Abstract
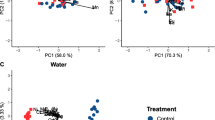
The research presented here was conducted to ascertain the effectiveness of recovery technologies in remediating a compromised marine environment. The multidisciplinary approach aims to integrate traditional chemical-physical analysis and to assess the biological parameters of Mytilus galloprovincialis within different experimental mesocosms (W, G, and B). In particular, this system was designed to reproduce sediment resuspension in a marine environment, which is thought to be one cause of contaminant release. The study combined morphological and ultrastructural observations with DNA damage assessment and mRNA expression of those genes involved in cellular stress responses. The tissues of mussels maintained in the polluted mesocosm showed a higher accumulation of Pb and Hg than in those maintained in restored mesocosm. This observation correlates well with mRNA expression of MT10 and data on DNA damage. The outcome of the biological evaluation consolidates the chemical characterization and supports the concept that the remediation method should be evaluated at an early stage, both to analytically determine the reduction of toxic components and to assess its ultimate impact on the biological system.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GAPDH :
-
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- β2M :
-
Beta-2 microglobulin
- HPRT1 :
-
Hypoxanthine phosphoribosyl transferase 1
- βActin :
-
Beta actin
- Tbp :
-
TATA box-binding protein
- RPL13 :
-
Ribosomal protein L13
- CAT :
-
Catalase
- CYP4Y1 :
-
Mytilus cytochrome P450
- GSTP1 :
-
Glutathione S-transferase
- HSP70 :
-
Heat Shock Protein 70
- HSP90 :
-
Heat Shock Protein 90
- MT10 :
-
Metallothionein 10
- SOD1 :
-
Superoxide dismutase 1
References
Auffret M, Rousseau S, Boutet I, Tanguy A, Baron J, Moraga D, Duchemin M (2006) A multiparametric approach for monitoring immunotoxic responses in mussels from contaminated sites in Western Mediterranea. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 63:393–405
Ausili A, Gabellini M, Cammarata G, Fattorini D, Benedetti M, Pisanelli B, Gorbi S, Regoli F (2008) Ecotoxicological and human health risk in a petrochemical district of southern Italy. Mar Environ Res 66:215–217
Baršienė J, Lazutka J, Šyvokienė J, Dedonyė V, Rybakovas A, Bjornstad A, Anders OK (2004) Analysis of micronuclei in blue mussels and fish from the Baltic and the North Seas. Environ Toxicol 19:365–371
Bebianno MJ, Lopes B, Guerra L, Hoarau P, Ferreira AM (2007) Glutathione S-tranferases and cytochrome P450 activities in Mytilus galloprovincialis from the south coast of Portugal: effect of abiotic factors. Environ Int 33:550–558
Bianchi N, Baccetti N, Leonzio C, Giovacchini P, Ancora S (2018) Temporal and geographical variations of mercury and selenium in eggs of Larus michahellis and Larus audouinii from central Mediterranean islands. Chem Ecol 34:595–609
Bolognesi C, Cirillo S (2014) Genotoxicity biomarkers in aquatic bioindicators. Curr Zool 60:273–284
Bolognesi C, Hayashi M (2011) Micronucleus assay in aquatic animals. Mutagenesis 26:205–213
Caliani I, Porcelloni S, Mori G, Frenzilli G, Ferraro M, Marsili L, Casini S, Fossi MC (2009) Genotoxic effects of produced waters in mosquito fish (Gambusia affinis). Ecotoxicology 18:75–80
Cappello T, Maisano M, D’Agata A, Natalotto A, Mauceri A, Fasulo S (2013) Effects of environmental pollution in caged mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis). Mar Environ Res 91:52–60
Cappello S, Genovese M, Denaro R, Santisi S, Volta A, Bonsignore M, Mancini G, Giuliano L, Genovese L, Yakimov MM (2015) Quick stimulation of Alcanivorax sp. by bioemulsificant EPS2003 on microcosm oil spill simulation. Braz J Microbiol 45(4):1317–1323
Corsolini S, Ancora S, Bianchi N, Mariotti G, Leonzio C, Christiansen JS (2014) Organotropism of persistent organic pollutants and heavy metals in the Greenland shark Somniosus microcephalus in NE Greenland. Mar Pollut Bull 87:381–387
Dermont G, Bergeron M, Mercier G, Richer-Lafleche M (2008) Soil washing for metal removal: a review of physical/chemical technologies and field applications. J Hazard Mater 152:1–31
Di Leonardo R, Bellanca A, Capotondi L, Cundy A, Neri R (2007) Possible impacts of Hg and PAH contamination on benthic foraminiferal assemblages: an example from the Sicilian coast, central Mediterranean. Sci Total Environ 388:168–183
