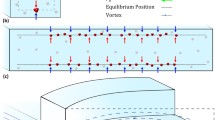
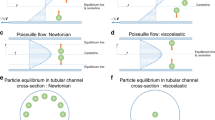
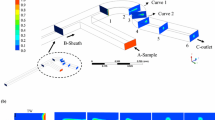
Abstract
Despite the stereotype that secondary flow fields induced by surface grooves are effective for microfluidic mixing and increase the entropy of different fluid flows, many efforts have been made to utilize the grooves for particle separation and focusing, decreasing the entropy of particle distribution. As part of these efforts, hydrophoresis has been proposed to define deterministic particle trajectories in grooved microchannels. Due to the simple, cloggingfree, and high-throughput characteristics, hydrophoresis has become increasingly promising for blood separation in clinical applications and sheathless particle focusing in flow cytometric applications. In this review, I introduce and summarize the basic physics, design parameters, design principles, and applications of hydrophoresis to improve the fundamental understanding of hydrophoresis and expand its use. I also discuss the challenges of hydrophoresis and forecast its future direction.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khoo, B.L., Grenci, G., Lim, Y.B., Lee, S.C., Han, J., & Lim, C.T. Expansion of patient-derived circulating tumor cells from liquid biopsies using a CTC microfluidic culture device. Nat. Protoc.13, 34–58 (2018).
Ma, Y.-H.V., Middleton, K., You, L. & Sun, Y. A review of microfluidic approaches for investigating cancer extravasation during metastasis. Microsyst. Nanoeng.4, 17104 (2018).
Cho, H., Kim, J., Song, H., Sohn, K.Y., Jeon, M., & Han, K.-H. Microfluidic technologies for circulating tumor cell isolation. Analyst143, 2936–2970 (2018).
Khoo, B.L., Grenci, G., Jing, T., Lim, Y.B., Lee, S.C., Thiery, J.P., Han, J., & Lim, C.T. Liquid biopsy and therapeutic response: Circulating tumor cell cultures for evaluation of anticancer treatment. Sci. Adv.2, e1600274 (2016).
Nagrath, S., Sequist, L.V., Maheswaran, S., Bell, D. W., Irimia, D., Ulkus, L., Smith, M.R., Kwak, E.L., Digumarthy, S., Muzikansky, A., Ryan, P., Balis, U. J., Tompkins, R.G., Haber, D.A., & Toner, M. Isolation of rare circulating tumor cells in cancer patients by microchip technology. Nature450, 1235–1239 (2007).
Lin, Z., Luo, G., Du, W., Kong, T., Liu, C., & Liu, Z. Recent advances in microfluidic platforms applied in cancer metastasis: Circulating tumor cells’ (CTCs) isolation and tumor-on-a-chip. Small16, e1903899 (2019).
Karabacak, N.M., Spuhler, P.S., Fachin, F., Lim, E. J., Pai, V., Ozkumur, E., Martel, J.M., Kojic, N., Smith, K., Chen, P.I., Yang, J., Hwang, H., Morgan, B., Trautwein, J., Barber, T.A., Stott, S.L., Maheswaran, S., Kapur, R., Haber, D.A., & Toner, M. Microfluidic, marker-free isolation of circulating tumor cells from blood samples. Nat. Protoc.9, 694–710 (2014).
Gao, Y., Xi, H., Wei, B., Cui, J., Zhang, K., Li, H., Cai, A., Shen, W., Li, J., Rosell, R., Chao, J., Chen, T., Klempner, S., Qiao, Z., & Chen, L. Association between liquid biopsy and prognosis of gastric cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Oncol.9, 1222 (2019).
Rossi, G. & Ignatiadis, M. Promises and pitfalls of using liquid biopsy for precision medicine. Cancer Res.79, 2798–2804 (2019).
Lim, S.B., Di Lee, W., Vasudevan, J., Lim, W.-T. & Lim, C.T. Liquid biopsy: one cell at a time. npj Precis. Oncol.3, 23 (2019).
Di Carlo, D. Technologies for the directed evolution of cell therapies. SLAS Technol.24, 359–372 (2019).
