Abstract
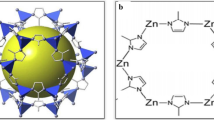
Zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8), composed of Zn ions and imidazolate ligands, is a class of metal-organic frameworks, which possesses a similar structure as conventional aluminosilicate zeolites. This material exhibits inherent porous property, high loading capacity, and pH-sensitive degradation, as well as exceptional thermal and chemical stability. Extensive research effort has been devoted to relevant research aspects ranging from synthesis methods, property characterization to potential applications of ZIF-8. This review focuses on the recent development of ZIF-8 synthesis methods and its promising applications in drug delivery. The potential risks of using ZIF-8 for drug delivery are also summarized.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheetham A K, Rao C N, Feller R K. Structural diversity and chemical trends in hybrid inorganic-organic framework materials. Chemical Communications, 2006, (46): 4780–4795
Li J R, Kuppler R J, Zhou H C. Selective gas adsorption and separation in metal-organic frameworks. Chemical Society Reviews, 2009, 38(5): 1477–1504
Ferey G, Mellot-Draznieks C, Serre C, Millange F. Crystallized frameworks with giant pores: Are there limits to the possible? Accounts of Chemical Research, 2005, 38(4): 217–225
O’Keeffe M, Peskov M A, Ramsden S J, Yaghi O M. The reticular chemistry structure resource (RCSR) database of, and symbols for, crystal nets. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2008, 41(12): 1782–1789
Banerjee R, Phan A, Wang B, Knobler C, Furukawa H, O’Keeffe M, Yaghi O M. High-throughput synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks and application to CO2 capture. Science, 2008, 319(5865): 939–943
Moggach S A, Bennett T D, Cheetham A K. The effect of pressure on zif-8: Increasing pore size with pressure and the formation of a high-pressure phase at 1.47 gpa. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2009, 48(38): 7087–7089
Fairen-Jimenez D, Moggach S A, Wharmby M T, Wright P A, Parsons S, Duren T. Opening the gate: Framework flexibility in ZIF-8 explored by experiments and simulations. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(23): 8900–8902
Wang F, Tan Y X, Yang H, Zhang H X, Kang Y, Zhang J. A new approach towards tetrahedral imidazolate frameworks for high and selective CO2 uptake. Chemical Communications, 2011, 47(20): 5828–5830
Li Y, Liang F, Bux H, Yang W, Caro J. Zeolitic imidazolate framework ZIF-7 based molecular sieve membrane for hydrogen separation. Journal of Membrane Science, 2010, 2010(1-2): 48–54
Liu Y, Hu E, Khan E A, Lai Z. Synthesis and characterization of ZIF-69 membranes and separation for CO2/CO mixture. Journal of Membrane Science, 2010, 2010(1-2): 36–40
McCarthy M C, Varela-Guerrero V, Barnett G V, Jeong H K. Synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate framework films and membranes with controlled microstructures. Langmuir, 2010, 26(18): 14636–14641
Jiang H L, Liu B, Akita T, Haruta M, Sakurai H, Xu Q. Au@ZIF-8: CO oxidation over gold nanoparticles deposited to metal-organic framework. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2009, 131(32): 11302–11303
Chizallet C, Lazare S, Bazer-Bachi D, Bonnier F, Lecocq V, Soyer E, Quoineaud A A, Bats N. Catalysis of transesterification by a nonfunctionalized metal-organic framework: Acido-basicity at the external surface of ZIF-8 probed by FTIR and ab initio calculations. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(35): 12365–12377
Wu H, Zhou W, Yildirim T. Hydrogen storage in a prototypical zeolitic imidazolate framework-8. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2007, 129(17): 5314–5315
Murray L J, Dinca M, Long J R. Hydrogen storage in metal-organic frameworks. Chemical Society Reviews, 2009, 38(5): 1294–1314
