Abstract
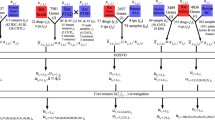
DrugMatrix is a valuable toxicogenomic dataset, which provides in vivo transcriptome data corresponding to hundreds of chemical drugs. However, the relationships between drugs and how those drugs affect the biological process are still unknown. The high dimensionality of the microarray data hinders its application. The aims of this study are to (1) represent the transcriptome data by lower-dimensional vectors, (2) compare drug similarity, (3) represent drug combinations by adding vectors and (4) infer drug mechanism of action (MoA) and genotoxicity features. We borrowed the latent semantic analysis (LSA) technique from natural language processing to represent treatments (drugs with multiple concentrations and time points) by dense vectors, each dimension of which is an orthogonal biological feature. The gProfiler enrichment tool was used for the 100-dimensional vector feature annotation. The similarity between treatments vectors was calculated by the cosine function. Adding vectors may represent drug combinations, treatment times or treatment doses that are not presented in the original data. Drug–drug interaction pairs had a higher similarity than random drug pairs in the hepatocyte data. The vector features helped to reveal the MoA. Differential feature expression was also implicated for genotoxic and non-genotoxic carcinogens. An easy-to-use Web tool was developed by Shiny Web application framework for the exploration of treatment similarities and drug combinations (https://bioinformatics.fafu.edu.cn/drugmatrix/). We represented treatments by vectors and provided a tool that is useful for hypothesis generation in toxicogenomic, such as drug similarity, drug repurposing, combination therapy and MoA.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets analyzed are available in the NCBI GEO repository, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE57822.
References
Asgari E, Mofrad MR (2015) Continuous distributed representation of biological sequences for deep proteomics and genomics. PLoS ONE 10:e0141287
Attia TZ, Yamashita T, Miyamoto M, Koizumi A, Yasuhara Y, Node J, Erikawa Y, Komiyama Y, Horii C, Yamada M, Omar MA, Abdelmageed OH, Derayea SM, Uno T (2012) Comparison of cytochrome p450 mediated metabolism of three central nervous system acting drugs. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 60:1544–1549
Bakhiya N, Abraham K, Gurtler R, Appel KE, Lampen A (2011) Toxicological assessment of 3-chloropropane-1,2-diol and glycidol fatty acid esters in food. Mol Nutr Food Res 55:509–521
Barrett T, Troup DB, Wilhite SE, Ledoux P, Rudnev D, Evangelista C, Kim IF, Soboleva A, Tomashevsky M, Edgar R (2007) NCBI GEO: mining tens of millions of expression profiles–database and tools update. Nucleic Acids Res 35:D760–765
Catena C, Colussi G, Nait F, Martinis F, Pezzutto F, Sechi LA (2014) Aldosterone and the heart: still an unresolved issue? Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 5:168
Chang W, Cheng J, Allaire JJ, Xie Y, McPherson J (2015) Shiny: web application framework for R. R package version 0.11 1:106
Chen JS, Lin SY, Tso WL, Yeh GC, Lee WS, Tseng H, Chen LC, Ho YS (2006) Checkpoint kinase 1-mediated phosphorylation of Cdc25C and bad proteins are involved in antitumor effects of loratadine-induced G2/M phase cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis. Mol Carcinog 45:461–478
Chen HH, Cheng PW, Ho WY, Lu PJ, Lai CC, Tseng YM, Fang HC, Sun GC, Hsiao M, Liu CP, Tseng CJ (2016) Renal denervation improves the baroreflex and GABA system in chronic kidney disease-induced hypertension. Sci Rep 6:38447
Cheng F, Kovacs IA, Barabasi AL (2019) Network-based prediction of drug combinations. Nat Commun 10:1197
Conklin DJ, Boor PJ (1998) Allylamine cardiovascular toxicity: evidence for aberrant vasoreactivity in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 148:245–251
EPA (2006) Toxicological review of dichlorobenzenes. U.S Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC
Ganter B, Tugendreich S, Pearson CI, Ayanoglu E, Baumhueter S, Bostian KA, Brady L, Browne LJ, Calvin JT, Day GJ, Breckenridge N, Dunlea S, Eynon BP, Furness LM, Ferng J, Fielden MR, Fujimoto SY, Gong L, Hu C, Idury R, Judo MS, Kolaja KL, Lee MD, McSorley C, Minor JM, Nair RV, Natsoulis G, Nguyen P, Nicholson SM, Pham H, Roter AH, Sun D, Tan S, Thode S, Tolley AM, Vladimirova A, Yang J, Zhou Z, Jarnagin K (2005) Development of a large-scale chemogenomics database to improve drug candidate selection and to understand mechanisms of chemical toxicity and action. J Biotechnol 119:219–244
Ganter B, Snyder RD, Halbert DN, Lee MD (2006) Toxicogenomics in drug discovery and development: mechanistic analysis of compound/class-dependent effects using the DrugMatrix database. Pharmacogenomics 7:1025–1044
Gilron I, Jensen TS, Dickenson AH (2013) Combination pharmacotherapy for management of chronic pain: from bench to bedside. Lancet Neurol 12:1084–1095