Campos-González, R., Skelley, A.M., Gandhi, K., Inglis, D.W., Sturm, J.C., Civin, C.I., & Ward, T. Deterministic lateral displacement: The next-generation CAR T-cell processing? SLAS Technol.23, 338–351 (2018).
Chiu, P.-L., Chang, C.-H., Lin, Y.-L., Tsou, P.-H. & Li, B.-R. Rapid and safe isolation of human peripheral blood B and T lymphocytes through spiral microfluidic channels. Sci. Rep.9, 8145 (2019).
Vormittag, P., Gunn, R., Ghorashian, S. & Veraitch, F.S. A guide to manufacturing CAR T cell therapies. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol.53, 164–181 (2018).
Ito, Y. & Shinomiya, K. A new continuous-flow cell separation method based on cell density: Principle, apparatus, and preliminary application to separation of human buffy coat. J. Clin. Apher.16, 186–191 (2001).
Feige, U., Overwien, B. & Sorg, C. Purification of human blood monocytes by hypotonic density gradient centrifugation in Percoll. J. Immunol. Methods54, 309–315 (1982).
Wang, K., Marshall, M.K., Garza, G. & Pappas, D. Open-tubular capillary cell affinity chromatography: Single and tandem blood cell separation. Anal. Chem.80, 2118–2124 (2008).
Hertz, C.M., Graves, D.J., Lauffenburger, D.A. & Serota, F.T. Use of cell affinity chromatography for separation of lymphocyte subpopulations. Biotechnol. Bioeng.27, 603–612 (1985).
Meyer, T.P., Zehnter, I., Hofmann, B., Zaisserer, J., Burkhart, J., Rapp, S., Weinauer, F., Schmitz, J. & Illert, W.E. Filter Buffy Coats (FBC): a source of peripheral blood leukocytes recovered from leukocyte depletion filters. J. Immunol. Methods307, 150–166 (2005).
He, M., Huang, H., Wang, M., Chen, A., Ning, X., Yu, K., Li, Q., Li, W., Ma, L., Chen, Z., Wang, X., & Sun, Q. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting analysis of heterotypic cell-in-cell structures. Sci. Rep.5, 9588 (2015).
Fukuda, H., Takahashi, J., Watanabe, K., Hayashi, H., Morizane, A., Koyanagi, M., Sasai, Y., & Hashimoto, N. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting-based purification of embryonic stem cell-derived neural precursors averts tumor formation after transplantation. Stem Cells24, 763–771 (2006).
Handgretinger, R., Lang, P., Schumm, M., Taylor, G., Neu, S., Koscielnak, E., Niethammer, D., & Klingebiel, T. Isolation and transplantation of autologous peripheral CD34+ progenitor cells highly purified by magnetic-activated cell sorting. Bone Marrow Transplant.21, 987–993 (1998).
Govers, C., Berrevoets, C., Treffers-Westerlaken, E., Broertjes, M. & Debets, R. Magnetic-activated cell sorting of TCR-engineered T cells, using tCD34 as a gene marker, but not peptide-MHC multimers, results in significant numbers of functional CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Hum. Gene Ther: Methods.23, 213–224 (2012).
Fu, A.Y., Spence, C., Scherer, A., Arnold, F.H. & Quake, S.R. A microfabricated fluorescence-activated cell sorter. Nat. Biotechnol.17, 1109 (1999).
Hu, X., Bessette, P.H., Qian, J., Meinhart, C.D., Daugherty, P.S., & Soh, H.T. Marker-specific sorting of rare cells using dielectrophoresis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.102, 15757–15761 (2005).
Wang, X.-B., Yang, J., Huang, Y., Vykoukal, J., Becker, F.F., & Gascoyne, P.R. Cell separation by dielectrophoretic field-flow-fractionation. Anal. Chem.72, 832–839 (2000).
Adams, J.D., Kim, U. & Soh, H.T. Multitarget magnetic activated cell sorter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.105, 18165–18170 (2008).
Inglis, D.W., Riehn, R., Sturm, J.C. & Austin, R.H. Microfluidic high gradient magnetic cell separation. J. Appl. Phys.99, 08K101 (2006).