Ma S, Zhou H C. Gas storage in porous metal-organic frameworks for clean energy applications. Chemical Communications, 2010, 46(1): 44–53
Harbuzaru B V, Corma A, Rey F, Jorda J L, Ananias D, Carlos L D, Rocha J. A miniaturized linear pH sensor based on a highly photoluminescent self-assembled europium(III) metal-organic framework. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2009, 48(35): 6476–6479
Lu G, Hupp J T. Metal-organic frameworks as sensors: A ZIF-8 based fabry-perot device as a selective sensor for chemical vapors and gases. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(23): 7832–7833
Lu D, An Y, Feng S, Li X, Fan A, Wang Z, Zhao Y. Imidazole-bearing polymeric micelles for enhanced cellular uptake, rapid endosomal escape, and on-demand cargo release. AAPS PharmS-ciTech, 2018, 19(6): 2610–2619
Li X, Gao M, Xin K, Zhang L, Ding D, Kong D, Wang Z, Shi Y, Kiessling F, Lammers T, Cheng J, Zhao Y. Singlet oxygen-responsive micelles for enhanced photodynamic therapy. Journal of Controlled Release, 2017, 260: 12–21
Li J, Meng X, Deng J, Lu D, Zhang X, Chen Y, Zhu J, Fan A, Ding D, Kong D, Wang Z, Zhao Y. Multifunctional micelles dually responsive to hypoxia and singlet oxygen: Enhanced photodynamic therapy via interactively triggered photosensitizer delivery. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(20): 17117–17128
Meng X, Deng J, Liu F, Guo T, Liu M, Dai P, Fan A, Wang Z, Zhao Y. Triggered all-active metal organic framework: Ferroptosis machinery contributes to the apoptotic photodynamic antitumor therapy. Nano Letters, 2019, 19(11): 7866–7876
Park K S, Ni Z, Cote A P, Choi J Y, Huang R, Uribe-Romo F J, Chae H K, O’Keeffe M, Yaghi O M. Exceptional chemical and thermal stability of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2006, 103(27): 10186–10191
Rohani S, Isimjan T, Mohamed A, Kazemian H, Salem M, Wang T. Fabrication, modification and environmental applications of TiO2 nanotube arrays (TNTAs) and nanoparticles. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2011, 6(1): 112–122
Kida K, Okita M, Fujita K, Tanaka S, Miyake Y. Formation of high crystalline ZIF-8 in an aqueous solution. CrystEngComm, 2013, 15(9): 1794
Huang X C, Lin Y Y, Zhang J P, Chen X M. Ligand-directed strategy for zeolite-type metal-organic frameworks: Zinc(II) imidazolates with unusual zeolitic topologies. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2006, 45(10): 1557–1559
Zhang J P, Zhu A X, Lin R B, Qi X L, Chen X M. Pore surface tailored sod-type metal-organic zeolites. Advanced Materials, 2011, 23(10): 1268–1271
Zhu A X, Lin R B, Qi X L, Liu Y, Lin Y Y, Zhang J P, Chen X M. Zeolitic metal azolate frameworks (MAFs) from ZnO/Zn(OH)2 and monoalkyl-substituted imidazoles and 1,2,4-triazoles: Efficient syntheses and properties. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2012, 157: 42–49
Cravillon J, Münzer S, Lohmeier S J, Feldhoff A, Huber K, Wiebcke M. Rapid room-temperature synthesis and characterization of nanocrystals of a prototypical zeolitic imidazolate framework. Chemistry of Materials, 2009, 21(8): 1410–1412
Cravillon J, Nayuk R, Springer S, Feldhoff A, Huber K, Wiebcke M. Controlling zeolitic imidazolate framework nano- and micro-crystal formation: Insight into crystal growth by time-resolved in situ static light scattering. Chemistry of Materials, 2011, 23(8): 2130–2141
Cravillon J, Schröder C A, Bux H, Rothkirch A, Caro J, Wiebcke M. Formate modulated solvothermal synthesis of ZIF-8 investigated using time-resolved in situ X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy. CrystEngComm, 2012, 14(2): 492–498
Nune S K, Thallapally P K, Dohnalkova A, Wang C, Liu J, Exarhos G J. Synthesis and properties of nano zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. Chemical Communications, 2010, 46(27): 4878–4880
