Abstract
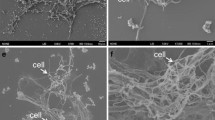
A strictly anaerobic, dissimilatory Fe(III)-reducing hyperthermophilic archaeon, designated as strain IOH1T, was isolated from a new deep-sea hydrothermal vent (Onnuri Vent Field) area in the Central Indian Ocean ridge. Strain IOH1T showed > 99% 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity with Thermococcus celericrescens TS2T (99.4%) and T. siculi DSM 12349T (99.2%). Additional three species T. barossii SHCK-94T (99.0%), T. celer Vu13T (98.8%), and T. piezophilus (98.6%) showed > 98.6% of 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity, however, the maximum OrthoANI value is 89.8% for the genome of T. celericrescens TS2T. Strain IOH1T cells are coccoid, 1.2–1.8 μm in diameter, and motile by flagella. Growth was at 70–82°C (optimum 80°C), pH 5.4–8.0 (optimum pH 6.0) with 2–4% (optimum 3%) NaCl. Growth of strain IOH1T was enhanced by starch, pyruvate, D(+)-maltose and maltodextrin as a carbon sources, and elemental sulfur as an electron acceptor; clearly different from those of related species T. celecrescens DSM 17994T and T. siculi DSM 12349T. Strain IOH1T, T. celercrescence DSM 17994T, and T. siculi DSM 12349T reduced soluble Fe(III)-citrate present in the medium, whereas the amount of total cellular proteins increased with the concomitant accumulation of Fe(II). We determined a circular chromosome of 2,234 kb with an extra-chromosomal archaeal plasmid, pTI1, of 7.7 kb and predicted 2,425 genes. The DNA G + C content was 54.9 mol%. Based on physiological properties, phylogenetic, and genome analysis, we proposed that strain IOH1T (= KCTC 15844T = JCM 39077T) is assigned to a new species in the genus Thermococcus and named Thermococcus indicus sp. nov.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi, D.H., Kwon, Y.M., Chiura, H.X., Yang, E.C., Bae, S.S., Kang, S.G., Lee, J.H., Yoon, H.S., and Kim, S.J. 2015. Extracellular vesicles of the hyperthermophilic archaeon “Thermococcus onnurineus” NA1T. Appl. Environ. Microbiol.81, 4591–4599.
Cossu, M., Da Cunha, V., Toffano-Nioche, C., Forterre, P., and Oberto, J. 2015. Comparative genomics reveals conserved positioning of essential genomic clusters in highly rearranged Thermococcales chromosomes. Biochimie118, 313–321.
Duffaud, G.D., d’Hennezel, O.B., Peek, A.S., Reysenbach, A.L., and Kelly, R.M. 1998. Isolation and characterization of Thermococcus barossii, sp. nov., a hyperthermophilic archaeon isolated from a hydrothermal vent flange formation. Syst. Appl. Microbiol.21, 40–49.
Felsenstein, J. 1981. Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J. Mol. Evol.17, 368–376.
Fiala, G. and Stetter, K.O. 1986. Pyrococcus furiosus sp. nov. represents a novel genus of marine heterotrophic archaebacteria growing optimally at 100°C. Arch. Microbiol.145, 56–61.
Fitch, W.M. 1971. Toward defining the course of evolution: Minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst. Zool.20, 406–416.
Godfroy, A., Lesongeur, F., Raguénès, G., Quérellou, J., Antoine, E., Meunier, J.R., Guezennec, J., and Barbier, G. 1997. Thermococcus hydrothermalis sp. nov., a new hyperthermophilic archaeon isolated from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol.47, 622–626.
Grote, R., Li, L., Tamaoka, J., Kato, C., Horikoshi, K., and Antranikian, G. 1999. Thermococcus siculi sp. nov., a novel hyperthermophilic archaeon isolated from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent at the Mid-Okinawa trough. Extremophiles3, 55–62.
Hungate, R.E. 1969. Chapter IV - A roll tube method for cultivation of strict anaerobes. In Norris, J.R. and Ribbons, D.W. (eds.) Methods in Microbiology, vol. 3. pp. 117–132. Academic Press Inc, London, UK.
Jannasch, H.W. and Mottl, M.J. 1985. Geomicrobiology of deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Science229, 717–725.
Jukes, T.H. and Cantor, C.R. 1969. Chapter 24 - Evolution of protein molecules. In Munro, H.N. (ed.) Mammalian Protein Metabolism, vol. 3, pp. 21–132. Academic Press.
Kim, M.S., Bae, S.S., Kim, Y.J., Kim, T.W., Lim, J.K., Lee, S.H., Choi, A.R., Jeon, J.H., Lee, J.H., Lee, H.S., et al. 2013. CO-Dependent H2 production by genetically engineered Thermococcus onnurineus NA1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol.79, 2048–2053.
Kim, Y.J., Lee, H.S., Kim, E.S., Bae, S.S., Lim, J.K., Matsumi, R., Lebedinsky, A.V., Sokolova, T.G., Kozhevnikova, D.A., Cha, S.S., et al. 2010. Formate-driven growth coupled with H2 production. Nature467, 352–355.
