Abstract
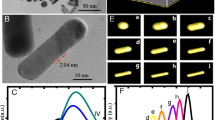
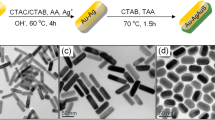
Au nanorods were prepared through seed growth method. Their lengths and diameters were controlled by adjusting Ag+ content in the growth solution. Ethyl orthosilicate were hydrolyzed in alkali solutions to obtain SiO2-coated Au nanostructures. Au nanorods with ideal morphologies and sizes could only be obtained under the presence of a certain Ag+ concentration in the growth solution. Without Ag+, only some irregular nanoparticles were generated without nanorods. Longitudinal plasma absorption of Au nanorods shifts first to red shift and then to blue with the increase of Ag+ in the growth solution, while transverse plasma absorption hardly changes. However, longitudinal plasma absorption of silica-coated Au nanorods has a blue shift with the increase of the thickness of silica, while the transverse plasma has a slight red shift. Therefore, by coating Au nanorods with silica and by adjusting their aspect ratio by using different Ag+ concentration in the growth solution, Au nanoparticles can be synthesized for applications requiring absorption in specific UV regions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Peng W, Wenjing S, Qiang W, Jingwen M, Xinhui S, Qing J, Xiaolian S (2019) Iodine-labeled Au nanorods with high radiochemical stability for imaging-guided radiotherapy and photothermal therapy. ACS Appl Nano Mater 2:1374–1381
Xiaonan G, Lulu J, Bo H, Fanpeng K, Xiaojun L, Kehua X, Bo T (2018) Au−Se-bond-based nanoprobe for imaging MMP-2 in tumor cells under a high-thiol environment. Anal Chem 90:4719–4724
Zhenping G, Taishi Z, Hai Z, Da L, Sreelatha S, Qinghua X (2019) Simultaneous imaging and selective photothermal therapy through aptamer-driven Au nanosphere clustering. J Phys Chem Lett 10:183–188
Juan W, Jie H, Chunhua Z, Na H, Juqun X, Lei F (2018) Gold nanorods/polypyrrole/m-SiO2 core/shell hybrids as drug nanocarriers for efficient chemo-photothermal therapy. Langmuir. 34:14661–14669
Yitong W, Ling W, Miaomiao Y, Shuli D, Jingcheng H (2017) Near-infrared-light-responsive magnetic DNA microgels for photon and magneto-manipulated cancer therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:28185–28194
Chih-Chia H, Tzu-Ming L (2015) Controlled Au−polymer nanostructures for multiphoton imaging, prodrug delivery, and chemo−photothermal therapy platforms. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:25259–25269
Nazila M, Laurent D, Herrick S, van der Ad E, de Rijk JW, Tiago AGS, Dipanjan B, Johannes DM, de Krijn P. J, Catherine L (2017) Superior stability of Au/SiO2 compared to Au/TiO2 catalysts for the selective hydrogenation of butadiene. ACS Catal 7:5594–5603
Soo Ik P, Hyon-Min S (2019) Synthesis of prolate-shaped Au nanoparticles and Au nanoprisms and study of catalytic reduction reactions of 4-nitrophenol. ACS Omega 4:7874–7883
Xiaohua H, Prashant KJ, Ivan HE, Mostafa AE (2007) Gold nanoparticles: interesting optical properties and recent applications in cancer diagnostics and therapy. Nanomed. 2:681–693
Catherine JM, Tapan KS, Anand MG, Christopher JO, Jinxin G, Linfeng G, Simona EH, Tan L (2005) Anisotropic metal nanoparticles: synthesis, assembly, and optical applications. J Phys Chem B 109:13857–13870
Luis M, Marzán L (2006) Tailoring surface plasmons through the morphology and assembly of metal nanoparticles. Langmuir. 22:32–41
Nadine H, Michael JF, Paul M, Michael BC (2008) Tunable infrared absorption by metal nanoparticles: the case for gold rods and shells. Gold Bull 41:5–14
Bing H, Xiaoqing G, Lin S, Yonglong Z, Ke H, Jiawei L, Jun G, Zhang W, Zhiyong T (2017) Geometry-modulated magnetoplasmonic optical activity of Au nanorod-based nanostructures. Nano Lett 17:6083–6089
Andrej G, Volker S, Thomas AB, David JN (2013) Coherent multiphoton photoelectron emission from single Au nanorods: the critical role of plasmonic electric near-field enhancement. ACS Nano 7:87–99
Charles RM (1994) Nanomaterials: a membrane-based synthetic approach. Science 266:1961–1965
Veronica MC, Charles RM (1998) Preparation and stability of template-synthesized metal nanorod sols in organic solvents. J Phys Chem B 102:9985–9990
Benjamin RM, Dermody DJ, Brian DR, Mingming FL, Andrew L, Natan MJ, Mallouk TE (1999) Orthogonal self-assembly on colloidal gold-platinum nanorods. Adv Mater 11:1021–1025
