Abstract
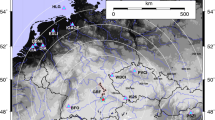
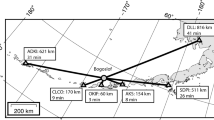
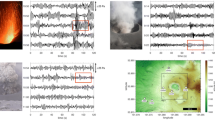
The 2016–2017 shallow submarine eruption of Bogoslof volcano produced numerous infrasound signals over 9 months that were recorded on six Alaska Volcano Observatory (AVO) arrays at ranges of 59 to over 800 km from the volcano. The lack of geophysical monitoring near Bogoslof and the repeated production of volcanic clouds to flight levels made monitoring by remote infrasound critical during the eruption; for the first time, AVO relied extensively on automated infrasound detections from regional arrays to dispatch timely notifications of the ongoing activity. Most of the 70 eruptive events were detected on at least one array, but no array detected all of the events mainly because atmospheric conditions were highly variable during the eruption. Acoustic propagation modeling helps explain some of the variation in array detections but also highlights limitations in regional propagation models. To our knowledge, this is the first example of well-recorded infrasound from an explosive eruption occurring in shallow seawater, providing extensive insights into eruption dynamics in this unique environment. The dominance of low-frequency infrasound (0.1–1 Hz) is attributed to eruptions occurring beneath tens of meters of seawater. Higher-frequency infrasound signals were mostly limited to eruptions where the vent was isolated from major interaction with seawater or in several cases where a lava dome grew above sea level.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnoult KM, Olson JV, Szuberla CAL et al (2010) Infrasound observations of the 2008 explosive eruptions of Okmok and Kasatochi volcanoes, Alaska. J Geophys Res Atmos 115:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010JD013987
Arrowsmith SJ, Hedlin MAH (2005) Observations of infrasound from surf in southern California. Geophys Res Lett 32:L09810. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005GL022761
Behnke SA, McNutt SR (2014) Using lightning observations as a volcanic eruption monitoring tool. Bull Volcanol 76:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00445-014-0847-1
Belousov A, Belousova M (2009) Eruptive process, effects and deposits of the 1996 and the ancient basaltic phreatomagmatic eruptions in Karymskoye Lake, Kamchatka. Russia Volcaniclastic Sediment Lacustrine Settings:35–60. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781444304251.ch3
Ceranna L, Le Pichon A, Green DN, Mialle P (2009) The Buncefield explosion: a benchmark for infrasound analysis across Central Europe. Geophys J Int 177:491–508. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2008.03998.x
Christie DR, Campus P (2009) The IMS infrasound network: design and establishment of infrasound stations. In: Le Pichon A, Blanc E, Hauchecorne A (eds) Infrasound monitoring for atmospheric studies. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 29–75
Coombs ML, Wech A, Haney MM et al (2018) Short-term forecasting and detection of explosions during the 2016–2017 eruption of Bogoslof volcano. Alaska Front Earth Sci doi. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2018.00122
Coombs M, Wallace K, Cameron C, Lyons J, Wech A, Angeli K, Cervelli P (2019) Overview, chronology, and impacts of the 2016–2017 eruption of Bogoslof volcano, Alaska. Bull Volcanol 81:62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00445-019-1322-9
De Angelis S, Fee D, Haney M, Schneider D (2012) Detecting hidden volcanic explosions from Mt. Cleveland Volcano, Alaska with infrasound and ground-coupled airwaves. Geophys Res Lett 39:L21312. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012GL053635
De Groot-Hedlin CD, Hedlin MAH, Drob DP (2009) Atmospheric variability and infrasound monitoring. In: Le Pichon A, Blanc E, Hauchecorne A (eds) Infrasound monitoring for atmospheric studies. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 475–507
Drob DP, Picone JM, Garce M (2003) Global morphology of infrasound propagation. J Geophys Res:108, 4680. doi: https://doi.org/10.1029/2002JD003307, D21
Drob DP, Broutman D, Hedlin MA et al (2013) A method for specifying atmospheric gravity wavefields for long-range infrasound propagation calculations. J Geophys Res Atmos 118:3933–3943. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012JD018077
Drob DP, Emmert JT, Meriwether JW et al (2015) An update to the horizontal wind model (HWM): the quiet time thermosphere. Earth Sp Sci 2:301–319. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014EA000089
Evers LG, Brown D, Heaney KD et al (2014) Evanescent wave coupling in a geophysical system: airborne acoustic signals from the mw 8.1 Macquarie ridge earthquake. Geophys Res Lett 41:1644–1650. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013GL058801
Fee D, Garcés M (2007) Infrasonic tremor in the diffraction zone. Geophys Res Lett 34:L16826. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007gl030616
Fee D, Garces M, Steffke A (2010a) Infrasound from Tungurahua volcano 2006–2008: Strombolian to Plinian eruptive activity. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 193:67–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2010.03.006
Fee D, Steffke A, Garces M (2010b) Characterization of the 2008 Kasatochi and Okmok eruptions using remote infrasound arrays. J Geophys Res 115:D00L10. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009jd013621