Jung, J. & Han, K.-H. Lateral-driven continuous magnetophoretic separation of blood cells. Appl. Phys. Lett.93, 223902 (2008).
MacDonald, M.P., Spalding, G.C. & Dholakia, K. Microfluidic sorting in an optical lattice. Nature426, 421–424 (2003).
Wang, M.M., Tu, E., Raymond, D.E., Yang, J.M., Zhang, H., Hagen, N., Dees, B., Mercer, E.M., Forster, A.H., Kariv, I., Marchand, P.J., & Butler, W.F. Microfluidic sorting of mammalian cells by optical force switching. Nat. Biotechnol.23, 83–87 (2005).
Petersson, F., Åberg, L., Swärd-Nilsson, A.-M. & Laurell, T. Free flow acoustophoresis: microfluidic-based mode of particle and cell separation. Anal. Chem.79, 5117–5123 (2007).
Shi, J., Huang, H., Stratton, Z., Huang, Y. & Huang, T.J. Continuous particle separation in a microfluidic channel via standing surface acoustic waves (SSAW). Lab Chip9, 3354–3359 (2009).
Li, X., Chen, W., Liu, G., Lu, W. & Fu, J. Continuous-flow microfluidic blood cell sorting for unprocessed whole blood using surface-micromachined microfiltration membranes. Lab Chip14, 2565–2575 (2014).
Sethu, P., Sin, A., & Toner, M. Microfluidic diffusive filter for apheresis (leukapheresis). Lab Chip6, 83–89 (2006).
Huang, L.R., Cox, E.C., Austin, R.H. & Sturm, J.C. Continuous particle separation through deterministic lateral displacement. Science304, 987–990 (2004).
Morton, K.J., Loutherback, K., Inglis, D.W., Tsui, O.K., Sturm, J.C., Chou, S.Y., & Austin, R.H. Hydrodynamic metamaterials: Microfabricated arrays to steer, refract, and focus streams of biomaterials. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.105, 7434–7438 (2008).
McGrath, J., Jimenez, M. & Bridle, H. Deterministic lateral displacement for particle separation: a review. Lab Chip14, 4139–4158 (2014).
Zeming, K.K., Ranjan, S. & Zhang, Y. Rotational separation of non-spherical bioparticles using I-shaped pillar arrays in a microfluidic device. Nat. Commun.4, 1625 (2013).
Davis, J.A., Inglis, D.W., Morton, K.J., Lawrence, D.A., Huang, L.R., Chou, S.Y., Sturm, J.C., & Austin, R.H. Deterministic hydrodynamics: taking blood apart. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.103, 14779–14784 (2006).
Yamada, M., Nakashima, M., & Seki, M. Pinched flow fractionation: continuous size separation of particles utilizing a laminar flow profile in a pinched microchannel. Anal. Chem.76, 5465–5471 (2004).
Vig, A.L. & Kristensen, A. Separation enhancement in pinched flow fractionation. Appl. Phys. Lett.93, 203507 (2008).
Nho, H.W. & Yoon, T.H. Enhanced separation of colloidal particles in an AsPFF device with a tilted sidewall and vertical focusing channels (t-AsPFF-v). Lab Chip13, 773–776 (2013).
Yamada, M. & Seki, M. Hydrodynamic filtration for on-chip particle concentration and classification utilizing microfluidics. Lab Chip5, 1233–1239 (2005).
Di Carlo, D. Inertial microfluidics. Lab Chip9, 3038–3046 (2009).
Zhang, J., Yan, S., Yuan, D., Alici, G., Nguyen, N.-T., Warkiani, M.E. & Li, W. Fundamentals and applications of inertial microfluidics: a review. Lab Chip16, 10–34 (2016).
Chung, A.J. A minireview on inertial microfluidics fundamentals: Inertial particle focusing and secondary flow. BioChip J.13, 53–63 (2019).
Kim, G.-Y., Han, J.-I. & Park, J.-K. Inertial microfluidics-based cell sorting. BioChip J.12, 257–267 (2018).
Di Carlo, D., Irimia, D., Tompkins, R.G. & Toner, M. Continuous inertial focusing, ordering, and separation of particles in microchannels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.104, 18892–18897 (2007).