van der Zande BMI, Böhmer MR, Fokkink LGJ, Schönenberger C (2000) Colloidal dispersions of gold rods: synthesis and optical properties. Langmuir 16:451–458
Evans P, Hendren WR, Atkinson R, Wurtz GA, Dickson W, Zayats AV, Pollard RJ (2006) Growth and properties of gold and nickel nanorods in thin film alumina. Nanotechnology 17:5746–5753
Yuying Y, Sersing C, Chienliang L, Chris W. CR (1997) Gold nanorods: electrochemical synthesis and optical properties. J Phys Chem B 101:6661–6664
Sersing C, Chaowen S, Chengdah C, Weicheng L, Chris W CR (1999) The shape transition of gold nanorods. Langmuir 15:701–709
Franklin K, song JH, Yang P (2002) Photochemical synthesis of gold nanorods. J Am Chem Soc 124:14316–14317
Yasuro N, Koji N, Hideya K, Sunao Y (2003) Rapid synthesis of gold nanorods by the combination of chemical reduction and photoirradiation processes; morphological changes depending on the growing processes. Chem Commun 18:2376–2377
Miranda RO, Temer AS (2005) Effects of intensity and energy of CW UV light on the growth of gold nanorods. J Phys Chem B 109:15724–15734
Koji N, Ni Y, Sunao Y (2007) Photochemical reactions of ketones to synthesize gold nanorods. Langmuir 23:10353–10356 10353
Placido T, Comparelli R, Giannici F, Cozzoli PD, Capitani G, Striccoli M, Angela A (2009) Photochemical synthesis of water-soluble gold nanorods: the role of silver in assisting anisotropic growth. Chem Mater 21:4192–4202
Nikhil RJ, Latha G, Catherine JM (2001) Wet chemical synthesis of high aspect ratio cylindrical gold nanorods. J Phys Chem B 105:4065–4067
Jana NR, Latha G, Catherine JM (2001) Seed-mediated growth approach for shape-controlled synthesis of spheroidal and rod-like gold nanoparticles using a surfactant template. Adv Mater 13:1389–1393
Tapan KS, Catherine JM (2004) Seeded high yield synthesis of short Au nanorods in aqueous solution. Langmuir. 20:6414–6420
Muhammad I, Yong-Il C, Giyoong T (2007) An enhanced synthesis of gold nanorods by the addition of pluronic (F-127) via a seed mediated growth process. J Mater Chem 17:335–342
Ye X, Linghua J, Humeyra C, Jun C, Xing G, Zheng C, Vicky Doan N, Kang Y, Nader E, Kagan CR (2012) Improved size-tunable synthesis of monodisperse gold nanorods through the use of aromatic additives. ACS Nano 6:2804–2817
Thearith U, Luis ML, Paul M (2001) Optical properties of thin films of Au@SiO2 particles. J Phys Chem B 105:3441–3452
JoséLuis M, João Paulo C, Andres G, Ovidio P, Umapada P (2017) Fabrication of monodispersed Au@SiO2 nanoparticles with highly stable silica layers by ultrasound-assisted stober method. J Phys Chem C 121:9543–9551
Xinbing J, Ben QL, Xiaoli Q, Huan Y, Jinyou S, Zhang H (2019) Multilayered dual functional SiO2@Au@SiO2@QD nanoparticles for simultaneous intracellular heating and temperature measurement. Langmuir 35:6367–6378
Xueyuan L, Yang X, Chen Y, Chen W, Jiang J, Jiangtao D, Hua Y, Xuezhong D (2019) Dual enhanced electrochemiluminescence of aminated Au@SiO2/CdS quantum dot superstructures: electromagnetic field enhancement and chemical enhancement. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:4488–4499
Li H, Deng Q, Bin L, Jianhui Y, Biao W (2016) Fabrication of core@spacer@shell Aunanorod@mSiO2@Y2O3: Er nanocomposites with enhanced upconversion fluorescence. RSC Adv 6:13343–13348
Li H, Jianmiao K, Yang J, Biao W (2016) Distance dependence of fluorescence enhancement in Au nanoparticle@mesoporous silica@europium complex. J Phys Chem C 120:16907–16912
Li H, Kang J, Yang J, Biao W (2016) Fabrication of Aunanoparticle@mSiO2@Y2O3:Eu nanocomposites with enhanced fluorescence. J Alloys Compd 673:283–288
Funding
This work was supported by The Natural Science Foundation of National Natural Science Foundation of China (51702006), Shaanxi Education Department Project (17JS009), Ph.D. Research Project of Baoji University of Arts And Sciences (ZK2017027), the Doctoral Scientific Research Foundation of East China University of Technology (DHBK2018039), and the Project of Educational Commission of Jiangxi Province of China (GJJ180408).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 770 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, Lq., Li, Hq., Zhao, Ww. et al. Preparation and plasmon resonance properties of Au nanorods and Aunanorods@SiO2. Gold Bull 53, 31–37 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13404-020-00271-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13404-020-00271-4