Bennett T D, Saines P J, Keen D A, Tan J C, Cheetham A K. Ballmilling-induced amorphization of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIFs) for the irreversible trapping of iodine. Chemistry (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany), 2013, 19(22): 7049–7055
He M, Yao J, Li L, Wang K, Chen F, Wang H. Synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate framework-7 in a water/ethanol mixture and its ethanol-induced reversible phase transition. ChemPlusChem, 2013, 78(10): 1222–1225
Shen K, Zhang L, Chen X, Liu L, Zhang D, Han Y, Chen J, Long J, Luque R, Li Y, Chen B. Ordered macro-microporous metal-organic framework single crystals. Science, 2018, 359(6372): 206–210
Hu L, Yan Z, Zhang J, Peng X, Mo X, Wang A, Chen L. Surfactant aggregates within deep eutectic solvent-assisted synthesis of hierarchical ZIF-8 with tunable porosity and enhanced catalytic activity. Journal of Materials Science, 2019, 54(16): 11009–11023
Chen Y, Tang S. Solvothermal synthesis of porous hydrangea-like zeolitic imidazole framework-8 (ZIF-8) crystals. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2019, 276: 68–74
Troyano J, Carne-Sanchez A, Avci C, Imaz I, Maspoch D. Colloidal metal-organic framework particles: The pioneering case of ZIF-8. Chemical Society Reviews, 2019, 48(23): 5534–5546
Pan Y, Liu Y, Zeng G, Zhao L, Lai Z. Rapid synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) nanocrystals in an aqueous system. Chemical Communications, 2011, 47(7): 2071–2073
Tanaka S, Kida K, Okita M, Ito Y, Miyake Y. Size-controlled synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) crystals in an aqueous system at room temperature. Chemistry Letters, 2012, 41(10): 1337–1339
Gross A F, Sherman E, Vajo J J. Aqueous room temperature synthesis of cobalt and zinc sodalite zeolitic imidizolate frameworks. Dalton Transactions (Cambridge, England), 2012, 41(18): 5458–5460
Yao J, He M, Wang K, Chen R, Zhong Z, Wang H. High-yield synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks from stoichiometric metal and ligand precursor aqueous solutions at room temperature. CrystEngComm, 2013, 15(18): 3601
He M, Yao J, Liu Q, Wang K, Chen F, Wang H. Facile synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 from a concentrated aqueous solution. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2014, 184: 55–60
Seoane B, Zamaro J M, Tellez C, Coronas J. Sonocrystallization of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIF-7, ZIF-8, ZIF-11 and ZIF-20). CrystEngComm, 2012, 14(9): 3103
Cho H Y, Kim J, Kim S N, Ahn W S. High yield 1-L scale synthesis of ZIF-8 via a sonochemical route. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2013, 169: 180–184
Suslick K S, Hammerton D A, Cline R E. Sonochemical hot spot. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1986, 108(18): 5641–5642
Son W J, Kim J, Kim J, Ahn W S. Sonochemical synthesis of MOF-5. Chemical Communications, 2008, (47): 6336–6338
Schlesinger M, Schulze S, Hietschold M, Mehring M. Evaluation of synthetic methods for microporous metal-organic frameworks exemplified by the competitive formation of [Cu2(btc)3(H2O)3] and. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2010, 2010(1-2): 121–127
Fernández-Bertrán J F, Hernández M P, Reguera E, Yee-Madeira H, Rodriguez J, Paneque A, Llopiz J C. Characterization of mechanochemically synthesized imidazolates of Ag+1, Zn+2, Cd+2, and Hg+2: Solid state reactivity of nd10 cations. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2006, 67(8): 1612–1617
Adams C J, Colquhoun H M, Crawford P C, Lusi M, Orpen A G. Solid-state interconversions of coordination networks and hydrogen-bonded salts. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2007, 119(7): 1142–1146
Beldon P J, Fabian L, Stein R S, Thirumurugan A, Cheetham A K, Friscic T. Rapid room-temperature synthesis of zeolitic imidazo-late frameworks by using mechanochemistry. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2010, 49(50): 9640–9643