Sollier, E., Go, D.E., Che, J., Gossett, D.R., O’Byrne, S., Weaver, W.M., Kummer, N., Rettig, M., Goldman, J., Nickols, N., McCloskey, S., Kulkarni, R.P., & Di Carlo, D. Size-selective collection of circulating tumor cells using Vortex technology. Lab Chip14, 63–77 (2014).
Wu, Z., Chen, Y., Wang, M. & Chung, A.J. Continuous inertial microparticle and blood cell separation in straight channels with local microstructures. Lab Chip16, 532–542 (2016).
Warkiani, M.E., Khoo, B.L., Wu, L., Tay, A.K., Bhagat, A.A., Han, J. & Lim, C.T. Ultra-fast, labelfree isolation of circulating tumor cells from blood using spiral microfluidics. Nat. Protoc.11, 134–148 (2016).
Wang, X., Liedert, C., Liedert, R. & Papautsky, I. A disposable, roll-to-roll hot-embossed inertial microfluidic device for size-based sorting of microbeads and cells. Lab Chip16, 1821–1830 (2016).
Choi, S. & Park, J.-K. Continuous hydrophoretic separation and sizing of microparticles using slanted obstacles in a microchannel. Lab Chip7, 890–897 (2007).
Choi, S., Song, S., Choi, C. & Park, J.-K. Continuous blood cell separation by hydrophoretic filtration. Lab Chip7, 1532–1538 (2007).
Choi, S., Song, S., Choi, C. & Park, J.-K. Sheathless focusing of microbeads and blood cells based on hydrophoresis. Small4, 634–641 (2008).
Choi, S. & Park, J.-K. Sheathless hydrophoretic particle focusing in a microchannel with exponentially increasing obstacle arrays. Anal. Chem.80, 3035–3039 (2008).
Choi, S. & Park, J.-K. Mirror-embedded microchannel for three-dimensional measurement of particle position. Appl. Phys. Lett.93, 191909 (2008).
Choi, S., Song, S., Choi, C. & Park, J.-K. Hydrophoretic sorting of micrometer and submicrometer particles using anisotropic microfluidic obstacles. Anal. Chem.81, 50–55 (2009).
Choi, S., Song, S., Choi, C. & Park, J.-K. Microfluidic self-sorting of mammalian cells to achieve cell cycle synchrony by hydrophoresis. Anal. Chem.81, 1964–1968 (2009).
Choi, S. & Park, J.-K. Tuneable hydrophoretic separation using elastic deformation of poly(dimethylsiloxane). Lab Chip9, 1962–1965 (2009).
Choi, S. & Park, J.-K. Optically coated mirror-embedded microchannel to measure hydrophoretic particle ordering in three dimensions. Small5, 2205–2211 (2009).
Choi, S., Kim, S.-H. & Park, J.-K. Optical path-length modulation for three-dimensional particle measurement in mirror-embedded microchannels. Lab Chip10, 335–340 (2010).
Choi, S., Ku, T., Song, S., Choi, C. & Park, J.-K. Hydrophoretic high-throughput selection of platelets in physiological shear-stress range. Lab Chip11, 413–418 (2011).
Song, S. & Choi, S. Design rules for size-based cell sorting and sheathless cell focusing by hydrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. A1302, 191–196 (2013).
Song, S. & Choi, S. Field-free, sheathless cell focusing in exponentially expanding hydrophoretic channels for microflow cytometry. Cytometry, Part A83, 1034–1040 (2013).
Song, S. & Choi, S. Continuous medium exchange and cell isolation by size-selective passage through slanted micro-obstacles. J. Micromech. Microeng.24, 025007 (2014).
Song, S. & Choi, S. Inertial modulation of hydrophoretic cell sorting and focusing. Appl. Phys. Lett.104, 074106 (2014).
Song, S., Kim, M. S. & Choi, S. Smart microfluidic pipette tip enabled by flow-rate insensitive particle ordering. Small10, 4123–4129 (2014).
Song, S., Kim, M.S., Lee, J. & Choi, S. A continuous-flow microfluidic syringe filter for size-based cell sorting. Lab Chip15, 1250–1254 (2015).
