Abstract
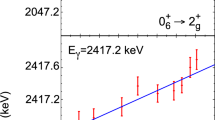
The \(^{22}\hbox {Na}(p,\gamma )^{23}\hbox {Mg}\) reaction is responsible for destruction of the long-lived radionuclide \(^{22}\hbox {Na}\) produced during nova explosions. Since the reaction proceeds through resonances from levels in \(^{23}\hbox {Mg}\) above the proton threshold at 7.581 MeV, the properties of these levels such as excitation energies, spins, and parities are crucial ingredients to determine the \(^{22}\hbox {Na}(p,\gamma )^{23}\hbox {Mg}\) reaction rate. Despite recent studies of these levels, their spins are not well constrained in many cases. We have measured the \(^{24}\mathrm{Mg}(p,d)^{23}\hbox {Mg}\) transfer reaction to determine spectroscopic properties of these levels at the Holifield Radioactive Ion Beam Facility at Oak Ridge National Laboratory. The spin of the \(E_{x}\) = 7.788 MeV level in \(^{23}\hbox {Mg}\) is constrained to be \(J^{\pi }\) = (3/2\(^+\), 5/2\(^+\)) through the present work. The astrophysical \(^{22}\hbox {Na}(p,\gamma )^{23}\hbox {Mg}\) reaction rate at nova temperatures is updated accordingly. Nova nucleosynthesis model calculations using the newly updated \(^{22}\hbox {Na}(p,\gamma )^{23}\hbox {Mg}\) reaction rate shows that the final weighted abundance of the radionuclide \(^{22}\hbox {Na}\) is increased by 42% compared to that obtained by using the previous \(^{22}\hbox {Na}(p,\gamma )^{23}\hbox {Mg}\) reaction rate of Sallaska et al. for a 1.35 \(M_{\odot }\) ONeMg white dwarf.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
This manuscript has no associated data or the data will not be deposited. [Authors’ comment: All data generated during this study are contained in the published article.]
References
M. Hernanz, J. José, New Astron. Rev. 48, 35 (2004)
A.L. Sallaska et al., Phys. Rev. C 83, 034611 (2011)
S.E. Boggs, New Astron. Rev. 50, 604 (2006)
A. De Angelis et al., J. High Energy Astrophys. 19, 1 (2018)
D.D. Clayton, F. Hoyle, Astrophys. J. 187, L101 (1974)
J. José, A. Coc, M. Hernanz, Astrophys. J. 520, 347 (1999)
C. Iliadis, A. Champagne, J. José, S. Starrfield, P. Tupper, Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 142, 105 (2002)
W.R. Hix, M.S. Smith, S. Starrfield, A. Mezzacappa, D.L. Smith, Nucl. Phys. A 718, 620 (2003)
M. Wang, G. Audi, F.G. Kondev, W.J. Huang, S. Naimi, X. Xu, Chin. Phys. C 41, 030003 (2017)
S. Seuthe, C. Rolfs, U. Schröder, W.H. Schulte, E. Somorjai, H.P. Trautvetter, F.B. Waanders, Nucl. Phys. A 514, 471 (1990)
F. Stegmüller, C. Rolfs, S. Schmidt, W.H. Schulte, H.P. Trautvetter, R.W. Kavanagh, Nucl. Phys. A 601, 168 (1996)
A.F. Iyudin et al., Astron. Astrophys. 300, 422 (1995)
L.C. Haun, N.R. Roberson, Nucl. Phys. A 140, 333 (1970)
H. Nann, A. Saha, B.H. Wildenthal, Phys. Rev. C 23, 606 (1981)
S. Schmidt, C. Rolfs, W.H. Schulte, H.P. Trautvetter, R.W. Kavanagh, C. Hategan, S. Faber, B.D. Valnion, G. Graw, Nucl. Phys. A 591, 227 (1995)
R.L. Kozub, Phys. Rev. 172, 1078 (1968)
J. Källne, B. Fagerström, Phys. Scr. 11, 79 (1975)
D.W. Miller et al., Phys. Rev. C 20, 2008 (1979)
S. Kubono et al., Z. Phys. A 348, 59 (1994)
D.W. Bardayan et al., Phys. Rev. C 63, 065802 (2001)
R.B. Firestone, Nucl. Data Sheets 108, 1 (2007)
D.G. Jenkins et al., Phys. Rev. C 87, 064301 (2013)
P.D. Kunz. http://spot.colorado.edu/~kunz/(unpublished)
I.Y. Lee, Nucl. Phys. A 520, 641c (1990)
A. Krämer-Flecken, T. Morek, R.M. Lieder, W. Gast, G. Hebbinghaus, H.M. Jäger, W. Urban, Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 275, 333 (1989)
A. Saastamoinen et al., Phys. Rev. C 83, 045808 (2011)
O.S. Kirsebom et al., Phys. Rev. C 93, 025802 (2016)
M. Wiescher, K. Langanke, Z. Phys. A 325, 309 (1986)
V. Tripathi, S.L. Tabor, A. Volya, S.N. Liddick, P.C. Bender, N. Larson, C. Prokop, S. Suchyta, P.L. Tai, J.M. VonMoss, Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 262501 (2013)
R.J. Tighe, J.C. Batchelder, D.M. Moltz, T.J. Ognibene, M.W. Rowe, J. Cerny, B.A. Brown, Phys. Rev. C 52, R2298 (1995)
S.J. Jin et al., Phys. Rev. C 88, 035801 (2013)
R.H. Cyburt et al., Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 189, 240 (2010)
C. Iliadis, R. Longland, A.E. Champagne, A. Coc, R. Fitzgerald, Nucl. Phys. A 841, 31 (2010)
S. Starrfield, C. Iliadis, W.R. Hix, F.X. Timmes, W.M. Sparks, Astrophys. J. 692, 1532 (2009)
S. Starrfield, J.W. Truran, M.C. Wiescher, W.M. Sparks, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 296, 502 (1998)
J. José, M. Hernanz, Astrophys. J. 494, 680 (1998)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government Ministry of Education, Science, and Technology (MEST) Nos. NRF-2013M7A1A1075764, NRF-2016R1A5A1013277, and NRF-2019R1F1A1058370. This research was supported in part by the National Nuclear Security Administration under the Stewardship Science Academic Alliances program through the U.S.DOE Cooperative Agreement No. DE-FG52-08NA285. 52 with Rutgers University and Oak Ridge Associated Universities. This work was also supported in part by the Office of Nuclear Physics, Office of Science of the U.S.DOE under Contracts No. DE-FG02-96ER40955 with Tennessee Technological University, No. DE-FG02-96ER40983 with the University of Tennessee, and DE-AC-05-00OR22725 at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, and by the National Science Foundation under Contract No. PHY-1713857 with University of Notre Dame.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Philip J. Woods
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwag, M.S., Chae, K.Y., Ahn, S. et al. Spin assignments for \(^{23}\hbox {Mg}\) levels and the astrophysical \(^{22}\hbox {Na}(p,\gamma )^{23}\hbox {Mg}\) reaction. Eur. Phys. J. A 56, 108 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1140/epja/s10050-020-00106-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1140/epja/s10050-020-00106-y