Braga D, Curzi M, Johansson A, Polito M, Rubini K, Grepioni F. Simple and quantitative mechanochemical preparation of a porous crystalline material based on a 1D coordination network for uptake of small molecules. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2006, 45(1): 142–146
Friscic T, Reid D G, Halasz I, Stein R S, Dinnebier R E, Duer M J. Ion- and liquid-assisted grinding: Improved mechanochemical synthesis of metal-organic frameworks reveals salt inclusion and anion templating. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2010, 49(4): 712–715
Tanaka S, Kida K, Nagaoka T, Ota T, Miyake Y. Mechanochemical dry conversion of zinc oxide to zeolitic imidazolate framework. Chemical Communications, 2013, 49(72): 7884–7886
Cao S, Bennett T D, Keen D A, Goodwin A L, Cheetham A K. Amorphization of the prototypical zeolitic imidazolate framework ZIF-8 by ball-milling. Chemical Communications, 2012, 48(63): 7805–7807
Lewis D W, Ruiz-Salvador A R, Gómez A, Rodriguez-Albelo L M, Coudert F X, Slater B, Cheetham A K, Mellot-Draznieks C. Zeolitic imidazole frameworks: Structural and energetics trends compared with their zeolite analogues. CrystEngComm, 2009, 11(11): 2272
Tan J C, Cheetham A K. Mechanical properties of hybrid inorganic-organic framework materials: Establishing fundamental structure-property relationships. Chemical Society Reviews, 2011, 40(2): 1059–1080
Tan J C, Bennett T D, Cheetham A K. Chemical structure, network topology, and porosity effects on the mechanical properties of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2010, 107(22): 9938–9943
Cliffe M J, Mottillo C, Stein R S, Bucar D K, Friscic T. Accelerated aging: A low energy, solvent-free alternative to solvothermal and mechanochemical synthesis of metal-organic materials. Chemical Science (Cambridge), 2012, 3(8): 2495
Mottillo C, Lu Y, Pham M H, Cliffe M J, Do T O, Friscic T. Mineral neogenesis as an inspiration for mild, solvent-free synthesis of bulk microporous metal-organic frameworks from metal (Zn, Co) oxides. Green Chemistry, 2013, 15(8): 2121
Lee J, Farha O K, Roberts J, Scheidt K A, Nguyen S T, Hupp J T. Metal-organic framework materials as catalysts. Chemical Society Reviews, 2009, 38(5): 1450–1459
Xiao D J, Bloch E D, Mason J A, Queen W L, Hudson M R, Planas N, Borycz J, Dzubak A L, Verma P, Lee K, Bonino F, Crocellà V, Yano J, Bordiga S, Truhlar D G, Gagliardi L, Brown C M, Long J R. Oxidation of ethane to ethanol by N2O in a metal-organic framework with coordinatively unsaturated iron(II) sites. Nature Chemistry, 2014, 6(7): 590–595
Nguyen L T L, Le K K A, Truong H X, Phan N T S. Metal-organic frameworks for catalysis: The knoevenagel reaction using zeolite imidazolate framework ZIF-9 as an efficient heterogeneous catalyst. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2012, 2(3): 521–528
Tran U P N, Le K K A, Phan N T S. Expanding applications of metal-organic frameworks: Zeolite imidazolate framework ZIF-8 as an efficient heterogeneous catalyst for the knoevenagel reaction. ACS Catalysis, 2011, 1(2): 120–127
Hu Y, Zheng S, Zhang F. Fabrication of MIL-100(Fe)@SiO2@-Fe3O4 core-shell microspheres as a magnetically recyclable solid acidic catalyst for the acetalization of benzaldehyde and glycol. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2016, 10(4): 534–541
Farha O K, Yazaydin A O, Eryazici I, Malliakas C D, Hauser B G, Kanatzidis M G, Nguyen S T, Snurr R Q, Hupp J T. De novo synthesis of a metal-organic framework material featuring ultrahigh surface area and gas storage capacities. Nature Chemistry, 2010, 2(11): 944–948
Rosi N L, Eckert J, Eddaoudi M, Vodak D T, Kim J, O’Keeffe M, Yaghi O M. Hydrogen storage in microporous metal-organic frameworks. Science, 2003, 300(5622): 1127–1129
Yang S, Lin X, Lewis W, Suyetin M, Bichoutskaia E, Parker J E, Tang C C, Allan D R, Rizkallah P J, Hubberstey P, Champness N R, Mark Thomas K, Blake A J, Schröder M. A partially interpenetrated metal-organic framework for selective hysteretic sorption of carbon dioxide. Nature Materials, 2012, 11(8): 710–716
