Abstract
Narrow-band imaging (NBI) laryngoscopy is an optical-biopsy technique used for screening and diagnosing cancer of the laryngeal tract, reducing the biopsy risks but at the cost of some drawbacks, such as large amount of data to review to make the diagnosis. The purpose of this paper is to develop a deep-learning-based strategy for the automatic selection of informative laryngoscopic-video frames, reducing the amount of data to process for diagnosis. The strategy leans on the transfer learning process that is implemented to perform learned-features extraction using six different convolutional neural networks (CNNs) pre-trained on natural images. To test the proposed strategy, the learned features were extracted from the NBI-InfFrames dataset. Support vector machines (SVMs) and CNN-based approach were then used to classify frames as informative (I) and uninformative ones such as blurred (B), with saliva or specular reflections (S), and underexposed (U). The best-performing learned-feature set was achieved with VGG 16 resulting in a recall of I of 0.97 when classifying frames with SVMs and 0.98 with the CNN-based classification. This work presents a valuable novel approach towards the selection of informative frames in laryngoscopic videos and a demonstration of the potential of transfer learning in medical image analysis.

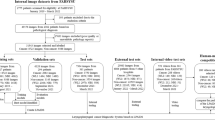
Flowchart of the proposed approach to automatic informative-frame selection in laryngoscopic videos. The approach leans on the transfer learning process, which is implemented to perform learned-features extraction using different convolutional neural networks (CNNs) pre-trained on natural images. Frame classification is performed exploiting two different classifiers: support vector machines and fine-tuned CNNs.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maier-Hein L, Vedula SS, Speidel S, Navab N, Kikinis R, Park A, Eisenmann M, Feussner H, Forestier G, Giannarou S et al (2017) Surgical data science for next-generation interventions. Nat Biomed Eng 1(9):691
Campochiaro PA (2015) Molecular pathogenesis of retinal and choroidal vascular diseases. Progress in Retinal and Eye Research
Moccia S, De Momi E, El Hadji S, Mattos LS (2018) Blood vessel segmentation algorithms – Review of methods, datasets and evaluation metrics. Comput Methods Prog Biomed 158:71–91
Piazza C, Del Bon F, Peretti G, Nicolai P (2012) Narrow band imaging in endoscopic evaluation of the larynx. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 20(6):472–476
Moccia S, De Momi E, Guarnaschelli M, Savazzi M, Laborai A, Guastini L, Peretti G, Mattos LS (2017) Confident texture-based laryngeal tissue classification for early stage diagnosis support. J Med Imaging 4(3):034,502
Araújo T, Santos CP, De Momi E, Moccia S (2019) Learned and handcrafted features for early-stage laryngeal SCC diagnosis. Med Biol Eng Comput 57(12):2683–2692
Essert C, Fernandez-Vidal S, Capobianco A, Haegelen C, Karachi C, Bardinet E, Marchal M, Jannin P (2015) Statistical study of parameters for deep brain stimulation automatic preoperative planning of electrodes trajectories. Int J CARS 10(12):1973–1983
Moccia S, Foti S, Routray A, Prudente F, Perin A, Sekula RF, Mattos LS, Balzer JR, Fellows-Mayle W, De Momi E et al (2018) Toward improving safety in neurosurgery with an active handheld instrument. Ann Biomed Eng, pp 1–15
Gómez P, Semmler M, Sch’́utzenberger A, Bohr C, D’́ollinger M (2019) Low-light image enhancement of high-speed endoscopic videos using a convolutional neural network. Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing, pp 1–13
Wang Z, Bovik AC, Sheikh HR, Simoncelli EP (2004) Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans Image Process 13(4):600–612
Moccia S, Vanone GO, De Momi E, Laborai A, Guastini L, Peretti G, Mattos LS (2018) Learning-based classification of informative laryngoscopic frames. Comput Methods Prog Biomed 158:21–30
Perperidis A, Akram A, Altmann Y, McCool P, Westerfeld J, Wilson D, Dhaliwal K, McLaughlin S (2017) Automated detection of uninformative frames in pulmonary optical endomicroscopy. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 64(1):87–98
Goodfellow I, Bengio Y, Courville A, Bengio Y (2016) Deep Learning, vol 1. MIT Press, Cambridge
Esteva A, Kuprel B, Novoa RA, Ko J, Swetter SM, Blau HM, Thrun S (2017) Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature 542(7639):115–118
Wang Q, Zheng Y, Yang G, Jin W, Chen X, Yin Y (2018) Multiscale rotation-invariant convolutional neural networks for lung texture classification. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 22(1): 184–195
Nanni L, Ghidoni S, Brahnam S (2017) Handcrafted vs. non-handcrafted features for computer vision classification. Pattern Recogn 71:158–172
Poplin R, Varadarajan AV, Blumer K, Liu Y, McConnell MV, Corrado GS, Peng L, Webster DR (2018) Prediction of cardiovascular risk factors from retinal fundus photographs via deep learning. Nature Biomedical Engineering, p 1
Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, Krause J, Satheesh S, Ma S, Huang Z, Karpathy A, Khosla A, Bernstein M et al (2015) Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int J Comput Vis 115(3):211–252
Bashar MK, Kitasaka T, Suenaga Y, Mekada Y, Mori K (2010) Automatic detection of informative frames from wireless capsule endoscopy images. Med Image Anal 14(3):449–470
Atasoy S, Mateus D, Meining A, Yang GZ, Navab N (2012) Endoscopic video manifolds for targeted optical biopsy. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 31(3):637–653