Fee D, McNutt SR, Lopez TM et al (2013) Combining local and remote infrasound recordings from the 2009 Redoubt Volcano eruption. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 259:100–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2011.09.012
Fee D, Matoza RS (2013) An overview of volcano infrasound: From hawaiian to plinian, local to global. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 249:123–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2012.09.002
Fee D, Haney MM, Matoza RS et al (2017) Volcanic tremor and plume height hysteresis from Pavlof volcano, Alaska. Science (80- ) 355:45–48. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aah6108
Fee D, Lyons J, Haney M, Wech A, Waythomas C, Diefenbach AK, Lopez T, Van Eaton A, Schneider D (2020) Seismo-acoustic evidence for vent drying during shallow submarine eruptions at Bogoslof volcano, Alaska. Bull Volcanol 82:2. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00445-019-1326-5
Godin OA (2006) Anomalous transparency of water-air interface for low-frequency sound. Phys Rev Lett 97:164301. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.97.164301
Green DN, Evers LG, Fee D et al (2013) Hydroacoustic, infrasonic and seismic monitoring of the submarine eruptive activity and sub-aerial plume generation at south Sarigan, may 2010. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 257:31–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2013.03.006
Green DN, Nippress A (2019) Infrasound signal duration: the effects of propagation distance and waveguide structure. Geophys J Int 216:1974–1988. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggy530
Green DN, Vergoz J, Gibson R et al (2011) Infrasound radiated by the Gerdec and Chelopechene explosions: propagation along unexpected paths. Geophys J Int 185:890–910. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2011.04975.x
Haney MM, Van Eaton AR, Lyons JJ et al (2018) Volcanic thunder from explosive eruptions at Bogoslof volcano, Alaska. Geophys Res Lett 5:3429–3435. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017GL076911
Haney MM, Van Eaton AR, Lyons JJ, Kramer RL, Fee D, Iezzi AM, Dziak RP, Anderson J, Johnson JB, Lapierre JL, Stock M (2020a) Characteristics of thunder and electromagnetic pulses from volcanic lightning at Bogoslof volcano, Alaska. Bull Volcanol 82:15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00445-019-1349-y
Haney MM, Fee D, McKee KF, Lyons JJ, Matoza RS, Wech AG, Tepp G, Searcy C, Mikesell TD (2020b) Co-eruptive tremor from Bogoslof volcano: seismic wavefield composition at regional distances. Bull Volcanol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00445-019-1347-0
Ichihara M, Ripepe M, Goto A, Oshima H, Aoyama H, Iguchi M, Tanaka K, Taniguchi H (2009) Airwaves generated by an underwater explosion: implications for volcanic infrasound. J Geophys Res 114:B03210. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JB005792
Iezzi AM, Schwaiger HF, Fee D, Haney MM (2019) Application of an updated atmospheric model to explore volcano infrasound propagation and detection in Alaska. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 371:192–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2018.03.009
Johnson JB, Aster RC (2005) Relative partitioning of acoustic and seismic energy during Strombolian eruptions. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 148:334–354
Johnson JB, Ripepe M (2011) Volcano infrasound: a review. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 206:61–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2011.06.006
Loewen MM, Izbekov P, Moshrefzadeh J, Coombs M, Larsen J, Graham N, Harbin M, Waythomas C, Wallace K (2019) Petrology of the 2016–2017 eruption of Bogoslof Island, Alaska. Bull Volcanol 81:72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00445-019-1333-6
Lopez T, Clarisse L, Schwaiger H, Van Eaton AR, Fee D, Carn S, Prata F, Searcy C, Lyons J, Wech A, Haney M, Wallace K (2020) Insights into eruption processes at Bogoslof volcano through evaluation of event SO2 masses and comparison with complementary datasets. Bull Volcanol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00445-019-1348-z
Lyons JJ, Haney MM, Fee D, Wech AG, Waythomas CF (2019) Infrasound from giant bubbles during explosive submarine eruptions of Bogoslof volcano. Alaska Nat Geosci doi 12:952–958. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-019-0461-0
Marchetti E, Ripepe M, Harris AJL, Delle Donne D (2009) Tracing the differences between Vulcanian and Strombolian explosions using infrasonic and thermal radiation energy. Earth Planet Sci Lett 279:273–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2009.01.004
Mastin LG, Witter JB (2000) The hazards of eruptions through lakes and seawater. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 97:195–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-0273(99)00174-2
Matoza RS, Le Pichon A, Vergoz J et al (2011) Infrasonic observations of the June 2009 Sarychev peak eruption, Kuril Islands: implications for infrasonic monitoring of remote explosive volcanism. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 200:35–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2010.11.022
McGimsey RG, Neal CA, Searcy CK et al (2010) The may 2010 submarine eruption from south Sarigan seamount. Northern Mariana Islands AGU Fall Meet Abstr:T11E–T107E