Al-Janabi N, Alfutimie A, Siperstein F R, Fan X. Underlying mechanism of the hydrothermal instability of Cu3(BTC)2 metal-organic framework. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2016, 10(1): 103–107
Wang Y, Li C, Meng F, Lv S, Guo J, Liu X, Wang C, Ma Z. CuAlCl4 doped MIL-101 as a high capacity CO adsorbent with selectivity over N2. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2014, 8(3): 340–345
Ma W, Jiang Q, Yu P, Yang L, Mao L. Zeolitic imidazolate framework-based electrochemical biosensor for in vivo electrochemical measurements. Analytical Chemistry, 2013, 85(15): 7550–7557
Liu S, Xiang Z, Hu Z, Zheng X, Cao D. Zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 as a luminescent material for the sensing of metal ions and small molecules. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2011, 21(18): 6649
Liu S, Wang L, Tian J, Luo Y, Chang G, Asiri A M, Al-Youbi A O, Sun X. Application of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 nanoparticles for the fluorescence-enhanced detection of nucleic acids. ChemPlusChem, 2012, 77(1): 23–26
Ojha R P, Lemieux P A, Dixon P K, Liu A J, Durian D J. Statistical mechanics of a gas-fluidized particle. Nature, 2004, 427(6974): 521–523
Ferey G, Mellot-Draznieks C, Serre C, Millange F, Dutour J, Surble S, Margiolaki I. A chromium terephthalate-based solid with unusually large pore volumes and surface area. Science, 2005, 309(5743): 2040–2042
Eddaoudi M, Moler D B, Li H, Chen B, Reineke T M, O’Keeffe M, Yaghi O M. Modular chemistry: Secondary building units as a basis for the design of highly porous and robust metal-organic carboxylate frameworks. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2001, 34(4): 319–330
Chen B, Xiang S, Qian G. Metal-organic frameworks with functional pores for recognition of small molecules. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2010, 43(8): 1115–1124
Sun C Y, Qin C, Wang X L, Yang G S, Shao K Z, Lan Y Q, Su Z M, Huang P, Wang C G, Wang E B. Zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 as efficient pH-sensitive drug delivery vehicle. Dalton Transactions (Cambridge, England), 2012, 41(23): 6906–6909
Lu G, Li S, Guo Z, Farha O K, Hauser B G, Qi X, Wang Y, Wang X, Han S, Liu X, et al. Imparting functionality to a metal-organic framework material by controlled nanoparticle encapsulation. Nature Chemistry, 2012, 4(4): 310–316
Venna S R, Jasinski J B, Carreon M A. Structural evolution of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(51): 18030–18033
Broadley M R, White P J, Hammond J P, Zelko I, Lux A. Zinc in plants. New Phytologist, 2007, 173(4): 677–702
Zheng H, Zhang Y, Liu L, Wan W, Guo P, Nystrom A M, Zou X. One-pot synthesis of metal-organic frameworks with encapsulated target molecules and their applications for controlled drug delivery. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(3): 962–968
Wang H, Li T, Li J, Tong W, Gao C. One-pot synthesis of poly (ethylene glycol) modified zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 nanoparticles: Size control, surface modification and drug encapsulation. Colloids and Surfaces. A, Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2019, 568: 224–230
Horcajada P, Chalati T, Serre C, Gillet B, Sebrie C, Baati T, Eubank J F, Heurtaux D, Clayette P, Kreuz C, et al. Porous metal-organic-framework nanoscale carriers as a potential platform for drug delivery and imaging. Nature Materials, 2010, 9(2): 172–178
Soomro N A, Wu Q, Amur S A, Liang H, Ur Rahman A, Yuan Q, Wei Y. Natural drug physcion encapsulated zeolitic imidazolate framework, and their application as antimicrobial agent. Colloids and Surfaces. B, Biointerfaces, 2019, 182: 110364
