Abstract
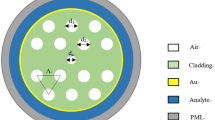
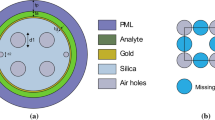
In this article, a single solid core flat fiber (SSCFF) refractive index sensor based on surface plasmon resonance (SPR) is proposed and analyzed numerically using the finite element method (FEM). The proposed flat fiber consists of a single array of five circular holes. Among them the central hole is made of GeO2-doped silica which is forming the core. Other holes are filled with air and situated symmetrically on both sides of the central solid core. The upper flat surface of the fiber is coated with a thin plasmonic gold layer which is protected by an active titanium dioxide layers. Analyte is situated on top of these layers. The wavelength interrogation technique is applied to study the coupling characteristics between the core-guided mode and the surface plasmon mode as well as for the refractive index measurement. Numerical analysis results show that this sensor is able to detect high refractive index analytes from 1.49 to 1.54 with a good linear response. Additionally, the dependence of surface plasmonic resonance wavelength on analyte refractive index is studied. The maximum wavelength sensitivity of this sensor is found to be 4782 nm/RIU with a high resolution of 2.09 × 10−5 RIU. The effects of different structural parameters on loss spectrum are studied in detail to optimize this SSCFF structure. In comparison to traditional PCF, this SSCFF structure is fabrication complexity free as well as a suitable candidate for developing portable devices and high refractive index analyte sensors, particularly chemical and protein sensors.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang T (2017) Highly sensitive SPR sensor based on D-shaped photonic crystal fiber coated with indium tin oxide at near-infrared wavelength. Plasmonics 12:583–588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0301-7
Hu DJJ, Ho HP (2017) Recent advances in plasmonic photonic crystal fiber: design, fabrication and applications. Adv Opt Photon 9:257–314. https://doi.org/10.1364/AOP.9.000257
Lu JGJ, Li Y, Han Y, Liu Y (2018) D-shaped photonic crystal fiber plasmonic refractive index sensor based on gold grating. Appl Opt 57:5268–5272. https://doi.org/10.1364/AO.57.005268
De M, Gangopadhyay TK, Singh VK (2019) Prospects of photonic crystal fiber as physical sensor: an overview. Sensors 19:464. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19030464
Zhao Y, Deng ZQ, Li J (2014) Photonic crystal fiber based surface plasmon resonance chemical sensors. Sensors Actuators B Chem 202:557–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.05.127
Lu J, Stappen TV, Spasic D, Delport F, Vermeire S, Gils A, Lammertyn J (2016) Fiber optic-SPR platform for fast and sensitive infliximab detection in serum of inflammatory bowel disease patients. Biosens Bioelectron 79:173–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.11.087
Zhang L, Fang M (2010) Nanomaterials in pollution trace detection and environmental improvement. Nano Today 5:128–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2010.03.002
Kretschmann E, Raether H (1968) Radiative decay of non-radiative surface plasmons excited by light. Z Naturforsch A 23:2135–2136
Jorgenson RC, Yee SS (1993) A fiber-optic chemical sensor based on surface plasmon resonance. Sensors Actuators B Chem 12:213–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/0925-4005(93)80021-3
Slavík R, Homola J, Čtyroký J (1999) Single-mode optical fiber surface plasmon resonance sensor. Sensors Actuators B Chem 54:74–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4005(98)00314-1
Trouillet A, Ronot-Trioli C, Veillas C, Gagnaire H (1996) Chemical sensing by surface plasmon resonance in a multimode optical fibre. Pure Appl Opt J Eur Opt Soc Part A 5:227–237. https://doi.org/10.1088/0963-9659/5/2/006
Zhang XY, Zhang T, Hu AM, Xue XJ, Wu PQ, Chen QY (2011) Tunable microring resonator based on dielectric-loaded surface plasmon polariton waveguides. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 11(5):10520–10524. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2011.4094
Shao LY, Shevchenko Y, Albert J (2010) Intrinsic temperature sensitivity of tilted fiber Bragg grating based surface plasmon resonance sensors. Opt Express 18:11464–11471. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.18.011464
Schuster T, Herschel R, Neumann N, Schaffer CG (2012) Miniaturized long-period fiber grating assisted surface plasmon resonance sensor. J Lightwave Technol 30:1003–1008
Chau YFC, Chao CTC, Chiang HP, Lim CM, Voo NY, Mahadi AH (2018) Plasmonic effects in composite metal nanostructures for sensing applications. J Nanopart Res 20:190–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-018-4293-4
Kumara NTRN, Chau YFC, Huang JW et al (2016) Plasmonic spectrum on 1D and 2D periodic arrays of rod-shape metal nanoparticle pairs with different core patterns for biosensor and solar cell applications. J Opt 18:115003. https://doi.org/10.1088/2040-8978/18/11/115003
Russell P (2003) Photonic crystal Fibres. Science 299:358–362
De M, Gangwar RK, Singh VK (2017) Designing of highly birefringence, dispersion shifted decagonal photonic crystal fiber with low confinement loss. Photonics Nanostruct Fundam Appl 26:15–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.photonics.2017.06.002
Yang KY, Chau YF, Huang YW et al (2011) Design of high birefringence and low confinement loss photonic crystal fibers with five rings hexagonal and octagonal symmetry air-holes in fiber cladding. J Appl Phys 109:093103. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3583560
Rifat AA, Hasan MR, Ahmed R, Butt H (2017) Photonic crystal fiber-based plasmonic biosensor with external sensing approach. J Nanophotonics 12:012503-1–10. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.jnp.12.019901