Kim, M., Oh, H.S., Park, S.C., and Chun, J. 2014. Towards a taxonomic coherence between average nucleotide identity and 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity for species demarcation of prokaryotes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol.64, 346–351.
Kotsyurbenko, O.R., Simankova, M.V., Nozhevnikova, A.N., Zhilina, T.N., Bolotina, N.P., Lysenko, A.M., and Osipov, G.A. 1995. New species of psychrophilic acetogens: Acetobacterium bakii sp. nov., A. paludosum sp. nov., A. fimetarium sp. nov. Arch. Microbiol.163, 29–34.
Krupovic, M., Gonnet, M., Hania, W.B., Forterre, P., and Erauso, G. 2013. Insights into dynamics of mobile genetic elements in hyperthermophilic environments from five new Thermococcus plasmids. PLoS One8, e49044.
Kuwabara, T., Minaba, M., Iwayama, Y., Inouye, I., Nakashima, M., Marumo, K., Maruyama, A., Sugai, A., Itoh, T., Ishibashi, J., et al. 2005. Thermococcus coalescens sp. nov., a cell-fusing hyperthermophilic archaeon from Suiyo Seamount. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol.55, 2507–2514.
Kuwabara, T., Minaba, M., Ogi, N., and Kamekura, M. 2007. Thermococcus celericrescens sp. nov., a fast-growing and cell-fusing hyperthermophilic archaeon from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol.57, 437–443.
Lee, H.S., Kang, S.G., Bae, S.S., Lim, J.K., Cho, Y., Kim, Y.J., Jeon, J.H., Cha, S.S., Kwon, K.K., Kim, H.T., et al. 2008. The complete genome sequence of Thermococcus onnurineus NA1 reveals a mixed heterotrophic and carboxydotrophic metabolism. J. Bacteriol.190, 7491–7499.
Lee, I., Kim, Y.O., Park, S.C., and Chun, J. 2016. OrthoANI: An improved algorithm and software for calculating average nucleotide identity. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol.66, 1100–1103.
Lilley, M.D., Feely, R.A., and Trefry, J.H. 1995. Chemical and biochemical transformations in hydrothermal plumes. Am. Geophys. Union91, 369–391.
Lim, J.K., Bae, S.S., Kim, T.W., Lee, J.H., Lee, H.S., and Kang, S.G. 2012. Thermodynamics of formate-oxidizing metabolism and implications for H2 production. Appl. Environ. Microbiol.78, 7393–7397.
Lim, J.K., Kang, S.G., Lebedinsky, A.V., Lee, J.H., and Lee, H.S. 2010. Identification of a novel class of membrane-bound [NiFe]-hydrogenases in Thermococcus onnurineus NA1 by in silico analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol.76, 6286–6289.
Lim, J.K., Mayer, F., Kang, S.G., and Müller, V. 2014. Energy conservation by oxidation of formate to carbon dioxide and hydrogen via a sodium ion current in a hyperthermophilic archaeon. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA111, 11497–11502.
Lossouarn, J., Dupont, S., Gorlas, A., Mercier, C., Bienvenu, N., Marguet, E., Forterre, P., and Geslin, C. 2015. An abyssal mobilome: Viruses, plasmids and vesicles from deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Res. Microbiol.166, 742–752.
Marreiros, B.C., Batista, A.P., Duarte, A.M., and Pereira, M.M. 2013. A missing link between complex I and group 4 membrane-bound [NiFe] hydrogenases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta1827, 198–209.
Mayer, F., Lim, J.K., Langer, J.D., Kang, S.G., and Müller, V. 2015. Na+ Transport by the A1AO-ATP synthase purified from Thermococcus onnurineus and reconstituted into liposomes. J. Biol. Chem.290, 6994–7002.
Miroshnichenko, M.L., Gongadze, G.M., Rainey, F.A., Kostyukova, A.S., Lysenko, A.M., Chernyh, N.A., and Bonch-Osmolovskaya, E.A. 1998. Thermococcus gorgonarius sp. nov. and Thermococcus pacificus sp. nov.: heterotrophic extremely thermophilic archaea from New Zealand submarine hot vents. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol.48, 23–29.
Miroshnichenko, M.L., Hippe, H., Stackebrandt, E., Kostrikina, N.A., Chernyh, N.A., Jeanthon, C., Nazina, T.N., Belyaev, S.S., and Bonch-Osmolovskaya, E.A. 2001. Isolation and characterization of Thermococcus sibiricus sp. nov. from a Western Siberia high-temperature oil reservoir. Extremophiles5, 85–91.
Ramakrishnan, V. and Adams, M.W.W. 1995. Preparation of genomic DNA from sulfur-dependent hyperthermophilic Archaea. In Robb, F.T. and Place, A.R. (eds.), Archaea: a laboratory manual / Thermophiles, pp. 95–96. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, USA.
Rittmann, S.K.R., Lee, H.S., Lim, J.K., Kim, T.W., Lee, J.H., and Kang, S.G. 2015. One-carbon substrate-based biohydrogen production: microbes, mechanism, and productivity. Biotechnol. Adv.33, 165–177.
