Abstract
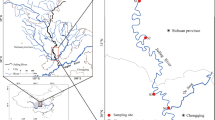
The deposition and release of heavy metals in sediments often lead to their diffusion in lakes, especially for dispersed elements such as cadmium (Cd), which indirectly introduces pollutants into the food chain. The high rate of deposition or release of heavy metals in sediments is a problem to be solved. Southwest China is most famous in the world for the continuous distribution of karst area, for holding the largest area of bare carbonate rocks and for experiencing the strongest karst development in the world. The trace metals in 15 sites of Yelang Lake were determined by diffusive gradients in thin-films (DGT) method. The distribution and release mechanism of Cr, Ni, Cu, Cd, Zn and Pb under high geochemical backgrounds in the karst area of Guizhou Province in Southwest China were discussed. Based on the DGT concentration and pore water analysis, the distribution order of these heavy metal contents is usually upstream (SC), middle (DCB) and downstream (SW) areas of the lake, which increases during the dry season and decreases during the wet season. There was no significant difference in concentration between 0–4 and 4–8 cm depth (p < 0.05). The R values of heavy metals in the dry and wet seasons were highest with cadmium (Cd) and lowest with chromium (Cr) and lead (Pb). The results of the metal geo-accumulation index (Igeo) and the potential ecological risk index are highest on Cd and lowest on Cr. The mean concentrations of Cr, Cd, Zn, Ni (DCB, SW), Pb (SC, DCB) and Cu (SC) are between the corresponding threshold effect level and the probable effect level, and the average potential ecological risk is ranked in descending order of Cd > Pb > Zn > Cu > Ni > Cr. These three areas are at medium risk levels and the potential ecological risks increases from upstream to downstream. The deposition rate of heavy metals in Yelang Lake sediment was higher than the release rate and the ecological risk from heavy metals was relatively low. Since Cd is the main ecological risk factor in the lake, more attention needs to be given to Cd contamination in the Yelang Lake basin of the karst area.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali MM, Ali ML, Islam MS, Rahman MZ (2016) Preliminary assessment of heavy metals in water and sediment of Karnaphuli River, Bangladesh. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 5:27–35
Amato ED, Simpson SL, Jarolimek CV, Jolley DF (2014) Diffusive gradients in thin films technique provide a robust prediction of metal bioavailability and toxicity in estuarine sediments. Environ Sci Technol 48(8):4485–4494
Amirbahman A, Lake BA, Norton SA (2013) Seasonal phosphorus dynamics in the surficial sediment of two shallow temperate lakes: a solid-phase and pore-water study. Hydrobiologia 701(1):65–77
Asiabi H, Yamini Y, Shamsayei M, Tahmasebi E (2017) Highly selective and efficient removal and extraction of heavy metals by layered double hydroxides intercalated with the diphenylamine-4-sulfonate: a comparative study. Chem Eng J 323:212–223
Bartkowiak A, Brezaboruta B, Lemanowicz J (2016) Assessment of the content of heavy metals and the potential pathogenic microorganisms in soil under illegal dumping sites. Environ Earth Sci 75(21):1401
Besten PJD, Deckere ED, Babut MP, Power B, Delvalls TA, Zago C, Oen AMP, Heise S (2003) Biological effects-based sediment quality in ecological risk assessment for European waters. J Soils Sediments 3(3):144–162
Bi S, Yang Y, Xu C, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Zhang X (2017) Distribution of heavy metals and environmental assessment of surface sediment of typical estuaries in eastern China. Mar Pollut Bull 121(1–2):357–366
Chowdhury M, Bakri DA (2006) Diffusive nutrient flux at the sediment-water interface in the suma park reservoir. Aust Hydrol Sci J 51(1):144–156
Closs LG (1980) Introduction to exploration geochemistry. Earth Sci Rev 16:0–374
