Abstract
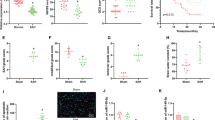
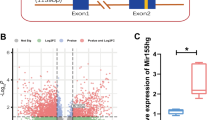
Hypoxic-ischemic brain damage (HIBD) represents one of the leading causes of neonatal mortality and permanent neurological disability worldwide. Compelling studies have identified implication of microRNAs (miRNAs) in HIBD. However, the molecular mechanism of miR-21 underlying the disease pathogenesis is unknown. The present study aims to explore the role of miR-21 in neonatal rats with HIBD. HIBD rat models were developed by carotid artery ligation and hypoxia treatment, and in vitro cell models were induced by oxygen–glucose deprivation. Through RT-qPCR and western blot analysis, high expression of CCL3 and poor expression of miR-21 were detected in brain tissues of rats with HIBD. Results of dual-luciferase reporter gene assay demonstrated that miR-21 could target and downregulate CCL3. The effect of miR-21 on the neurobehavioral ability of rats, the pathological characteristics of brain tissues, neuron apoptosis and as well as its impact on the NF-κB signaling pathway-related factors was examined by gain- and loss-of-function experiments. The obtained data suggested that upregulation of miR-21 resulted in significantly reduced cerebral infarct volume and degree of brain tissue damage, and improved neurobehavioral ability and memory ability in rats with HIBD through downregulation of CCL3. Besides, overexpression of miR-21 downregulated CCL3 to repress IKKα/β and p65 phosphorylation both in vivo and in vitro, hence disrupting the NF-κB signaling pathway. Taken together, the key findings of the current study underlie the cerebral protective effect of miR-21 against HIBD in neonatal rats through the inhibition of CCL3.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Busl KM, Greer DM (2010) Hypoxic-ischemic brain injury: pathophysiology, neuropathology and mechanisms. NeuroRehabilitation 26(1):5–13
Huang R, Zhang J, Ren C, Zhang X, Gu L, Dong Y, Zhang J, Zhang J (2019) Effect of erythropoietin on Fas/FasL expression in brain tissues of neonatal rats with hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. NeuroReport 30(4):262–268
Zhao F, Qu Y, Liu H, Du B, Mu D (2014) Umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells co-modified by TERT and BDNF: a novel neuroprotective therapy for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Int J Dev Neurosci 38:147–154
Peng T, Jia YJ, Wen QQ, Guan WJ, Zhao EY, Zhang BA (2010) Expression of microRNA in neonatal rats with hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi 12(5):373–376
Ma Q, Zhang L (2015) Epigenetic programming of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in response to fetal hypoxia. Prog Neurobiol 124:28–48
Rupaimoole R, Slack FJ (2017) MicroRNA therapeutics: towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 16(3):203–222
Fang H, Li HF, Yang M, Wang RR, Wang QY, Zheng PC, Zhang FX, Zhang JP (2019) microRNA-128 enhances neuroprotective effects of dexmedetomidine on neonatal mice with hypoxic-ischemic brain damage by targeting WNT1. Biomed Pharmacother 113:108671
Zhang XL, An BF, Zhang GC (2019) MiR-27 alleviates myocardial cell damage induced by hypoxia/reoxygenation via targeting TGFBR1 and inhibiting NF-kappaB pathway. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 35(10):607–614
Xu HX, Pan W, Qian JF, Liu F, Dong HQ, Liu QJ (2019) MicroRNA21 contributes to the puerarininduced cardioprotection via suppression of apoptosis and oxidative stress in a cell model of ischemia/reperfusion injury. Mol Med Rep 20(1):719–727
Guzik-Kornacka A, Sliwa A, Plucinska G, Lukasiuk K (2011) Status epilepticus evokes prolonged increase in the expression of CCL3 and CCL4 mRNA and protein in the rat brain. Acta Neurobiol Exp 71(2):193–207
Hattermann K, Knerlich-Lukoschus F, Lucius R, Mehdorn M, Held-Feindt J (2015) Erythropoietin and CCL3 antagonise their functional properties during neuroinflammation. Neurol Res 37(11):1025–1028
Kuijpers M, van Gassen KL, de Graan PN, Gruol D (2010) Chronic exposure to the chemokine CCL3 enhances neuronal network activity in rat hippocampal cultures. J Neuroimmunol 229(1–2):73–80
Hsu CJ, Wu MH, Chen CY, Tsai CH, Hsu HC, Tang CH (2013) AMP-activated protein kinase activation mediates CCL3-induced cell migration and matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression in human chondrosarcoma. Cell Commun Signal 11:68
Kielland A, Camassa LM, Dohlen G, Munthe LA, Blomhoff R, Amiry-Moghaddam M, Carlsen H (2012) NF-kappaB activity in perinatal brain during infectious and hypoxic-ischemic insults revealed by a reporter mouse. Brain Pathol 22(4):499–510