Almeida P V, Shahbazi M A, Makila E, Kaasalainen M, Salonen J, Hirvonen J, Santos H A. Amine-modified hyaluronic acid-functionalized porous silicon nanoparticles for targeting breast cancer tumors. Nanoscale, 2014, 6(17): 10377–10387
Abednejad A, Ghaee A, Nourmohammadi J, Mehrizi A A. Hyaluronic acid/carboxylated zeolitic imidazolate framework film with improved mechanical and antibacterial properties. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2019, 222: 115033
Shu F, Lv D, Song X L, Huang B, Wang C, Yu Y, Zhao S C. Fabrication of a hyaluronic acid conjugated metal organic framework for targeted drug delivery and magnetic resonance imaging. RSC Advances, 2018, 8(12): 6581–6589
Liedana N, Galve A, Rubio C, Tellez C, Coronas J. CAF@ZIF-8: One-step encapsulation of caffeine in MOF. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2012, 4(9): 5016–5021
de Matas M, Edwards H G M, Lawson E E, Shields L, York P. Ft-Raman spectroscopic investigation of a pseudopolymorphic transition in caffeine hydrate. Journal of Molecular Structure, 1998, 1998(1-3): 97–104
Chu C, Lin H, Liu H, Wang X, Wang J, Zhang P, Gao H, Huang C, Zeng Y, Tan Y, Liu G, Chen X. Tumor microenvironment-triggered supramolecular system as an in situ nanotheranostic generator for cancer phototherapy. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(23): 1605928
Robinson J T, Welsher K, Tabakman S M, Sherlock S P, Wang H, Luong R, Dai H. High performance in vivo near-IR (>1 mm) imaging and photothermal cancer therapy with carbon nanotubes. Nano Research, 2010, 3(11): 779–793
Li M, Yang X, Ren J, Qu K, Qu X. Using graphene oxide high near-infrared absorbance for photothermal treatment of alzheimer’s disease. Advanced Materials, 2012, 24(13): 1722–1728
Yang K, Feng L, Shi X, Liu Z. Nano-graphene in biomedicine: Theranostic applications. Chemical Society Reviews, 2013, 42(2): 530–547
Dykman L, Khlebtsov N. Gold nanoparticles in biomedical applications: Recent advances and perspectives. Chemical Society Reviews, 2012, 41(6): 2256–2282
Khlebtsov N, Dykman L. Biodistribution and toxicity of engineered gold nanoparticles: A review of in vitro and in vivo studies. Chemical Society Reviews, 2011, 40(3): 1647–1671
Ren X, Chen H, Yang V, Sun D. Iron oxide nanoparticle-based theranostics for cancer imaging and therapy. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2014, 8(3): 253–264
Zhang S, Sun C, Zeng J, Sun Q, Wang G, Wang Y, Wu Y, Dou S, Gao M, Li Z. Ambient aqueous synthesis of ultrasmall PEGylated Cu2 x Se nanoparticles as a multifunctional theranostic agent for multimodal imaging guided photothermal therapy of cancer. Advanced Materials, 2016, 28(40): 8927–8936
Wang Y, Wu Y, Liu Y, Shen J, Lv L, Li L, Yang L, Zeng J, Wang Y, Zhang L W, et al. BSA-mediated synthesis of bismuth sulfide nanotheranostic agents for tumor multimodal imaging and thermoradiotherapy. Advanced Functional Materials, 2016, 26(29): 5335–5344
Gao F, Sun M, Xu L, Liu L, Kuang H, Xu C. Biocompatible cup-shaped nanocrystal with ultrahigh photothermal efficiency as tumor therapeutic agent. Advanced Functional Materials, 2017, 27(24): 1700605
Song S, Shen H, Yang T, Wang L, Fu H, Chen H, Zhang Z. Indocyanine green loaded magnetic carbon nanoparticles for near infrared fluorescence/magnetic resonance dual-modal imaging and photothermal therapy of tumor. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(11): 9484–9495
Zhou B, Li Y, Niu G, Lan M, Jia Q, Liang Q. Near-infrared organic dye-based nanoagent for the photothermal therapy of cancer. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(44): 29899–29905
Li Y, Xu N, Zhou J, Zhu W, Li L, Dong M, Yu H, Wang L, Liu W, Xie Z. Facile synthesis of a metal-organic framework nanocarrier for NIR imaging-guided photothermal therapy. Biomaterials Science, 2018, 6(11): 2918–2924
Li Y, Xu N, Zhu W, Wang L, Liu B, Zhang J, Xie Z, Liu W. Nanoscale melittin@zeolitic imidazolate frameworks for enhanced anticancer activity and mechanism analysis. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(27): 22974–22984