Cole RF, Mills GA, Hale MS, Parker R, Bolam T, Teasdale PR, Bennett WW, Fones GR (2017) Development and evaluation of new diffusive gradients in thin-films technique for measuring organotin compounds in coastal sediment pore water. Talanta 178:670–678
Davison W, Fones GR, Harper M, Teasdale P, Zhang H (2000) Dialysis, DET and DGT: in situ diffusional techniques for studying water, sediments, and soils. In: Buffle J, Horvai G (Eds) In-situ monitoring of aquatic systems: chemical analysis and speciation, vol 804. IUPAC. Wiley, New York, pp 495–569
Ding X, Ye S, Yuan H, Krauss KW (2018) Spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in coastal surface sediments in the Hebei province offshore area, Bohai Sea, China. Mar Pollut Bull 131(Pt A):655–661
Estrada ES, Juhel G, Han P, Kelly BC, Lee WK, Bayen S (2016) Multi-tool assessment of trace metals in mangroves combining sediment and clam sampling, dgt passive samplers and caged mussels. Sci Total Environ 574:847
Fu J, Zhao C, Luo Y, Liu C, Kyzas GZ, Luo Y, Zhao D, An S, Zhu H (2014) Heavy metals in surface sediments of the Jialu River, China: their relations to environmental factors. J Hazard Mater 270(3):102–109
Furdek M, Mikac N, Bueno M, Tessier E, Cavalheiro J, Monperrus M (2016) Organotin persistence in contaminated marine sediments and pore waters: in situ degradation study using species-specific stable isotopic tracers. J Hazard Mater 307:263–273
Gao Y, Lehto N (2012) A simple laser ablation ICPMS method for the determination of trace metals in a resin gel. Talanta 92(1):78–83
Gao Y, Leermakers M, Elskens M, Billon G, Ouddane B, Fischer JC, Baeyens W (2007) High-resolution profiles of thallium, manganese, and iron assessed by DET and DGT techniques in riverine sediment pore waters. Sci Total Environ 373(2–3):526–533
Gimpel J, Zhang H, Davison W, Edwards AC (2003) In situ trace metal speciation in lake surface waters using dgt, dialysis, and filtration. Environ Sci Technol 37(1):138–146
Gupta AK, Sinha S (2007) Assessment of single extraction methods for the prediction of bioavailability of metals to Brassica Juncea, L. Czern. (Var. Vaibhav) grown on tannery waste contaminated soil. J Hazard Mater 149(1):144–150
Han X, Lu X, Qinggeletu WuY (2017) Health risks and contamination levels of heavy metals in dust from parks and squares of an industrial city in the semi-arid area of China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14(8):886
He J, Lü C, Fan Q, Xue H, Bao J (2011) Distribution of avs-sem, transformation mechanism and risk assessment of heavy metals in the Nanhai Lake in China. Environ Earth Sci 64(8):2025–2037
Hu J, Zhou S, Wu P, Qu K (2017) Assessment of the distribution, bioavailability and ecological risks of heavy metals in the lake water and surface sediments of the Caohai plateau wetland, China. PLoS ONE 12(12):1–15
Hurley T, Sadiq R, Mazumder A (2012) Adaptation and evaluation of the Canadian council of ministers of the environment water quality index (CCMEWQI) for use as an effective tool to characterize drinking source water quality. Water Res (Oxf) 46(11):3544–3552
Kastratović V, Jaćimović Ž, Bigović M, Đurović D, Krivokapić S (2016) Environmental status and geochemical assessment sediments of Lake Skadar, Montenegro. Environ Monit Assess 188(8):1–15
Kong X, Andersson PU, Thomson ES, Pettersson JBC (2012) Ice formation via deposition mode nucleation on bare and alcohol-covered, graphite surfaces. J Phys Chem C 116(16):8964–8974
Kükrer S (2018) Vertical and horizontal distribution, source identification, ecological and toxic risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Lake Aygir, Kars, Turkey. Environ Forensics 19(2):122–133
Li F, Zhang J, Jiang W, Liu C, Zhang Z, Zhang C, Zeng G (2017) Spatial health risk assessment and hierarchical risk management of mercury in soils from a typical contaminated site, China. Environ Geochem Health 39(4):923–934
Li F, Xiao M, Zhang J, Liu C, Qiu Z, Cai Y (2018) Spatial distribution, chemical fraction and fuzzy comprehensive risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments from the Honghu Lake, China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15(2):207
