Abstract
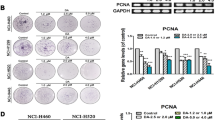
Lung cancer is the primary reason of cancer death worldwide, with an annual incidence of ~1.3 million cases. Therefore, finding better and more effective methods to treat lung cancer has become very pressing. PDB-1 is a new C-27-carboxylated-lupane-triterpenoid derivative isolated from Potentilla discolor Bunge and is a type of compound that is rarely found in natural sources. This research investigated the effects of a novel triterpenoid compound PDB-1 on the expression of proteins regulating cancer proliferation, migration, and invasion in A549 and H460 cells. The results showed that PDB-1 inhibited the proliferation of A549 and H460 cells and that this inhibition was accompanied by decreased PCNA. Wound, transwell migration, and invasion assays showed that cell migration and invasion of lung cancer cells were significantly inhibited by PDB-1 in a dose-dependent manner. The results of western blot showed that PDB-1 decreased the level of p-FAK, which lead to the downregulation of MMP-2 and MMP-9 and decreased the potential for metastasis. Furthermore, after cells were treated with PDB-1, the expression levels of p-p38, p-ERK, and p-JNK were also dramatically decreased. Simultaneously, this study firstly showed that the PDB-1 can suppress the activation of the ERK/MAPK signaling pathway by inhibiting FAK expression, accordingly inhibiting the proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung cancer cells. Our study offered a molecular foundation for the potential application of PDB-1 on the therapy of lung cancer and the development of new antitumor drugs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bauvois B (2012) New facets of matrix metalloproteinases MMP-2 and MMP-9 as cell surface transducers: outside-in signaling and relationship to tumor progression. Biochim Biophys Acta 1825:29–36
Bharat J, Michele B, Strugnell SS, Cecile B, Parton RG, Nabi IR (2013) Phosphocaveolin-1 is a mechanotransducer that induces caveola biogenesis via Egr1 transcriptional regulation. J Cell Biol 200:681–681
Brew K, Nagase H (2010) The tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs): an ancient family with structural and functional diversity. Biochim Biophys Acta 1803:55–71
Chen YY, Liu FC, Chou PY, Chien YC, Chang WS, Huang GJ, Wu CH et al. (2012) Ethanol extracts of fruiting bodies of Antrodia cinnamomea suppress CL1-5 human lung adenocarcinoma cells migration by inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase-2/9 through ERK, JNK, p38, and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Evid Based Complement Altern Med 2012:378415
Chun J, Kim YS (2013) Platycodin D inhibits migration, invasion, and growth of MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells via suppression of EGFR-mediated Akt and MAPK pathways. Chem Biol Interact 205:212–221
Cui S, Wang J, Wu Q, Qian J, Yang CS, Bo P (2017) Genistein inhibits the growth and regulates the migration and invasion abilities of melanoma cells via the FAK/paxillin and MAPK pathways. Oncotarget 8:21674–21691
Fidler IJ (2003) The pathogenesis of cancer metastasis: the ‘seed and soil’ hypothesis revisited. Nat Rev Cancer 3:453–458
Gum R, Lengyel E, Juarez J, Chen JH, Sato H, Seiki M, Boyd D (1996) Stimulation of 92-kDa gelatinase b promoter activity by ras is mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1-independent and requires multiple transcription factor binding sites including closely spaced PEA3/ets and AP-1 sequences. J Biol Chem 271:10672–10680
Hiscox S, Barnfather P, Hayes E, Bramble P, Christensen J, Nicholson RI, Barrett-Lee P (2011) Inhibition of focal adhesion kinase suppresses the adverse phenotype of endocrine-resistant breast cancer cells and improves endocrine response in endocrine-sensitive cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 125:659–669
Hood JD, Cheresh DA (2002) Role of integrins in cell invasion and migration. Nat Rev Cancer 2:91–100
Jeong KY (2018) Inhibiting focal adhesion kinase: a potential target for enhancing therapeutic efficacy in colorectal cancer therapy. World J Gastrointest Oncol 10:290–292
Jiao Y, Feng X, Zhan YP, Wang RF, Zheng S, Liu WG, Zeng XL et al. (2012) Matrix metalloproteinase-2 promotes αvβ3 integrin-mediated adhesion and migration of human melanoma cells by cleaving fibronectin. Plos ONE 7:e41591
Juríková M, Danihel Ľ, Polák Š, Varga I (2016) Ki67, PCNA, and MCM proteins: markers of proliferation in the diagnosis of breast cancer. Acta Histoche 118:544–552
Kratimenos P, Koutroulis I, Marconi D, Syriopoulou V, Delivoria-Papadopoulos M, Chrousos GP, Theocharis S (2014) Multi-targeted molecular therapeutic approach in aggressive neuroblastoma: the effect of focal adhesion kinase-Src-paxillin system. Expert Opin Ther Targets 18:1395–1406
Lee SJ, Park SS, Lee US, Kim WJ, Moon SK (2008) Signaling pathway for TNF-α-induced MMP-9 expression: mediation through p38 MAP kinase, and inhibition by anti-cancer molecule magnolol in human urinary bladder cancer 5637 cells. Int Immunopharmacol 8:1821–1826
Liu L, Xiong YY, Tian SF (2004) Expressions of VEGF and MMP-2 in gastric adenocarcinoma and their involvment in tumor invasion and metastasis. Cancer Res Prev Treat 31:14–16