Momota MR, Hasan MR (2018) Hollow-core silver coated photonic crystal fiber plasmonic sensor. Opt Mater 76:287–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2017.12.049
Rifat AA, Mahdiraji GA, Sua YM, Ahmed R, Shee YG, Adikan FR (2016) Highly sensitive multi-core flat fiber surface plasmon resonance refractive index sensor. Opt Express 24:2485–2495. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.24.002485
Tian M, Lu P, Chen L, Lv C, Liu D (2012) All-solid d-shaped photonic fiber sensor based on surface plasmon resonance. Opt Commun 285:1550–1554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2011.11.104
Luan N, Wang R, Lv W, Yao J (2015) Surface plasmon resonance sensor based on D-shaped microstructured optical fiber with hollow core. Opt Express 23:8576–8582. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.23.008576
Chen X, Xia L, Li C (2018) Surface plasmon resonance sensor based on a novel D-shaped photonic crystal fiber for low refractive index detection. IEEE Photonics J 10:6800709. https://doi.org/10.1109/JPHOT.2018.2790424
Dash JN, Jha R (2014) Graphene-based birefringent photonic crystal fiber sensor using surface plasmon resonance. IEEE Photon Technol Lett 26:1092–1095
Dash JN, Jha R (2015) On the performance of graphene-based D-shaped photonic crystal fibre biosensor using surface plasmon resonance. Plasmonics 10:1123–1131
Dutta A, Deka B, Sahu PP (2016) Planar waveguide optical sensors : from theory to applications. Springer International Publishing, Switzerland
Scott AM, Wang P, Cooper LJ et al (2005) High-power Yb-doped multicore ribbon fiber laser. Opt Lett 30:2906. https://doi.org/10.1364/ol.30.002906
Mahdiraji GA, Amirkhan F, Chow DM, Kakaie Z, Yong PS, Dambul KD, Adikan FRM (2014) Multicore flat fiber: a new fabrication technique. IEEE Photon Technol Lett 26:1972–1974. https://doi.org/10.1109/LPT.2014.2343637
Egorova O, Astapovich M, Semenov S, Salganskii M (2014) Multicore optical fiber with rectangular cross-section. Opt Lett 39:2168–2170. https://doi.org/10.15593/2411-4367/2016.01.02
Gangwar RK, Singh VK (2017) Highly sensitive surface plasmon resonance based D-shaped photonic crystal fiber refractive index sensor. Plasmonics 12:1367–1372. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0395-y
Search H, Journals C, Contact A, Iopscience M (2015) Infrared SPR sensitivity enhancement using ITO / TiO 2 / silicon. Europhys Lett 112:10001-p1–10001-p5. https://doi.org/10.1209/0295-5075/112/10001
Chau YFC, Chou Chao CT, Lim CM, Huang HJ, Chiang HP (2018) Depolying tunable metal-shell/dielectric core nanorod arrays as the virtually perfect absorber in the near-infrared regime. ACS Omega 3:7508–7516. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b00362
Aouani H, Wenger J, Gérard D, Rigneault H, Devaux E, Ebbesen TW, Mahdavi F, Xu T, Blair S (2009) Crucial role of the adhesion layer on the plasmonic fluorescence enhancement. ACS Nano 3:2043–2048. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn900460t
Jiao X, Goeckeritz J, Blair S, Oldham M (2009) Localization of near-field resonances in bowtie antennae: influence of adhesion layers. Plasmonics 4:37–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-008-9075-x
Brückner V (2011) To the use of Sellmeier formula. In: Elements of optical nerworking. Springer, p 217
Johnson PB, Christy RW (1972) Optical constant of the noble metals. Phys Rev B 6:4370–4379. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.6.4370
COMSOL Multiphysics. www.comsol.com
Auguste JL, Humbert G, Leparmentier S, Kudinova M, Martin PO, Delaizir G, Schuster K, Litzkendorf D (2014) Modified powder-in-tube technique based on the consolidation processing of powder materials for fabricating specialty optical fibers. Materials (Basel) 7:6045–6063. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma7086045
Armelao L, Barreca D, Bottaro G et al (2005) RF-sputtering of gold on silica surfaces: evolution from clusters to continuous films. Mater Sci Eng C 25:599–603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2005.06.007
Pathak AK, Bhardwaj V, Gangwar RK, De M, Singh VK (2016) Fabrication and characterization of TiO 2 coated cone shaped nano-fiber pH sensor. Opt Commun 386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optcom.2016.11.021
Li W, Hu C, Min Xia KY (2013) An experimental study of pH optical sensor using a section of no-core fiber. Sensors Actuators A Phys 199:260–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2014.12.020
Heng D, An Y, Hen E et al (2016) Free-space to few-mode-fiber coupling under atmospheric turbulence. Opt Express 24:18739–18744
Rifat AA, Mahdiraji GA, Ahmed R et al (2016) Copper-graphene-based photonic crystal fiber plasmonic biosensor. IEEE Photonics J 8:4800408. https://doi.org/10.1109/JPHOT.2015.2510632
An G, Li S, Yan X, Zhang X, Yuan Z, Wang H, Zhang Y, Hao X, Shao Y, Han Z (2017) Extra-broad photonic crystal fiber refractive index sensor based on surface plasmon resonance. Plasmonics 12:465–471. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0286-2
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by Frederick University under the EM LEADERS doctoral exchange program. Specifically, Moutusi De is grateful to Dr. Kyriacos Kalli, Associate Professor at Cyprus University of Technology, Cyprus, for the valuable discussion. Authors are also thankful to Indian Institute of Technology (ISM), Dhanbad, India, for providing partial simulation facilities for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De, M., Markides, C., Singh, V.K. et al. Analysis of a Single Solid Core Flat Fiber Plasmonic Refractive Index Sensor. Plasmonics 15, 1429–1437 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-020-01154-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-020-01154-2