Li H, Chai L, Yang Z, Liao Q, Liu Y, Ouyang B (2019) Seasonal and spatial contamination statuses and ecological risk of sediment cores highly contaminated by heavy metals and metalloids in the Xiangjiang River. Environ Geochem Health 41(3):1617–1633
Lin Q, Liu E, Zhang E, Li K, Shen J (2016) Spatial distribution, contamination and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Erhai Lake, a large eutrophic plateau lake in southwest China. CATENA 145:193–203
Lynch SFL, Batty LC, Byrne P (2017) Critical control of flooding and draining sequences on the environmental risk of Zn-contaminated riverbank sediments. J Soils Sediments 17(11):2691–2707
Ma X, Zuo H, Tian M, Zhang L, Meng J, Zhou X, Min N, Chang X, Liu Y (2016) Assessment of heavy metals contamination in sediments from three adjacent regions of the yellow river using metal chemical fractions and multivariate analysis techniques. Chemosphere 144(3):264–272
Ma JL, Li F, Jia XL, Zhang JD (2018) Pollution assessment and sources identification of heavy metals in surface sediments from the Nantaizi Lake, Middle China. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 111:012–020. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/111/1/012020
Maanan M, Saddik M, Maanan M, Chaibi M, Assobhei O, Zourarah B (2015) Environmental and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Nador lagoon, Morocco. Ecol Ind 48:616–626
Mellor A, Mobilia M, Zia RKP (2016) Characterization of the nonequilibrium steady state of a heterogeneous nonlinear q-voter model with zealotry. Europhys Lett 113(4):1–6
Muhammad I, Puschenreiter M, Wenzel WW (2012) Cadmium and Zn availability as affected by ph manipulation and its assessment by soil extraction, DGT and indicator plants. Sci Total Environ 416(2):490–500
Norton SB, Rodier DJ, Van SWH, Wood WP, Slimak MW, Gentile JH (2010) A framework for ecological risk assessment at the EPA. Environ Toxicol Chem 11(12):1663–1672
Ra K, Kim JK, Hong SH, Yim UH, Shim WJ, Lee SY, Kim Y, Lim J, Kim E, Kim K (2014) Assessment of pollution and ecological risk of heavy metals in the surface sediments of Ulsan bay, Korea. Ocean Sci J 49(3):279–289
Rao Q, Sun Z, Tian L, Li J, Sun W, Sun W (2018) Assessment of arsenic and heavy metal pollution and ecological risk in inshore sediments of the Yellow River estuary, China. Stoch Environ Res Risk Asses. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-018-1588-z
Song T, Peng W, Du H, Wang K, Zeng F (2014) Occurrence, spatial-temporal dynamics and regulation strategies of karst rocky desertification in Southwest China. Acta Ecol Sin 12:131–140
Song Z, Dong L, Shan B, Tang W (2017) Assessment of potential bioavailability of heavy metal in the sediments of land-freshwater interfaces by diffusive gradients in thin films. Chemosphere 191:218–225
Stiehl T, Rullkötter J, Nissenbaum A (2005) Molecular and isotopic characterization of lipids in cultured halophilic microorganisms from the Dead Sea and comparison with the sediment record of this hypersaline lake. Org Geochem 36(9):1242–1251
Sun C, Liu J, Wang Y, Sun L, Yu H (2013) Multivariate and geostatistical analyses of the spatial distribution and sources of heavy metals in agricultural soil in Dehui, northeast China. Chemosphere 92(5):517–523
Tang R, Ma K, Zhang Y, Mao Q (2013) The spatial characteristics and pollution levels of metals in urban street dust of Beijing. China Appl Geochem 35(4):88–98
Tian Y, Wang X, Luo J, Yu H, Zhang H (2017) Evaluation of holistic approaches to predicting the concentrations of metals in field-cultivated rice. Environ Sci Technol 42(20):7649
Tunca E, Mehmet A, Ülkü AŞ (2017) An ecological risk investigation of marine sediment from the Northern Mediterranean Coasts (Aegean Sea) using multiple methods of pollution determination. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(8):1–17
Ünlü S, Alpar B (2016) An assessment of trace element contamination in the freshwater sediments of Lake Iznik (now Turkey). Environ Earth Sci 75(2):140
Varol M, Şen B (2012) Assessment of nutrient and heavy metal contamination in surface water and sediments of the upper Tigris River, Turkey. CATENA 92(1):1–10