Di Leonardo R, Bellanca A, Angelone M, Leonardi M, Neri R (2008) Impact of human activities on the central Mediterranean offshore: evidence from Hg distribution in box-core sediments from the Ionian see. Appl Geochem 23:3756–3766
Di Leonardo R, Adelfio G, Bellanca A, Chiodi M, Mazzola S (2014a) Analysis and assessment of trace element contamination in offshore sediments of the Augusta Bay (SE Sicily): a multivariate statistical approach based on canonical correlation analysis and mixture density estimation approach. J Sea Res 85:428–442
Di Leonardo R, Mazzola A, Tramati CD, Vaccaro A, Vizzini S (2014b) Highly contaminated areas as sources of pollution for adjoining ecosystems: the case of Augusta Bay (central Mediterranean). Mar Pollut Bull 89:417–426
Duchemin MB, Auffret M, Wessel N, Fortier M, Morin Y, Pellerin J, Fournier M (2008) Multiple experimental approaches of immunotoxic effects of mercury chloride in the blue mussel, Mytilus edulis, through in vivo, in tubo and in vitro exposures. Environ Pollut 153:416–423
Evangelou MWH, Ebel M, Schaeffer A (2007) Chelate assisted phytoextraction of heavy metals from soil. Effect, mechanism, toxicity, and fate of chelating agents. Chemosphere 68:989–1003
Fasulo S, Guerriero G, Cappello S, Colasanti M, Schettino T, Leonzio C, Mancini G, Gornati R (2015) The “SYSTEMS BIOLOGY” in the study of xenobiotic effects on marine organisms for evaluation of the environmental health status: biotechnological applications for potential recovery strategies. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 14:339–345
Fenech M, Chang WP, Kirsch-Volders M, Holland N, Bonassi S, Zeiger E (2003) HUMN project: detailed description of the scoring criteria for the cytokinesis-block micronucleus assay using isolated human lymphocyte cultures. Mutat Res 534:65–75
Ficco P, Cammarata G, Bacci E (2009) Procedimento n. 5010/08 RGNR. Relazione di consulenza tecnica in merito all’origine dei contaminanti presenti nei sedimenti ed alle strategie per il risanamento della Rada di Augusta. Per conto della Procura della Repubblica presso il Tribunale ordinario di Siracusa, p 131
Francesconi KA, Lenanton RCJ, Caputi N, Jones S (1997) Long-term study of mercury concentrations in fish following cessation of a mercury-containing discharge. Mar Environ Res 43:27–40
Gagnon C, Fisher N (1997) Bioavailability of sediment-bound methyl and inorganic Hg to a marine bivalve. Environ Sci Technol 31:993–998
Galloway T, Lewis C, Hagger J (2010) In: Timmis KN, Mc-Genity T, van der Meer JR, de Lorenzo V (eds) Handbook of hydrocarbon and lipid microbiology. Springer-Verlag, Berlin-Heidelberg
Garmendia L, Soto M, Vicario U, Kim Y, Cajaravillea MP, Marigómez I (2011) Application of a battery of biomarkers in mussel digestive gland to assess long-term effects of the Prestige oil spill in Galicia and Bay of Biscay: tissue-level biomarkers and histopathology. J Environ Monit 13:915–932
Gazzetta Ufficiale Della Repubblica Italiana (G.U.R.I.) (2011) Decreto Ministero dell’ambiente e della tutela del territorio e del mare 8 novembre 2010, n. 260.Regolamento recante i criteri tecnici per la classificazione dello stato dei corpi idrici superficiali, per la modifica delle norme tecniche del decreto legislativo 3aprile 2006, n. 152, recante norme in materia ambientale, predisposto ai sensi dell’articolo 75, comma 3, del medesimo decreto legislativo. Supplemento n. 31alla Gazzetta Ufficiale 7 febbraio 2011 n. 30
George SG, Coombs TL (1977) The effects of chelatin agents on the uptake and accumulation of cadmium by Mytilus edulis. Mar Biol 39:261–278
Gornati R, Papis E, Rimoldi S, Terova G, Saroglia M, Bernardini G (2004) Rearing density influences the expression of stress-related genes in sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax, L.). Gene 341:111–118
Gornati R, Maisano M, Pirrone C, Cappello T, Rossi F, Borgese M, Giannetto A, Cappello S, Mancini G, Bernardini G, Fasulo S (2019) Mesocosm system to evaluate BF-MBR efficacy in mitigating oily-wastewater discharges: an integrated study on Mytilus galloprovincialis. Mar Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-019-09923-9
Hund-Rinke K, Kördel W (2003) Underlying issues in bioaccessibility and bioavailability: experimental methods. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 56:52–62