Ronimus, R.S., Reysenbach, A., Musgrave, D.R., and Morgan, H.W. 1997. The phylogenetic position of the Thermococcus isolate AN1 based on 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis: a proposal that AN1 represents a new species, Thermococcus zilligii sp. nov. Arch. Microbiol.168, 245–248.
Rudnicki, M.D. and Elderfield, H. 1993. A chemical model of the buoyant and neutrally buoyant plume above the TAG vent field, 26 degrees N, Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta57, 2939–2957.
Ryu, T., Woo, S., and Lee, N. 2019. The first reference transcriptome assembly of the stalked barnacle, Neolepas marisindica, from the Onnuri Vent Field on the Central Indian Ridge. Mar. Genomics48, 100679.
Saitou, N. and Nei, M. 1987. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol.4, 406–425.
Sapra, R., Bagramyan, K., and Adams, M.W.W. 2003. A simple energy-conserving system: proton reduction coupled to proton translocation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA100, 7545–7550.
Sapra, R., Verhagen, M.F., and Adams, M.W. 2000. Purification and characterization of a membrane-bound hydrogenase from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus. J. Bacteriol.182, 3423–3428.
Sato, T., Fukui, T., Atomi, H., and Imanaka, T. 2003. Targeted gene disruption by homologous recombination in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus kodakaraensis KOD1. J. Bacteriol.185, 210–220.
Schönheit, P. and Schäfer, T. 1995. Metabolism of hyperthermophiles. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol.11, 26–57.
Schut, G.J., Boyd, E.S., Peters, J.W., and Adams, M.W. 2012. The modular respiratory complexes involved in hydrogen and sulfur metabolism by heterotrophic hyperthermophilic archaea and their evolutionary implications. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol.37, 182–203.
Segata, N., Börnigen, D., Morgan, X.C., and Hutternhower, C. 2013. PhyloPhlAn is a new method for improved phylogenetic and taxonomic placement of microbes. Nat. Commum.4, 2304.
Slobodkin, A., Campbell, B., Cary, S.C., Bonch-Osmolovskaya, E., and Jeanthon, C. 2001. Evidence for the presence of thermophilic Fe(III)-reducing microorganisms in deep-sea hydrothermal vents at 13°N (East Pacific Rise). FEMS Microbiol. Ecol.36, 235–243.
Slobodkin, A.I., Jeanthon, C., L’Haridon, S., Nazina, T., Miroshnichenko, M., and Bonch-Osmolovskaya, E. 1999. Dissimilatory reduction of Fe(III) by thermophilic bacteria and archaea in deep subsurface petroleum reservoirs of Western Siberia. Curr. Microbiol.39, 99–102.
Soler, N., Gaudin, M., Marguet, E., and Forterre, P. 2011. Plasmids, viruses and virus-like membrane vesicles from Thermococcales. Biochem. Soc. Trans.39, 36–44.
Sørensen, J. 1982. Reduction of ferric iron in anaerobic, marine sediment and interaction with reduction of nitrate and sulfate. Appl. Environ. Microbiol.43, 319–324.
Stetter, K.O. 1999. Extremophiles and their adaptation to hot environments. FEBS Lett.452, 22–25.
Takai, K., Sugai, A., Itoh, T., and Horikoshi, K. 2000. Palaeococcus ferrophilus gen. nov., sp. nov., a barophilic, hyperthermophilic archaeon from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent chimney. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol.50, 489–500.
Tamura, K., Peterson, D., Peterson, N., Stecher, G., Nei, M., and Kumar, S. 2011. MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol.28, 2731–2739.
Tatusova, T., DiCuccio, M., Badretdin, A., Chetvernin, V., Nawrocki, E.P., Zaslavsky, L., Lomsadze, A., Pruitt, K.D., Borodovsky, M., and Ostell, J. 2016. NCBI prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res.44, 6614–6624.
Wayne, L.G., Brenner, D.J., Colwell, R.R., Grimond, P.A.D., Kandler, O., Krichevsky, M.I., Moore, L.H., Moore, W.E.C., Murray, R.G.E., Stackebrandt, E., et al. 1987. Report of the Ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol.37, 463–464.
Zierenberg, R.A. and Schiffmant, P. 1990. Microbial control of silver mineralization at a sea-floor hydrothermal site on the northern gorda ridge. Nature348, 155–157.
Zillig, W., Holz, I., Janekovic, D., Schäfer, W., and Reiter, W.D. 1983. The archaebacterium Thermococcus celer represents, a novel genus within the thermophilic branch of the archaebacteria. Syst. Appl. Microbiol.4, 88–94.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the KIOST In-house Program (PE99822) and the ‘Understanding of the deep-sea biosphere on seafloor hydrothermal vents in the Indian Ridge’ Program (No. 20170411) of the Ministry of Ocean and Fisheries of the Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://www.springerlink.com/content/120956
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, J.K., Kim, Y.J., Yang, JA. et al. Thermococcus indicus sp. nov., a Fe(III)-reducing hyperthermophilic archaeon isolated from the Onnuri Vent Field of the Central Indian Ocean ridge. J Microbiol. 58, 260–267 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-020-9424-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-020-9424-9