Kim, B. & Choi, S. Smart pipette and microfluidic pipette tip for blood plasma separation. Small12, 190–197 (2016).
Kim, B., Lee, J.K. & Choi, S. Continuous sorting and washing of cancer cells from blood cells by hydrophoresis. BioChip J.10, 81–87 (2015).
Kim, B., Choi, Y.J., Seo, H., Shin, E.-C. & Choi, S. Deterministic migration-based separation of white blood cells. Small12, 5159–5168 (2016).
Kim, B., Oh, S., You, D. & Choi, S. Microfluidic pipette tip for high-purity and high-throughput blood plasma separation from whole blood. Anal. Chem.89, 1439–1444 (2017).
You, D., Oh, S., Kim, B., Hahn, Y.K. & Choi, S. Rapid preparation and single-cell analysis of concentrated blood smears using a high-throughput blood cell separator and a microfabricated grid film. J. Chromatogr. A1507, 141–148 (2017).
Kim, B., You, D., Kim, Y.-J., Oh, I. & Choi, S. Motorized smart pipette for handheld operation of a microfluidic blood plasma separator. Sens. Actuators, B267, 581–588 (2018).
Kim, B., Shin, S., Lee, Y., Um, C., You, D., Yun, H., & Choi, S. High-throughput residual white blood cell counter enabled by microfluidic cell enrichment and reagent-containing patch integration. Sens. Actuators, B283, 549–555 (2019).
Shin, S., Kim, B., Kim, Y.-J. & Choi, S. Integrated microfluidic pneumatic circuit for point-of-care molecular diagnostics. Biosens. Bioelectron.133, 169–176 (2019).
Kim, B., Kang, D. & Choi, S. Handheld microflow cytometer based on a motorized smart pipette, a microfluidic cell concentrator, and a miniaturized fluorescence microscope. Sensors19, 2761 (2019).
Kim, B., Kim, K.H., Chang, Y., Shin, S., Shin, E.-C. & Choi, S. One-step microfluidic purification of white blood cells from whole blood for immunophenotyping. Anal. Chem.91, 13230–13236 (2019).
Lee, E., Kim, B. & Choi, S. An open-source programmable smart pipette for portable cell separation and counting. RSC Adv.9, 41877–41885 (2019).
Stroock, A.D., Dertinger, S.K., Ajdari, A., Mezić, I., Stone, H.A., & Whitesides, G.M. Chaotic mixer for microchannels. Science295, 647–651 (2002).
Stroock, A.D., Dertinger, S.K., Whitesides, G.M. & Ajdari, A. Patterning flows using grooved surfaces. Anal. Chem.74, 5306–5312 (2002).
Kim, D.S., Lee, S.W., Kwon, T.H. & Lee, S.S. A barrier embedded chaotic micromixer. J. Micromech. Microeng.14, 798–805 (2004).
Wang, H., Iovenitti, P., Harvey, E. & Masood, S. Numerical investigation of mixing in microchannels with patterned grooves. J. Micromech. Microeng.13, 801 (2003).
Schönfeld, F., & Hardt, S. Simulation of helical flows in microchannels. AIChE J.50, 771–778 (2004).
Kang, T.G. & Kwon, T.H. Colored particle tracking method for mixing analysis of chaotic micromixers. J. Micromech. Microeng.14, 891–899 (2004).
Lynn, N.S. & Dandy, D.S. Geometrical optimization of helical flow in grooved micromixers. Lab Chip7, 580–587 (2007).
Belliveau, N.M., Huft, J., Lin, P.J., Chen, S., Leung, A.K., Leaver, T.J., Wild, A.W., Lee, J.B., Taylor, R.J., Tam, Y.K., Hansen, C.L., & Cullis, P.R. Microfluidic synthesis of highly potent limit-size lipid nanoparticles for in vivo delivery of siRNA. Mol. Ther.- Nucleic Acids1, e37 (2012).
Maeki, M., Saito, T., Sato, Y., Yasui, T., Kaji, N., Ishida, A., Tani, H., Baba, Y., Harashima, H., & Tokeshi, M. A strategy for synthesis of lipid nano-particles using microfluidic devices with a mixer structure. RSC Adv.5, 46181–46185 (2015).