Park SY, Sargent D, Spofford I, Vosburgh KG, A-Rahim Y (2012) A colon video analysis framework for polyp detection. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 59(5):1408
Maghsoudi OH, Talebpour A, Soltanian-Zadeh H, Alizadeh M, Soleimani HA (2014) Informative and uninformative regions detection in WCE frames. J Adv Comput 3(1):12–34
Ishijima A, Schwarz RA, Shin D, Mondrik S, Vigneswaran N, Gillenwater AM, Anandasabapathy S, Richards-Kortum R (2015) Automated frame selection process for high-resolution microendoscopy. J Biomed Opt 20(4):046,014
Armin MA, Chetty G, Jurgen F, De Visser H, Dumas C, Fazlollahi A, Grimpen F, Salvado O (2015) Uninformative frame detection in colonoscopy through motion, edge and color features. In: International Workshop on Computer-Assisted and Robotic Endoscopy, Springer, pp 153–162
Kumar A, Kim J, Lyndon D, Fulham M, Feng D (2017) An ensemble of fine-tuned convolutional neural networks for medical image classification. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 21(1): 31–40
Yoo TK, Choi JY, Seo JG, Ramasubramanian B, Selvaperumal S, Kim DW (2019) The possibility of the combination of oct and fundus images for improving the diagnostic accuracy of deep learning for age-related macular degeneration: a preliminary experiment. Med Biol Eng Comput 57(3):677–687
Cheplygina V, Pena IP, Pedersen JH, Lynch DA, Sørensen L, de Bruijne M (2018) Transfer learning for multicenter classification of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 22 (5):1486–1496
Zhang R, Zheng Y, Mak TWC, Yu R, Wong SH, Lau JY, Poon CC (2017) Automatic detection and classification of colorectal polyps by transferring low-level CNN features from nonmedical domain. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 21(1):41–47
Behrens A (2008) Creating panoramic images for bladder fluorescence endoscopy. Acta Polytechnica 48 (3):50–54
Yosinski J, Clune J, Bengio Y, Lipson H (2014) How transferable are features in deep neural networks? In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 3320–3328
Pan SJ, Yang Q (2009) A survey on transfer learning. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 22(10):1345–1359
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2012) Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp 1097–1105
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2014) Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv:14091556
Szegedy C, Ioffe S, Vanhoucke V, Alemi AA (2017) Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning. Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence 4:12
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 770–778
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Identity mappings in deep residual networks. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, Springer, pp 630–645
Burges CJ (1998) A tutorial on support vector machines for pattern recognition. Data Min Knowl Disc 2 (2):121–167
Lin Y, Lv F, Zhu S, Yang M, Cour T, Yu K, Cao L, Huang T (2011) Large-scale image classification: fast feature extraction and SVM training. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, pp 1689–1696
Tajbakhsh N, Shin JY, Gurudu SR, Hurst RT, Kendall CB, Gotway MB, Liang J (2016) Convolutional neural networks for medical image analysis: full training or fine tuning? IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35 (5):1299–1312
Litjens G, Kooi T, Bejnordi BE, Setio AAA, Ciompi F, Ghafoorian M, Van der Laak JA, Van Ginneken B, Sánchez CI (2017) A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med Image Anal 42:60–88
Esmaeili N, Illanes A, Boese A, Davaris N, Arens C, Friebe M (2019) Novel automated vessel pattern characterization of larynx contact endoscopic video images. Int J CARS, pp 1–11
Glorot X, Bengio Y (2010) Understanding the difficulty of training deep feedforward neural networks. In: Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, pp 249–256
Li X, La R, Wang Y, Niu J, Zeng S, Sun S, Zhu J (2019) EEG-Based mild depression recognition using convolutional neural network. Med Biol Eng Comput 57(6):1341–1352
Dao TT (2019) From deep learning to transfer learning for the prediction of skeletal muscle forces. Med Biol Eng Comput 57(5):1049–1058
Singh R, Ahmed T, Singh R, Udmale SS, Singh SK (2019) Identifying tiny faces in thermal images using transfer learning. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, pp 1–10
Taylor ME, Stone P (2009) Transfer learning for reinforcement learning domains: a survey. J Mach Learn Res 10(Jul):1633–1685
Pan SJ, Shen D, Yang Q, Kwok JT (2008) Transferring localization models across space. In: Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp 1383–1388
Moccia S, Penza V, Vanone GO, De Momi E, Mattos LS (2016) Automatic workflow for narrow-band laryngeal video stitching. In: IEEE Annual International Conference of the Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, pp 1188–1191
Wilson AC, Roelofs R, Stern M, Srebro N, Recht B (2017) The marginal value of adaptive gradient methods in machine learning. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp 4148–4158
Bradley AP (1997) The use of the area under the ROC curve in the evaluation of machine learning algorithms. Pattern Recogn 30(7):1145–1159
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Ilaria Patrini and Michela Ruperti equally contributed to this paper
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patrini, I., Ruperti, M., Moccia, S. et al. Transfer learning for informative-frame selection in laryngoscopic videos through learned features. Med Biol Eng Comput 58, 1225–1238 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-020-02127-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-020-02127-7