Abstract
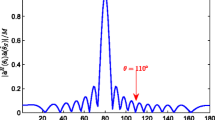
In this paper, we propose a novel parameter-free Landweber iteration (LI) method to improve the robustness of a beamformer based on the LI algorithm and the L-curve criterion. The critical aspect of the proposed method is the automatic parameter selection procedure, which determines the iteration stop number in a scenario-dependent manner. This parameter-free method can flexibly adapt to different communication environments. To further improve the computational efficiency, an accelerated parameter-free LI method is also proposed that incorporates the Newton iteration into the LI algorithm without compromising the robustness of the beamformer. Numerical experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed beamformer.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Bertero, P. Boccacci, Introduction to Inverse Problems in Imaging (IOP, Bristol, 1998)
B.D. Carlson, Covariance matrix estimation errors and diagonal loading in adaptive arrays. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 24(4), 397–401 (1988)
L. Du, J. Li, P. Stoica, Fully automatic computation of diagonal loading levels for robust adaptive beamforming. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 46(1), 449–458 (2010)
D.D. Feldman, L.J. Griffiths, A projection approach for robust adaptive beamforming. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 42(4), 867–876 (1994)
Y. Gu, A. Leshem, Robust adaptive beamforming based on interference covariance matrix reconstruction and steering vector estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 60(7), 3881–3885 (2012)
Y. Gu, N.A. Goodman, S. Hong, Y. Li, Robust adaptive beamforming based on interference covariance matrix sparse reconstruction. Signal Process. 96, 375–381 (2014)
M. Hanke, Accelerated Landweber iterations for the solution of ill-posed equations. Numer. Math. 60(3), 341–373 (1991)
M. Hanke, A. Neubauer, O. Scherzer, A convergence analysis of the Landweber iteration for nonlinear ill-posed problems. Numer. Math. 72(1), 21–37 (1995)
P.C. Hansen, Analysis of discrete ill-posed problems by means of the L-curve. SIAM Rev. 34(4), 561–580 (1992)
P.C. Hansen, Regularization tools: a Matlab package for analysis and solution of discrete ill-posed problems. Numer. Algorithms 6(1), 1–35 (1994)
P.C. Hansen, Rank-Deficient and Discrete Ill-Posed Problems: Numerical Aspects of Linear Inversion (SIAM, Philadelphia, 1998), pp. 187–192
X. Jiang, W. Zeng, A. Yasotharan, H.C. So, T. Kirubarajan, Robust beamforming by linear programming. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 62(7), 1834–1849 (2014)
B. Kaltenbacher, I. Tomba, Convergence rates for an iteratively regularized Newton–Landweber iteration in Banach space. Inverse Prob. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1088/0266-5611/29/2/025010
Y. Ke, C. Zheng, R. Peng, X. Li, robust adaptive beamforming using noise reduction preprocessing-based fully automatic diagonal loading and steering vector estimation. IEEE Access 5(99), 12974–12987 (2017)
J. Li, P. Stoica, Z. Wang, On robust Capon beamforming and diagonal loading. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 51(7), 1702–1715 (2003)
J. Li, P. Stoica, Robust Adaptive Beamforming (Wiley, Hoboken, 2006)
J. Landon, B.D. Jeffs, K.F. Warnick, Model-based subspace projection beamforming for deep interference nulling. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 60(3), 1215–1228 (2012)
L. Landweber, An iteration formula for Fredholm integral equations of the first kind. Am. J. Math. 73(3), 615–624 (1951)
R.G. Lorenz, S.P. Boyd, Robust minimum variance beamforming. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 53(5), 1684–1696 (2005)
S. Mohammadzadeh, O. Kukrer, Modified robust capon beamforming with approximate orthogonal projection onto the signal-plus-interference subspace. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 37(12), 5352–5368 (2018)
S. Mohammadzadeh, O. Kukrer, Robust adaptive beamforming with improved interferences suppression and a new steering vector estimation based on spatial power spectrum. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 38(9), 4162–4179 (2019)
D.A. Pados, G.N. Karystinos, An iterative algorithm for the computation of the MVDR filter. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 49(2), 290–300 (2001)
V. Pan, R. Schreiber, An improved Newton iteration for the generalized inverse of a matrix, with applications. SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comput. 12(5), 1109–1130 (1991)
J. Qian, Z. He, T. Liu, N. Huang, Robust beamforming based on steering vector and covariance matrix estimation. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 37(10), 4665–4682 (2018)
G. Schulz, Iterative Berechnung der reziproken matrix. Z. Angew. Math. Mech. 13(1), 57–59 (1933)
J.F. Sturm, Using SeDuMi 1.02, a MATLAB toolbox for optimization over symmetric cones. Optim. Methods Softw. 11(1–4), 625–653 (1999)
O. Scherzer, A modified Landweber iteration for solving parameter estimation problems. Appl. Math. Optim. 38(1), 45–68 (1998)
Y. Selén, R. Abrahamsson, P. Stoica, Automatic robust adaptive beamforming via ridge regression. Signal Process. 88(1), 33–49 (2008)
H.L. Van Trees, Optimum Array Processing (Wiley, Hoboken, 2002), pp. 439–443
S.A. Vorobyov, A.B. Gershman, Z.Q. Luo, Robust adaptive beamforming using worst-case performance optimization: a solution to the signal mismatch problem. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 51(2), 313–324 (2003)
J. Yang, X. Ma, C. Hou, Y. Liu, automatic generalized loading for robust adaptive beamforming. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 16(3), 219–222 (2009)
X. Yuan, L. Gan, Robust adaptive beamforming via a novel subspace method for interference covariance matrix reconstruction. Signal Process. 130, 233–242 (2017)
C. Zhou, Y. Gu, S. He, Z. Shi, A robust and efficient algorithm for coprime array adaptive beamforming. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 67(2), 1099–1112 (2018)
C. Zhou, Z. Shi, Y. Gu, Coprime array adaptive beamforming with enhanced degrees-of-freedom capability, in 2017 IEEE Radar Conference (Seattle, WA, 2017), pp. 1357–1361
M. Zhang, A. Zhang, Q. Yang, robust adaptive beamforming based on conjugate gradient algorithms. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 64(22), 6046–6057 (2016)
Z. Zheng, K. Liu, W. Wang, Y. Yang, J. Yang, Robust adaptive beamforming against mutual coupling based on mutual coupling coefficients estimation. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 66(10), 9124–9133 (2017)
Z. Zheng, Y. Zheng, W. Wang, H. Zhang, Covariance matrix reconstruction with interference steering vector and power estimation for robust adaptive beamforming. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 67(9), 8495–8503 (2018)
Z. Zheng, T. Yang, W. Wang, H.C. So, Robust adaptive beamforming via simplified interference power estimation. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TAES.2019.2899796
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Liu, W., Jin, M. et al. Parameter-Free Landweber Iteration Method for Robust Adaptive Beamforming. Circuits Syst Signal Process 39, 2716–2729 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-019-01270-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-019-01270-3