes OB, Storstein A (2017) Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 124:901–905. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-017-1686-y
Zhang Q, Deng J, Li YN, Gou Y, Yan XX, Li F, Pan AH (2019) Perceptions and attitudes toward brain donation among the Chinese people. Anat Sci Educ. https://doi.org/10.1002/ase.1886
Acknowledgements
The authors thank our participants and their families for their valuable contribution to the study. This study was funded by Singapore’s National Medical Research Council (ASLN by the Clinician-Scientist New Investigator Grant (CIRG/1416/2015) and Transition Award; LCST by the Singapore Parkinson’s disease Translational and Clinical Research flagship Grant (TCR12dec010)).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LCST, JYJF, ASLN and RJWC contributed to the study design and conception. All authors were involved in participant recruitment and data collection. ASLN, RJWC and SS analysed the data and wrote the first draft of the manuscript, while all authors revised the manuscript for intellectual content. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chan, R.J.W., Seah, S., Foo, J.Y.J. et al. Patient attitudes towards brain donation across both neurodegenerative and non-neurodegenerative neurological disorders. Cell Tissue Bank 21, 265–277 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-020-09819-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-020-09819-2