Zheng C, Zheng M, Gong P, Jia D, Zhang P, Shi B, Sheng Z, Ma Y, Cai L. Indocyanine green-loaded biodegradable tumor targeting nanoprobes for in vitro and in vivo imaging. Biomaterials, 2012, 33(22): 5603–5609
Zheng M, Yue C, Ma Y, Gong P, Zhao P, Zheng C, Sheng Z, Zhang P, Wang Z, Cai L. Single-step assembly of DOX/ICG loaded lipid-polymer nanoparticles for highly effective chemophotothermal combination therapy. ACS Nano, 2013, 7(3): 2056–2067
Mordon S, Devoisselle J M, Soulie-Begu S, Desmettre T. Indocyanine green: Physicochemical factors affecting its fluorescence in vivo. Microvascular Research, 1998, 55(2): 146–152
Wang T, Li S, Zou Z, Hai L, Yang X, Jia X, Zhang A, He D, He X, Wang K. A zeolitic imidazolate framework-8-based indocyanine green theranostic agent for infrared fluorescence imaging and photothermal therapy. Journal of Materials Chemistry. B, Materials for Biology and Medicine, 2018, 6(23): 3914–3921
Juzeniene A, Peng Q, Moan J. Milestones in the development of photodynamic therapy and fluorescence diagnosis. Photochemical & Photobiological Sciences, 2007, 6(12): 1234–1245
Lu D, Tao R, Wang Z. Carbon-based materials for photodynamic therapy: A mini-review. Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering, 2019, 13(2): 310–323
Juarranz Á, Jaén P, Sanz-Rodríguez F, Cuevas J, González S. Photodynamic therapy of cancer. Basic principles and applications. Clinical & Translational Oncology, 2008, 10(3): 148–154
Henderson B W, Dougherty T J. How does photodynamic therapy work? Photochemistry and Photobiology, 1992, 55(1): 145–157
Castano A P, Demidova T N, Hamblin M R. Mechanisms in photodynamic therapy: Part one-photosensitizers, photochemistry and cellular localization. Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy, 2004, 1(4): 279–293
Xu D, You Y, Zeng F, Wang Y, Liang C, Feng H, Ma X. Disassembly of hydrophobic photosensitizer by biodegradable zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 for photodynamic cancer therapy. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(18): 15517–15523
Xie Z, Liang S, Cai X, Ding B, Huang S, Hou Z, Ma P, Cheng Z, Lin J. O2-Cu/ZIF-8@Ce6/ZIF-8@F127 composite as a tumor microenvironment-responsive nanoplatform with enhanced photo-/chemodynamic antitumor efficacy. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(35): 31671–31680
Zhang C, Bu W, Ni D, Zhang S, Li Q, Yao Z, Zhang J, Yao H, Wang Z, Shi J. Synthesis of iron nanometallic glasses and their application in cancer therapy by a localized fenton reaction. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016, 55(6): 2101–2106
Tang Z, Liu Y, He M, Bu W. Chemodynamic therapy: Tumour microenvironment-mediated fenton and fenton-like reactions. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(4): 946–956
Lin L S, Song J, Song L, Ke K, Liu Y, Zhou Z, Shen Z, Li J, Yang Z, Tang W, Niu G, Yang H H, Chen X. Simultaneous Fenton-like ion delivery and glutathione depletion by MnO2-based nanoagent to enhance chemodynamic therapy. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(18): 4902–4906
Ma B, Wang S, Liu F, Zhang S, Duan J, Li Z, Kong Y, Sang Y, Liu H, Bu W, Li L. Self-assembled copper-amino acid nanoparticles for in situ glutathione “and” H2O2 sequentially triggered chemodynamic therapy. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2019, 141(2): 849–857
Chen Y, Deng J, Liu F, Dai P, An Y, Wang Z, Zhao Y. Energy-free, singlet oxygen-based chemodynamic therapy for selective tumor treatment without dark toxicity. Advanced Healthcare Materials, 2019, 8(18): 1900366
Leader B, Baca Q J, Golan D E. Protein therapeutics: A summary and pharmacological classification. Nature Reviews. Drug Discovery, 2008, 7(1): 21–39