Jha AN (2008) Ecotoxicological application and significance of the comet assay. Mutagenesis 23:207–222
Katagi T (2010) Bioconcentration, bioaccumulation, and metabolism of pesticides in aquatic organisms. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 204:1–132
Komárek M, Zeman J (2004) Dynamics of Cu, Zn, Cd, and Hg release from sediments at surface conditions. Bull Geosci 79:99–106 ISSN 1214–1119
Landrum PF, Harkey GA, Kukkonen J (1996) Evaluation of organic contaminant exposure in aquatic organisms: the significance of bioconcentration and bioaccumulation. In: Newman MC, Jagoe CH (eds) Ecotoxicology: a hierarchical treatment. Lewis Publishers, Tokyo
Li H, Ran Y (2012) Distribution and bioconcentration of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface water and fishes. Sci World J 2012:1–14
Long ER, MacDonald D, Smith S, Calder F (1995) Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environ Manag 19:81–97
Lorenzo JI, Beiras R, Mubiana VK, Blust R (2005) Copper uptake by Mytilus edulis in the presence of humic acids. Environ Toxicol Chem 24(4):973–980
Luciano A, Viotti P, Torretta V, Mancini G (2013) Numerical approach to modelling pulse-mode soil flushing on a Pb-contaminated soil. J Soils Sediments 13:43–55
MacDonald DD, Carr S, Clade FD, Long ED, Ingersoll CG (1996) Development and evaluation of sediment quality guidelines for Florida coastal waters. Ecotoxicology 5:253–278
Maisano M, Cappello T, Natalotto A, Vitale V, Parrino V, Giannetto A, Oliva S, Mancini G, Cappello S, Mauceri A, Fasulo S (2016) Effects of petrochemical contamination on caged marine mussels using a multi-biomarker approach: histological changes, neurotoxicity and hypoxic stress. Mar Environ Res 128:114–112
Manta DS, Bonsignore M, Oliveri E, Barra M, Tranchida G, Giaramita L, Mazzola S, Sprovieri M (2016) Fluxes and the mass balance of mercury in Augusta Bay (Sicily, southern Italy). Estuar Coast Shelf Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2016.08.013
Marigómez I, Soto M, Cajaraville MP, Angulo E, Giamberini L (2002) Cellular and subcellular distribution of metals in molluscs. Microsc Res Tech 56:358–392
Nolan C, Duke E, Lorenzon G, Sabbioni E, Marafante E (1984) Heavy metal uptake and intracellular binding in isolated gill preparations of Mytilus galloprovincialis L. Sci Total Environ 40:83–89
Odžak N, Zvonarić T, Gašpić ZK, Horvat M, Barić A (2000) Biomonitoring of Hg in the Kaštela Bay using transplanted mussels. Sci Total Environ 261:61–68
Palombella S, Pirrone C, Cherubino M, Valdatta L, Bernardini G, Gornati R (2017) Identification of reference genes for qPCR analysis during hASC long culture maintenance. PLoS One 12:1–12
Phillips DJH, Rainbow PS (1994) In: Chapman and Hall (ed) Biomonitoring of trace aquatic contaminants, 2nd edn. London, Springer
Pirrone C, Rossi F, Cappello S, Borgese M, Mancini G, Bernardini G, Gornati R (2018) Evaluation of biomarkers in Mytilus galloprovincialis as an integrated measure of BF-MBR efficiency in mitigating the impact of oily-wastewater discharge to marine environment: a microcosm approach. Aquat Toxicol 198:49–62
Poblete-Naredo I, Albores A (2016) Molecular biomarkers to assess health risks due to environmental contaminants exposure. Biomédica 36:309–335
Raftopoulou EK, Dimitriadis VK (2011) Comparative study of the accumulation and detoxification of Cu (essential metal) and Hg (nonessential metal) in the digestive gland and gills of mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis, using analytical and histochemical techniques. Chemosphere 83:1155–1165
Rainbow PS (1993) In: Dallinger R, Rainbow PS (eds) The significance of trace metal concentrations in marine invertebrates Lewis Publ, Boca Raton
Randall PM, Chattopadhyay S (2004) Advances in encapsulation technologies for the management of mercury-contaminated hazardous wastes. J Hazard Mater B 114:211–223
Randall PM, Chattopadhyay S (2013) Mercury contaminated sediment sites - an evaluation of remedial options. Environ Res 125:131–149
Rivaro P, Ianni C, Abelmoschi ML, Soggia F, Frache R (2009) Laboratory studies on the accumulation of inorganic mercury and methylmercury by the mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis, Lam) in relation to the presence of sediment. Toxicol Environ Chem 91(6):1159–1173