Morimoto R, Ossaka J (1955) The 1952–1953 submarine eruption of the Myojin reef near the Bayonnaise rocks, Japan. Tokyo Univ Earthq Res Inst Bull 33:221–250
Olson JV, Szuberla CAL (2005) Distribution of wave packet sizes in microbarom wave trains observed in Alaska. J Acoust Soc Am 117:1032–1037. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.1854651
Prosser WT (1911) Nature turned sorceress. Tech world mag XV:64–68
Pyle DM, Mather TA, Biggs J (2013) Remote sensing of volcanoes and volcanic processes: integrating observation and modelling—introduction. Geol Soc London, Spec Publ 380:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1144/sp380.14
Schneider D, Van Eaton AR, Wallace K (2020) Satellite observations of the 2016–17 eruption of Bogoslof volcano: aviation and ash fallout hazard implications from a water-rich eruption. Bull Volcanol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00445-020-1361-2
Schwaiger HF, Iezzi AM, Fee D (2019) AVO-G2S: a modified, open-source ground-to-space atmospheric specification for infrasound modeling. Comput Geosci 125:90–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2018.12.013
Schwaiger H, Lyons J, Iezzi A, Fee D (2020) Evolving infrasound detections from Bogoslof volcano, Alaska: insights from forward modelling. Bull Volcanol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00445-020-1360-3
Searcy CK, Power JA (2020) Seismic character and progression of explosive activity during the 2016–2017 eruption of Bogoslof volcano, Alaska. Bull Volcanol 82:12 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00445-019-1343-4
Smets PSM, Evers LG, Näsholm SP, Gibbons SJ (2015) Probabilistic infrasound propagation using. Geophys Res Lett 42:6510–6517. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015GL064992.1
Steffke AM, Fee D, Garces M, Harris (2010) Eruption chronologies, plume heights and eruption styles at Tungurahua volcano: integrating remote sensing techniques and infrasound. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 193:143–160
Tepp G, Dziak RP, Haney MM, Lyons JJ, Searcy C, Matsumoto H, Haxel J (2020) Seismic and hydroacoustic observations of the 2016–17 Bogoslof eruption. Bull Volcanol 82:4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00445-019-1344-3
Tepp G, Haney MM (2019) Comparison of short-term seismic precursors and explosion parameters during the 2016-2017 Bogoslof eruption. Bull Volcanol 81:63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00445-019-1323-8
Thelen WA, Cooper J (2015) An analysis of three new infrasound arrays around Kīlauea Volcano: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 2014–1253. US Geol Surv Open-File Rep 2014–1253 29
Van Eaton AR, Schneider DJ, Haney MM, Lyons JJ, Said R, Fee D, Holzworth RH, Mastin LG (2020) Did ice-charging generate volcanic lightning during the 2016–2017 eruption of Bogoslof volcano, Alaska? Bull Volcanol https://doi.org/10.1007/s00445-019-1350-5
Vergniolle S, Brandeis G (1996) Strombolian explosions: 1. A large bubble breaking at the surface of a lava column as a source of sound. J Geophys Res 101:20433. https://doi.org/10.1029/96JB01178
Walker KT, Hedlin MAH (2009) A review of wind-noise reduction methodologies. In: Le Pichon A, Blanc E, Hauchecorne A (eds) Infrasound monitoring for atmospheric studies. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 141–182
Waxler RM, Assink JD, Hetzer C, Velea D (2017) NCPAprop—A software package for infrasound propagation modeling. J Acoust Soc Am 141:3627. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.4987797
Waythomas CF, Cameron C (2018) Historical eruptions and hazards at Bogoslof volcano, Alaska. US Geol Surv Sci Investig Rep:2018–5085
Waythomas CF, Angeli K, Wessels R, Schneider D. (2020) 2016–2017 evolution of the submarine-subaerial edifice of Bogoslof volcano, Alaska, based on analysis of satellite imagery. Bull Volcanol (part of the Bogoslof Topical Collection)
Wech A, Tepp G, Lyons J, Haney M (2018) Using earthquakes, T waves, and infrasound to investigate the eruption of Bogoslof volcano, Alaska. Geophys Res Lett 45:6918–6925. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018GL078457
Acknowledgments
Initial observations and data gathering during the eruption response were performed by a large team at AVO, which is a cooperative program of the U.S. Geological Survey, the Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys, and the University of Alaska Fairbanks Geophysical Institute. Data used in this study are available at the IRIS-DMC. Any use of trade, firm or product names is for descriptive purposes only and does not imply endorsement by the US Government. We thank Silvio De Angelis, Rebecca Kramer, and an anonymous referee for thoughtful comments that improved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: C. Waythomas; Special Issue Editor N. Fournier
This paper constitutes part of a topical collection: The 2016-17 shallow submarine eruption of Bogoslof volcano, Alaska
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lyons, J.J., Iezzi, A., Fee, D. et al. Infrasound generated by the 2016–2017 shallow submarine eruption of Bogoslof volcano, Alaska. Bull Volcanol 82, 19 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00445-019-1355-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00445-019-1355-0