Nijboer CH, Heijnen CJ, Groenendaal F, May MJ, van Bel F, Kavelaars A (2008) Strong neuroprotection by inhibition of NF-kappaB after neonatal hypoxia-ischemia involves apoptotic mechanisms but is independent of cytokines. Stroke 39(7):2129–2137
Rice JE 3rd, Vannucci RC, Brierley JB (1981) The influence of immaturity on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the rat. Ann Neurol 9(2):131–141
Yan H, Rao J, Yuan J, Gao L, Huang W, Zhao L, Ren J (2017) Long non-coding RNA MEG3 functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate ischemic neuronal death by targeting miR-21/PDCD4 signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis 8(12):3211
Yang X, Zhong M, Chen J, Li T, Cheng Q, Dai Y (2018) HIF-1α repression of PTEN transcription mediates protective effects of BMSCs on neurons during hypoxia. Neuroscience 392:57–65
Gu Y, Zhang Y, Bi Y, Liu J, Tan B, Gong M, Li T, Chen J (2015) Mesenchymal stem cells suppress neuronal apoptosis and decrease IL-10 release via the TLR2/NFkappaB pathway in rats with hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Mol Brain 8(1):65
He XW, Shi YH, Zhao R, Liu YS, Li GF, Hu Y, Chen W, Cui GH, Su JJ, Liu JR (2019) Plasma levels of miR-125b-5p and miR-206 in acute ischemic stroke patients after recanalization treatment: a prospective observational study. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 28(6):1654–1661
Zhu X, Wei D, Chen O, Zhang Z, Xue J, Huang S, Zhu W, Wang Y (2016) Upregulation of CCL3/MIP-1alpha regulated by MAPKs and NF-kappaB mediates microglial inflammatory response in LPS-induced brain injury. Acta Neurobiol Exp 76(4):304–317
de Jager SC, Kraaijeveld AO, Grauss RW, de Jager W, Liem SS, van der Hoeven BL, Prakken BJ, Putter H, van Berkel TJ, Atsma DE, Schalij MJ, Jukema JW, Biessen EA (2008) CCL3 (MIP-1 alpha) levels are elevated during acute coronary syndromes and show strong prognostic power for future ischemic events. J Mol Cell Cardiol 45(3):446–452
Marciniak E, Faivre E, Dutar P, Alves Pires C, Demeyer D, Caillierez R, Laloux C, Buee L, Blum D, Humez S (2015) The Chemokine MIP-1alpha/CCL3 impairs mouse hippocampal synaptic transmission, plasticity and memory. Sci Rep 5:15862
Victoria ECG, de Brito Toscano EC, de Sousa Cardoso AC, da Silva DG, de Miranda AS, da Silva BL, Sugimoto MA, Sousa LP, de Assis Lima IV, de Oliveira ACP, Brant F, Machado FS, Teixeira MM, Teixeira AL, Rachid MA (2017) Knockdown of C–C chemokine receptor 5 (CCR5) is protective against cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury. Curr Neurovasc Res 14(2):125–131
Yao X, Wang Y, Zhang D (2018) microRNA-21 confers neuroprotection against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury and alleviates blood-brain barrier disruption in rats via the MAPK signaling pathway. J Mol Neurosci 65(1):43–53
Kim JH, Kim WS, Hong JY, Ryu KJ, Kim SJ, Park C (2017) Epstein-Barr virus EBNA2 directs doxorubicin resistance of B cell lymphoma through CCL3 and CCL4-mediated activation of NF-kappaB and Btk. Oncotarget 8(3):5361–5370
Zhao H, Chen Z, Xie LJ, Liu GF (2018) Suppression of TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling pathway improves cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Mol Neurobiol 55(5):4311–4319
Wu W, Zhong W, Lang B, Hu Z, He J, Tang X (2018) Thrombopoietin could protect cerebral tissue against ischemia-reperfusion injury by suppressing NF-kappaB and MMP-9 expression in rats. Int J Med Sci 15(12):1341–1348
Liu X, Zhang X, Wang F, Liang X, Zeng Z, Zhao J, Zheng H, Jiang X, Zhang Y (2017) Improvement in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through the TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway after Kudiezi injection in rats. Life Sci 191:132–140
Lu L, Xu H, Yang P, Xue J, Chen C, Sun Q, Yang Q, Lu J, Shi A, Liu Q (2018) Involvement of HIF-1alpha-regulated miR-21, acting via the Akt/NF-kappaB pathway, in malignant transformation of HBE cells induced by cigarette smoke extract. Toxicol Lett 289:14–21
Acknowledgements
We would like to give our sincere appreciation to the reviewers for their helpful comments on this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JL, SZ, YH and LS designed the study. JL and SZ collated the data, carried out data analyses and produced the initial draft of the manuscript. YH and LS contributed to drafting the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final submitted manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Zhang, S., Huang, Y. et al. miR-21 protects neonatal rats from hypoxic-ischemic brain damage by targeting CCL3. Apoptosis 25, 275–289 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-020-01596-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-020-01596-3