Abstract
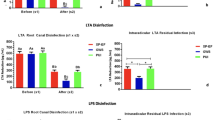
Apical periodontitis is caused by biofilm-mediated root canal infection. Early phase oral bacterial biofilms are inhibited by Lactobacillus plantarum lipoteichoic acid (Lp.LTA). However, mature biofilms that develop over 3 weeks are more resistant to traditional endodontic medicaments. Therefore, this study examined the effectiveness of Lp.LTA on disrupting mature Enterococcus faecalis biofilms, and on enhancing the effects of endodontic medicaments. LTA was purified from L. plantarum through butanol extraction followed by hydrophobic and ion-exchange chromatography. E. faecalis biofilms were formed over 3 weeks on glass bottom dishes and in dentin blocks obtained from human single-rooted premolars. These mature biofilms were treated with or without Lp.LTA for 1 h, followed by additional treatment with either chlorhexidine digluconate (CHX), calcium hydroxide (CH), or triple antibiotics for 24 h. Biofilms on glass were live/dead stained and quantified by ZEN through confocal laser microscopy. Bio-films in dentin were fixed, sputter coated and analyzed by ImageJ with scanning electron microscopy. Preformed E. faecalis mature biofilms on the culture dishes were dose-dependently disrupted by Lp.LTA. Lp.LTA potentiated the effects of CHX or CH on the disruption of mature biofilm. Interestingly, CHX-induced disruption of preformed E. faecalis mature biofilms was synergistically enhanced only when pre-treated with Lp.LTA. Furthermore, in the dentin block model, Lp.LTA alone reduced E. faecalis mature biofilm and pre-treatment with Lp.LTA promoted the anti-biofilm activity of CHX. Lp.LTA could be an anti-biofilm or supplementary agent that can be effective for E. faecalis-biofilm-induced diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn, K.B., Baik, J.E., Park, O.J., Yun, C.H., and Han, S.H. 2018a. Lactobacillus plantarum lipoteichoic acid inhibits biofilm formation of Streptococcus mutans. PLoS One13, e0192694.
Ahn, K.B., Baik, J.E., Yun, C.H., and Han, S.H. 2018b. Lipoteichoic acid inhibits Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation. Front. Microbiol.9, 327.
Arabaci, T., Türkez, H., Çanakçi, C.F., and Özgöz, M. 2013. Assessment of cytogenetic and cytotoxic effects of chlorhexidine digluconate on cultured human lymphocytes. Acta Odontol. Scand.71, 1255–1260.
Baik, J.E., Jang, K.S., Kang, S.S., Yun, C.H., Lee, K., Kim, B.G., Kum, K.Y., and Han, S.H. 2011. Calcium hydroxide inactivates lipoteichoic acid from Enterococcus faecalis through deacylation of the lipid moiety. J. Endod.37, 191–196.
Barie, P.S., Christou, N.V., Dellinger, E.P., Rout, W.R., Stone, H.H., and Waymack, J.P. 1990. Pathogenicity of the enterococcus in surgical infections. Ann. Surg.212, 155–159.
Bjarnsholt, T., Jensen, P.Ø., Fiandaca, M.J., Pedersen, J., Hansen, C.R., Andersen, C.B., Pressler, T., Givskov, M., and Høiby, N. 2009. Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms in the respiratory tract of cystic fibrosis patients. Pediatr. Pulmonol.44, 547–558.
Domenech, M., Ramos-Sevillano, E., Garcia, E., Moscoso, M., and Yuste, J. 2013. Biofilm formation avoids complement immunity and phagocytosis of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect. Immun.81, 2606–2615.
Flemming, H.C., Neu, T.R., and Wozniak, D.J. 2007. The EPS matrix: The “house of biofilm cells”. J. Bacteriol.189, 7945–7947.
Gu, Y.H., Yamasita, T., and Kang, K.M. 2018. Subchronic oral dose toxicity study of Enterococcus faecalis 2001 (EF 2001) in mice. Toxicol. Res.34, 55–63.
Haapasalo, M., Qian, W., Portenier, I., and Waltimo, T. 2007. Effects of dentin on the antimicrobial properties of endodontic medicaments. J. Endod.33, 917–925.
Hong, S.W., Baik, J.E., Kang, S.S., Kum, K.Y., Yun, C.H., and Han, S.H. 2016. Sodium hypochlorite inactivates lipoteichoic acid of Enterococcus faecalis by deacylation. J. Endod.42, 1503–1508.
Huycke, M.M., Sahm, D.F., and Gilmore, M.S. 1998. Multiple-drug resistant enterococci: The nature of the problem and an agenda for the future. Emerg. Infect. Dis.4, 239–249.
Jung, S., Park, O.J., Kim, A.R., Ahn, K.B., Lee, D., Kum, K.Y., Yun, C.H., and Han, S.H. 2019. Lipoteichoic acids of lactobacilli inhibit Enterococcus faecalis biofilm formation and disrupt the preformed biofilm. J. Microbiol.57, 310–315.
Kim, A.R., Ahn, K.B., Yun, C.H., Park, O.J., Perinpanayagam, H., Yoo, Y.J., Kum, K.Y., and Han, S.H. 2019. Lactobacillus plantarum lipoteichoic acid inhibits oral multispecies biofilm. J. Endod.45, 310–315.
Ko, J.S., Yang, H.R., Chang, J.Y., and Seo, J.K. 2007. Lactobacillus plantarum inhibits epithelial barrier dysfunction and interleukin-8 secretion induced by tumor necrosis factor-α. World J. Gastroenterol.13, 1962–1965.