Rossi F, Bernardini G, Bonfanti P, Colombo A, Prati M, Gornati R (2009) Effects of TCDD on spermatogenesis related Factor-2 (SRF-2): gene expression in Xenopus. Toxicol Lett 191:189–194
Rossi F, Palombella S, Pirrone C, Mancini G, Bernardini G, Gornati R (2016) Evaluation of tissue morphology and gene expression as biomarkers of pollution in mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis caging experiment. Aquat Toxicol 181:57–66
Sager DR (2002) Long-term variation in mercury concentrations in estuarine organisms with changes in releases into Lavaca Bay, Texas. Mar Pollut Bull 44:807–815
Satyro S, Race M, Marotta R, Dezotti M, Spasiano D, Mancini G (2014) Simulated solar photocatalytic processes for the simultaneous removal of EDDS, Cu(II), Fe(III) and Zn(II) in synthetic and real contaminated soil washing solutions. J Environ Chem Eng 2(4):1969–1979
Speciale A, Zena R, Calabrò C, Bertuccio C, Aragona M, Saija A, Trombetta D, Cimino F, Lo Cascio P (2018) Experimental exposure of blue mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) to high levels of benzo[α]pyrene and possible implications for human health. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 150:96–103
Sprovieri M, Oliveri E, Di Leonardo R, Romano E, Ausili A, Gabellini M, Barra M, Tranchida G, Bellanca A, Neri R, Budillon F, Saggiomo R, Mazzola S, Saggiomo V (2011) The key role played by the Augusta basin (southern Italy) in the mercury contamination of the Mediterranean Sea. J Environ Monit 13(6):1753–1760
Subirés-Munoz JD, García-Rubio A, Vereda-Alonso C, Gómez-Lahoz C, Rodríguez-Maroto JM, García-Herruzo F, Paz-García JM (2011) Feasibility study of the use of different extractant agents in the remediation of a mercury contaminated soil from Almaden. Sep Purif Technol 79:151–156
Tchounwou PB, Yedjou CG, Patlolla AK, Sutton DJ (2012) Heavy metals toxicity and the environment. Exp Suppl 101:133–164
Tunca E, Aydın M, Şahin ÜA (2018) An ecological risk investigation of marine sediment from the northern Mediterranean coasts (Aegean Sea) using multiple methods of pollution determination. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:7487–7503
U.S. EPA (1997) Technology alternatives for the remediation of soils contaminated with As, Cd, Cr, Hg, and Pb. EPA/540/S-97/500, US. EPA Office of Research and Development, Cincinnati, OH. https://semspub.epa.gov/work/05/921799.pdf. Accessed 25 March 2020
U.S. EPA (2007) Treatment technologies for mercury in soil, waste and water, EPA-542-R-07-003. https://clu-in.org/download/remed/542r07003.pdf. Accessed 25 March 2020
Vodyanitskii YN (2016) Standards for the contents of heavy metals in soils of some states. Ann Agrar Sci 14:257–263
Wang WX, Fisher NS (1999) Delineating metal accumulation pathways for marine invertebrates. Sci Tot Environ 237-238:459–472
Wang J, Feng X, Anderson CW, Xing Y, Shang L (2012) Remediation of mercury contaminated sites – a review. J Hazard Mater 221-222:1–18
Wasay S, Arnfalk P, Tokunaga S (1995) Remediation of a soil polluted by mercury with acidic potassium iodide. J Hazard Mater 44:93–102
Zang F, Wang S, Nan Z, Ma J, Yu Wang Y, Chen Y, Zhang Q, Lil Y (2017) Influence of pH on the release and chemical fractionation of heavy metals in sediment from a suburban drainage stream in an arid mine-based oasis. J Soils Sediments 17:2524–2536
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Silvia Palombella and Ilaria Armenia for their help during the mussel sampling campaign. The authors gratefully acknowledge “Centro Grandi Attrezzature per la Ricerca Biomedica” University of Insubria for making instruments available and for the hospitality. Marina Borgese is a PhD student of the Biotechnology, Biosciences and Surgical Technology course at Università degli Studi dell’Insubria.
Funding
This research was supported by grants of the Italian Ministry on Systems Biology: PRIN (Prot. T7 2010ARBL001/008) and FAR (Fondo comune di Ateneo per la Ricerca 2016 to RG and GB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ancora, S., Rossi, F., Borgese, M. et al. Assessing the Effect of Contaminated and Restored Marine Sediments in Different Experimental Mesocosms Using an Integrated Approach and Mytilus galloprovincialis as a Model. Mar Biotechnol 22, 411–422 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-020-09961-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-020-09961-8