Chen Z, Li N, Li S, Dharmarwardana M, Schlimme A, Gassensmith J J. Viral chemistry: The chemical functionalization of viral architectures to create new technology. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews. Nanomedicine and Nanobiotechnology, 2016, 8(4): 512–534
Mallamace F, Corsaro C, Mallamace D, Vasi S, Vasi C, Baglioni P, Buldyrev S V, Chen S H, Stanley H E. Energy landscape in protein folding and unfolding. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(12): 3159–3163
Carmichael S P, Shell M S. Entropic (de)stabilization of surface-bound peptides conjugated with polymers. Journal of Chemical Physics, 2015, 143(24): 243103
Wang C, Luan J, Tadepalli S, Liu K K, Morrissey J J, Kharasch E D, Naik R R, Singamaneni S. Silk-encapsulated plasmonic biochips with enhanced thermal stability. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(40): 26493–26500
Liang K, Ricco R, Doherty C M, Styles M J, Bell S, Kirby N, Mudie S, Haylock D, Hill A J, Doonan C J, Falcaro P. Biomimetic mineralization of metal-organic frameworks as protective coatings for biomacromolecules. Nature Communications, 2015, 6(1): 7240
Alsaiari S K, Patil S, Alyami M, Alamoudi K O, Aleisa F A, Merzaban J S, Li M, Khashab N M. Endosomal escape and delivery of CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing machinery enabled by nanoscale zeolitic imidazolate framework. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(1): 143–146
Wang J, Ye Y, Yu J, Kahkoska A R, Zhang X, Wang C, Sun W, Corder R D, Chen Z, Khan S A, et al. Core-shell microneedle gel for self-regulated insulin delivery. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(3): 2466–2473
Yang J, Cao Z. Glucose-responsive insulin release: Analysis of mechanisms, formulations, and evaluation criteria. Journal of Controlled Release, 2017, 263: 231–239
Yu J, Zhang Y, Ye Y, DiSanto R, Sun W, Ranson D, Ligler F S, Buse J B, Gu Z. Microneedle-array patches loaded with hypoxia-sensitive vesicles provide fast glucose-responsive insulin delivery. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(27): 8260–8265
Chen W H, Luo G F, Vazquez-Gonzalez M, Cazelles R, Sohn Y S, Nechushtai R, Mandel Y, Willner I. Glucose-responsive metal-organic-framework nanoparticles act as “smart” sense-and-treat carriers. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(8): 7538–7545
Weed R I, Reed C F, Berg G. Is hemoglobin an essential structural component of human erythrocyte membranes? Journal of Clinical Investigation, 1963, 42(4): 581–588
Ranji-Burachaloo H, Reyhani A, Gurr P A, Dunstan D E, Qiao G G. Combined fenton and starvation therapies using hemoglobin and glucose oxidase. Nanoscale, 2019, 11(12): 5705–5716
Mali P, Yang L, Esvelt K M, Aach J, Guell M, DiCarlo J E, Norville J E, Church G M. Rna-guided human genome engineering via Cas9. Science, 2013, 339(6121): 823–826
Cong L, Ran F A, Cox D, Lin S, Barretto R, Habib N, Hsu P D, Wu X, Jiang W, Marraffini L A, Zhang F. Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems. Science, 2013, 339(6121): 819–823
Li M, Tao Y, Shu Y, LaRochelle J R, Steinauer A, Thompson D, Schepartz A, Chen Z Y, Liu D R. Discovery and characterization of a peptide that enhances endosomal escape of delivered proteins in vitro and in vivo. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 137(44): 14084–14093
Acknowledgments
SMF and ZW acknowledge the financial support from the Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin (No. 19JCYBJC28400). XLZ and DYS acknowledge the funding support from the Basic Research General Program of Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Commission in 2020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, S., Zhang, X., Shi, D. et al. Zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) for drug delivery: A critical review. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 15, 221–237 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-020-1927-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11705-020-1927-8