Maeda K, Chung YS, Takatsuka S, Ogawa Y, Onoda N, Sawada T, Kato Y et al. (1995) Tumour angiogenesis and tumour cell proliferation as prognostic indicators in gastric carcinoma. Brit J Cancer 72:319–323
Marie C, Roux PP (2011) Activation and function of the MAPKs and their substrates, the MAPK-activated protein kinases. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 75:50–83
Mohamed A, Ahmed F, Hassan E, Sharon M, Khalid S (2014) The marine-derived sipholenol A-4-O-3’,4’-dichlorobenzoate inhibits breast cancer growth and motility in vitro and in vivo through the suppression of Brk and FAK signaling. Mar Drugs 12:2282–2304
Nimwegen MJV, Water BVD (2007) Focal adhesion kinase: a potential target in cancer therapy. Biochem Pharm 73:597–609
Okada T, Sinha S, Esposito I, Schiavon G, López-Lago MA, Su W, Pratilas CA et al. (2015) The Rho GTPase Rnd1 suppresses mammary tumorigenesis and EMT by restraining Ras-MAPK signalling. Nat Cell Biol 17:81–94
Parsons TJ (2003) Focal adhesion kinase: the first ten years. J Cell Sci 116:1409–1416
Reddy KB, Nabha SM, Atanaskova N (2003) Role of MAP kinase in tumor progression and invasion. Cancer Metast Rev 22:395–403
Reeves MJ, Newcomb PA, Remington PL, Marcus PM, Mackenzie WR (1996) Body mass and breast cancer. Relationship between method of detection and stage of disease. Cancer 77:301–307
Reno TA, Kim JY, Dan JR (2015) Triptolide inhibits lung cancer cell migration, invasion, and metastasis. Ann Thorac Surg 100:1817–1825
Ridley AJ, Schwartz MA, Keith B, Firtel RA, Ginsberg MH, Gary BJ, Thomas P et al. (2003) Cell migration: integrating signals from front to back. Science 302:1704–1709
Roomi MW, Monterrey JC, Kalinovsky T, Rath M, Niedzwiecki A (2009) Patterns of MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression in human cancer cell lines. Oncol Rep 21:1323–1333
Schultze A, Decker S, Otten J, Horst AK, Vohwinkel G, Schuch G, Bokemeyer C et al. (2010) TAE226-mediated inhibition of focal adhesion kinase interferes with tumor angiogenesis and vasculogenesis. Invest N Drugs 28:825–833
Seko Y, Takahashi N, Tobe K, Kadowaki T, Yazaki Y (1999) Pulsatile stretch activates mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) family members and focal adhesion kinase (p125FAK) in cultured rat cardiac myocytes. Biochem Biophy Res Commun 259:8–14
Sharpe R, Pearson A, Herrera-Abreu MT, Johnson D, Mackay A, Welti JC, Natrajan R et al. (2011) FGFR signaling promotes the growth of triple-negative and basal-like breast cancer cell lines both in vitro and in vivo. Clin Cancer Res 17:5275–5286
Shen KH, Hung SH, Yin LT, Huang CS, Chao CH, Liu CL, Shih YW (2010) Acacetin, a flavonoid, inhibits the invasion and migration of human prostate cancer DU145 cells via inactivation of the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biochem 333:279–291
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2017) Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin 67:7–30
Sinha D, Dutta K, Ganguly KK, Biswas J, Bishayee A (2015) A novel synthetic oleanane triterpenoid suppresses adhesion, migration, and invasion of highly metastatic melanoma cells by modulating gelatinase signaling axis. Mol Carcinog 54:654–667
Soon YY, Stockler MR, Askie LM, Boyer MJ (2009) Duration of chemotherapy for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. J Clin Oncol 27:3277–3283
Sulzmaier FJ, Jean C, Schlaepfer DD (2014) FAK in cancer: mechanistic findings and clinical applications. Nat Rev Cancer 14:598–610
Wang YH, Wu N, Pang B, Tong DD, Sun DL, Sun HM, Zhang CY et al. (2017) TRIB1 promotes colorectal cancer cell migration and invasion through activation MMP-2 via FAK/Src and ERK pathways. Oncotarget 8:47931–47942
Wang L, Zhang ZG, Zhang RL, Greqq SR, Hozeska-solqot A, LeTourneau Y, Wang Y et al. (2006) Matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP2) and MMP9 secreted by erythropoietin-activated endothelial cells promote neural progenitor cell migration. J Neurosci 26:5996–6003
Weiner TM, Craven RJ, Cance WG, Liu E (1993) Expression of focal adhesion kinase gene and invasive cancer. Lancet 342:1024–1025
Wu GS, Song YL, Yin ZQ, Guo JJ, Wang SP, Zhao WW, Chen XP et al. (2013) Ganoderiol A-enriched extract suppresses migration and adhesion of MDA-MB-231 cells by inhibiting FAK-SRC-paxillin cascade pathway. Plos ONE 8:e76620
Zhang JL, Hochwald SN (2014) The role of FAK in tumor metabolism and therapy. Pharm Ther 142:154–163
Zohrabian VM, Forzani B, Chau Z, Murali R, Jhanwar-Uniyal M (2009) Rho/ROCK and MAPK signaling pathways are involved in glioblastoma cell migration and proliferation. Anticancer Res 29:119–123
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Major Scientific and Technological Innovation Project of Shandong, China (No. 2019JZZY020612); the Provincial Key Research and Development Program of Shandong, China, (No. 2019JZZY020612, 2018GNC110008, 2019LYXZ011, and 2019LYXZ025); the Provincial Natural Science Foundation of Shandong, China (ZR2019MC072); and the Taishan Scholars’s Program of Shandong for Jin-yue Sun.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, Nn., Zhang, Rr., Liu, C. et al. PDB-1 from Potentilla discolor Bunge suppresses lung cancer cell migration and invasion via FAK/Src and MAPK signaling pathways. Med Chem Res 29, 887–896 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-020-02527-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-020-02527-2