Stott, S.L., Hsu, C.H., Tsukrov, D.I., Yu, M., Miyamoto, D.T., Waltman, B.A., Rothenberg, S.M., Shah, A.M., Smas, M.E., Korir, G.K., Floyd, F.P., Jr., Gilman, A.J., Lord, J.B., Winokur, D., Springer, S., Irimia, D., Nagrath, S., Sequist, L.V., Lee, R.J., Isselbacher, K.J., Maheswaran, S., Haber, D.A., & Toner, M. Isolation of circulating tumor cells using a microvortex-generating herringbone-chip. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A.107, 18392–18397 (2010).
Choi, S., Karp, J.M. & Karnik, R. Cell sorting by deterministic cell rolling. Lab Chip12, 1427–1430 (2012).
Choi, S., Levy, O., Coelho, M.B., Cabral, J.M., Karp, J.M., & Karnik, R. A cell rolling cytometer reveals the correlation between mesenchymal stem cell dynamic adhesion and differentiation state. Lab Chip14, 161–166 (2014).
Reschiglian, P., Zattoni, A., Roda, B., Michelini, E. & Roda, A. Field-flow fractionation and biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol.23, 475–483 (2005).
Yan, S., Zhang, J., Alici, G., Du, H., Zhu, Y., & Li, W. Isolating plasma from blood using a dielectrophoresis-active hydrophoretic device. Lab Chip14, 2993–3003 (2014).
Yan, S., Zhang, J., Li, M., Alici, G., Du, H., Sluyter, R., & Li, W. On-chip high-throughput manipulation of particles in a dielectrophoresis-active hydrophoretic focuser. Sci. Rep.4, 5060 (2014).
Yan, S., Zhang, J., Yuan, Y., Lovrecz, G., Alici, G., Du, H., Zhu, Y., & Li, W. A hybrid dielectrophoretic and hydrophoretic microchip for particle sorting using integrated prefocusing and sorting steps. Electrophoresis36, 284–291 (2015).
Yan, S., Zhang, J., Chen, H., Yuan, D., Alici, G., Du, H., Zhu, Y. & Li, W. Development of a novel magnetophoresis-assisted hydrophoresis microdevice for rapid particle ordering. Biomed. Microdevices18, 54 (2016).
Ateya, D.A., Erickson, J.S., Howell, P.B., Jr., Hilliard, L.R., Golden, J.P., & Ligler, F.S. The good, the bad, and the tiny: a review of microflow cytometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem.391, 1485–1498 (2008).
Vembadi, A., Menachery, A. & Qasaimeh, M.A. Cell cytometry: Review and perspective on biotechnological advances. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol.7, 147 (2019).
Asghari, M., Serhatlioglu, M., Ortac, B., Solmaz, M.E. & Elbuken, C. Sheathless microflow cytometry using viscoelastic fluids. Sci. Rep.7, 12342 (2017).
Bhagat, A. A., Kuntaegowdanahalli, S. S., Kaval, N., Seliskar, C. J. & Papautsky, I. Inertial microfluidics for sheath-less high-throughput flow cytometry. Biomed. Microdevices12, 187–195 (2010).
Martel, J.M. & Toner, M. Inertial focusing in microfluidics. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng.16, 371–396 (2014).
Mielczarek, W.S., Obaje, E.A., Bachmann, T.T. & Kersaudy-Kerhoas, M. Microfluidic blood plasma separation for medical diagnostics: is it worth it? Lab Chip16, 3441–3448 (2016).
Kersaudy-Kerhoas, M. & Sollier, E. Micro-scale blood plasma separation: from acoustophoresis to egg-beaters. Lab Chip13, 3323–3346 (2013).
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Samsung Research Funding Center of Samsung Electronics under Project Number SRFC-IT1502-54. I thank Byeongyeon Kim for her help with reference preparation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, S. Hydrophoresis — A Microfluidic Principle for Directed Particle Migration in Flow. BioChip J 14, 72–83 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-020-4107-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-020-4107-5