Wang Y, Huang XF, Hu JW (2014) Study on release potential of heavy metals in sediments from Baihua Lake by dredging simulation. Adv Mater Res 878:545–550
Wang S, Wu Z, Luo J (2017) Transfer mechanism, uptake kinetic process, and bioavailability of P, Cu, Cd, Pb and Zn in macrophyte rhizosphere using DGT. Environ Sci Technol 52(3):1096–1108
Wang GQ, Hu XQ, Zhu Y, Jiang H, Wang HQ (2018) Historical accumulation and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of a drinking water lake. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:24882–24894
Wu Z, He M, Lin C (2011) In situ measurements of concentrations of Cd Co, Fe, and Mn in estuarine porewater using DGT. Environ Pollut 159(5):1123
Wu Z, Wang S, He M, Wu F (2015) The measurement of metals by diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT) at sediment/water interface (SWI) of bay and remobilization assessment. Environ Earth Sci 73(10):6283–6295
Xu M, Liu HY, Luo K, Cui JL, Liu YP, Li JF (2017) Distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Yelang Lake. J Agro-Environ Sci 36(6):1202–1209 (in Chinese)
Yang C, Wu Y, Zhang F, Liu L, Pan R (2016a) Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediments from a source water reservoir. Chem Speciat Bioavailab 28(1–4):133–141
Yang Z, Liang T, Li K, Zhang Q, Wang L (2016b) The diffusion fluxes and sediment activity of phosphorus in the sediment-water interface of Poyang Lake. J Freshw Ecol 31(4):1–11
Yang Y, Jin Q, Fang J, Liu F, Li A, Tandon P, Shan A (2017) Spatial distribution, ecological risk assessment, and potential sources of heavy metal (loid)s in surface sediments from the Huai River within the Bengbu section, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24(12):1–11
Yin H, Cai Y, Duan H, Gao J, Fan C (2014) Use of DGT and conventional methods to predict sediment metal bioavailability to a field inhabitant freshwater snail (bellamya aeruginosa) from Chinese eutrophic lakes. J Hazard Mater 264(2):184
Yu R, Zhang W, Hu G, Lin C, Yang Q (2016) Heavy metal pollution and Pb isotopic tracing in the intertidal surface sediments of Quanzhou Bay, the southeast coast of China. Mar Pollut Bull 105(1):416–421
Zhang B, Lei P, Pan YA, Li J, Bi J, Shan B, Zhang H (2014) Pollution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediments from the tributaries in the main urban districts, Chongqing City. Acta Sci Circumstantiae 35(7):2185–2192
Zhang F, Zhang J, Wu R, Ma Q, Yang J (2016a) Ecosystem health assessment based on dpsirm framework and health distance model in Nansi Lake, China. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 30(4):1235–1247
Zhang W, Jin X, Di Z, Zhu X, Shan B (2016b) Heavy metals in surface sediments of the shallow lakes in eastern china: their relations with environmental factors and anthropogenic activities. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23(24):1–10
Zhou Y, Gu T, Yi W, Zhang T, Zhang Y (2019) The release mechanism of heavy metals from lab-scale vertical flow constructed wetlands treating road runoff. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:16588–16595
Zhu X, Chen B, Zhu L, Xing B (2017) Effects and mechanisms of biochar-microbe interactions in soil improvement and pollution remediation: a review. Environ Pollut 227:98
Acknowledgements
This project was funded by the joint projects of the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Karst Science Research Center in Guizhou Province, China (U1612442); the key laboratory of the Education Department of Guizhou Province, China (Qian JiaoHe [2016] 001); the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFC1802602).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, K., Liu, H., Yu, E. et al. Distribution and release mechanism of heavy metals in sediments of Yelang Lake by DGT. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 34, 793–805 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-020-01799-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-020-01799-9