Lee, J.K., Baik, J.E., Yun, C.H., Lee, K., Han, S.H., Lee, W., Bae, K.S., Baek, S.H., Lee, Y., Son, W.J., et al. 2009. Chlorhexidine gluconate attenuates the ability of lipoteichoic acid from Enterococcus faecalis to stimulate toll-like receptor 2. J. Endod.35, 212–215.
Love, R.M. 2001. Enterococcus faecalis-a mechanism for its role in endodontic failure. Int. Endod. J.34, 399–405.
Luppens, S.B., Reij, M.W., van der Heijden, R.W., Rombouts, F.M., and Abee, T. 2002. Development of a standard test to assess the resistance of Staphylococcus aureus biofilm cells to disinfectants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol.68, 4194–4200.
Mohamed, J.A., Huang, W., Nallapareddy, S.R., Teng, F., and Murray, B.E. 2004. Influence of origin of isolates, especially endocarditis isolates, and various genes on biofilm formation by Enterococcus faecalis. Infect. Immun.72, 3658–3663.
Nair, P.N. 2004. Pathogenesis of apical periodontitis and the causes of endodontic failures. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med.15, 348–381.
Noh, S.Y., Kang, S.S., Yun, C.H., and Han, S.H. 2015. Lipoteichoic acid from Lactobacillus plantarum inhibits PAM2CSK4-induced IL-8 production in human intestinal epithelial cells. Mol. Immunol.64, 183–189.
Peters, L.B., van Winkelhoff, A.J., Buijs, J.F., and Wesselink, P.R. 2002. Effects of instrumentation, irrigation and dressing with calcium hydroxide on infection in pulpless teeth with periapical bone lesions. Int. Endod. J.35, 13–21.
Ramfjord, S.P., Emslie, R.D., Greene, J.C., Held, A.J., and Waerhaug, J. 1968. Epidemiological studies of periodontal diseases. Am. J. Public Health Nations Health58, 1713–1722.
Ryu, Y.H., Baik, J.E., Yang, J.S., Kang, S.S., Im, J., Yun, C.H., Kim, D.W., Lee, K., Chung, D.K., Ju, H.R., et al. 2009. Differential immunostimulatory effects of Gram-positive bacteria due to their lipoteichoic acids. Int. Immunopharmacol.9, 127–133.
Sedgley, C.M., Lee, E.H., Martin, M.J., and Flannagan, S.E. 2008. Antibiotic resistance gene transfer between Streptococcus gordonii and Enterococcus faecalis in root canals of teeth ex vivo. J. Endod.34, 570–574.
Shen, Y., Stojicic, S., and Haapasalo, M. 2011. Antimicrobial efficacy of chlorhexidine against bacteria in biofilms at different stages of development. J. Endod.37, 657–661.
Stojicic, S., Shen, Y., and Haapasalo, M. 2013. Effect of the source of biofilm bacteria, level of biofilm maturation, and type of disinfecting agent on the susceptibility of biofilm bacteria to antibacterial agents. J. Endod.39, 473–477.
Sunde, P.T., Olsen, I., Debelian, G.J., and Tronstad, L. 2002. Micro-biota of periapical lesions refractory to endodontic therapy. J. Endod.28, 304–310.
Tagelsir, A., Yassen, G.H., Gomez, G.F., and Gregory, R.L. 2016. Effect of antimicrobials used in regenerative endodontic procedures on 3-week-old Enterococcus faecalis biofilm. J. Endod.42, 258–262.
Upadya, M., Shrestha, A., and Kishen, A. 2011. Role of efflux pump inhibitors on the antibiofilm efficacy of calcium hydroxide, chitosan nanoparticles, and light-activated disinfection. J. Endod.37, 1422–1426.
Vu, M., Rajgopal Bala, H., Cahill, J., Toholka, R., and Nixon, R. 2018. Immediate hypersensitivity to chlorhexidine. Australas. J. Dermatol.59, 55–56.
Wang, Z., Shen, Y., and Haapasalo, M. 2012. Effectiveness of endodontic disinfecting solutions against young and old Enterococcus faecalis biofilms in dentin canals. J. Endod.38, 1376–1379.
Wisplinghoff, H., Seifert, H., Tallent, S.M., Bischoff, T., Wenzel, R.P., and Edmond, M.B. 2003. Nosocomial bloodstream infections in pediatric patients in united states hospitals: Epidemiology, clinical features and susceptibilities. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J.22, 686–691.
Yoo, Y.J., Kwon, I., Oh, S.R., Perinpanayagam, H., Lim, S.M., Ahn, K.B., Lee, Y., Han, S.H., Chang, S.W., Baek, S.H., et al. 2017. Anti-fungal effects of synthetic human β-defensin-3-C15 peptide on Candida albicans-infected root dentin. J. Endod.43, 1857–1861.
Zorko, M. and Jerala, R. 2008. Alexidine and chlorhexidine bind to lipopolysaccharide and lipoteichoic acid and prevent cell activation by antibiotics. J. Antimicrob. Chemother.62, 730–737.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Seoul National University Dental Hospital (SNUDH) Research Fund (07-2015-0004), by the National Research Foundation of Korea, which is funded by the Korean government (NRF-2018R-1A5A2024418 and NRF-2019R1A2C2007041), and by the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare (HI17C1377), Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors deny any conflicts of interest related to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, A.R., Kang, M., Yoo, YJ. et al. Lactobacillus plantarum lipoteichoic acid disrupts mature Enterococcus faecalis biofilm. J Microbiol. 58, 314–319 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-020-9518-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-020-9518-4