Gray JM, Schrock S, Bishop M (1993) Estrogens and antiestrogens: actions and interactions with fluphenazine on food intake and body weight in rats. Am J Physiol 264:R1214–1218
Guo W, Calixto CPG, Tzioutziou N, Lin P, Waugh R, Brown JWS, Zhang R (2017) Evaluation and improvement of the regulatory inference for large co-expression networks with limited sample size. BMC Syst Biol 11:62
Gusenleitner D, Auerbach SS, Melia T, Gomez HF, Sherr DH, Monti S (2014) Genomic models of short-term exposure accurately predict long-term chemical carcinogenicity and identify putative mechanisms of action. PLoS ONE 9:e102579
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144:646–674
Hennekens CH, Dyken ML, Fuster V (1997) Aspirin as a therapeutic agent in cardiovascular disease: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation 96:2751–2753
Hey JA, Affrime M, Cobert B, Kreutner W, Cuss FM (1999) Cardiovascular profile of loratadine. Clin Exp Allergy 29(Suppl 3):197–199
High JP, Hassert GL Jr, Rubin B, Piala JJ, Burke JC, Craver BN (1960) Pharmacology of fluphenazine (prolixin). Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2:540–552
Huang J, Niu C, Green CD, Yang L, Mei H, Han JD (2013) Systematic prediction of pharmacodynamic drug–drug interactions through protein–protein-interaction network. PLoS Comput Biol 9:e1002998
Keiser MJ, Setola V, Irwin JJ, Laggner C, Abbas AI, Hufeisen SJ, Jensen NH, Kuijer MB, Matos RC, Tran TB, Whaley R, Glennon RA, Hert J, Thomas KL, Edwards DD, Shoichet BK, Roth BL (2009) Predicting new molecular targets for known drugs. Nature 462:175–181
Kong VK, Irwin MG (2007) Gabapentin: a multimodal perioperative drug? Br J Anaesth 99:775–786
Kopera H (1978) Anticholinergic and blood pressure effects of mianserin, amitriptyline and placebo. Br J Clin Pharmacol 5(Suppl 1):29S–34S
Law V, Knox C, Djoumbou Y, Jewison T, Guo AC, Liu Y, Maciejewski A, Arndt D, Wilson M, Neveu V, Tang A, Gabriel G, Ly C, Adamjee S, Dame ZT, Han B, Zhou Y, Wishart DS (2014) DrugBank 4.0: shedding new light on drug metabolism. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D1091–1097
Liu Y, Ji X, Tong WWL, Askhatova D, Yang T, Cheng H, Wang Y, Shi J (2018) Engineering multifunctional RNAi nanomedicine to concurrently target cancer hallmarks for combinatorial therapy. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 57:1510–1513
Meng HP, Maddaford TG, Pierce GN (1993) Effect of amiloride and selected analogues on postischemic recovery of cardiac contractile function. Am J Physiol 264:H1831–1835
Mikolov T, Sutskever I, Chen K, Corrado GS, Dean J (2013) Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 3111–3119
Mladenka P, Applova L, Patocka J, Costa VM, Remiao F, Pourova J, Mladenka A, Karlickova J, Jahodar L, Voprsalova M, Varner KJ, Sterba M, Tox OER, Researchers CHK, Collaborators (2018) Comprehensive review of cardiovascular toxicity of drugs and related agents. Med Res Rev 38:1332–1403
Mulas F, Li A, Sherr DH, Monti S (2017) Network-based analysis of transcriptional profiles from chemical perturbations experiments. BMC Bioinform 18:130
Perez LO, Gonzalez-Jose R, Garcia PP (2016) Prediction of non-genotoxic carcinogenicity based on genetic profiles of short term exposure assays. Toxicol Res 32:289–300
Reimand J, Arak T, Adler P, Kolberg L, Reisberg S, Peterson H, Vilo J (2016) g:Profiler-a web server for functional interpretation of gene lists (2016 update). Nucleic Acids Res 44:W83–89
Romer M, Backert L, Eichner J, Zell A (2014) ToxDBScan: large-scale similarity screening of toxicological databases for drug candidates. Int J Mol Sci 15:19037–19055
Rose FV, Barnea ER (1996) Response of human ovarian carcinoma cell lines to antiprogestin mifepristone. Oncogene 12:999–1003
Rundle-Thiele D, Head R, Cosgrove L, Martin JH (2016) Repurposing some older drugs that cross the blood-brain barrier and have potential anticancer activity to provide new treatment options for glioblastoma. Br J Clin Pharmacol 81:199–209
Sassa S (2006) Biological implications of heme metabolism. J Clin Biochem Nutr 38:138–155
Shen Y, Rahman M, Piccolo SR, Gusenleitner D, El-Chaar NN, Cheng L, Monti S, Bild AH, Johnson WE (2015) ASSIGN: context-specific genomic profiling of multiple heterogeneous biological pathways. Bioinformatics 31:1745–1753
Team RC (2013) R: a language and environment for statistical computing
Tremont-Lukats IW, Gilbert MR (2003) Advances in molecular therapies in patients with brain tumors. Cancer Control 10:125–137
Weichenthal S, Kulka R, Belisle P, Joseph L, Dubeau A, Martin C, Wang D, Dales R (2012) Personal exposure to specific volatile organic compounds and acute changes in lung function and heart rate variability among urban cyclists. Environ Res 118:118–123
Zhernovkov V, Santra T, Cassidy H, Rukhlenko O, Matallanas D, Krstic A, Kolch W, Lobaskin V, Kholodenko BN (2019) An integrative computational approach for a prioritization of key transcription regulators associated with nanomaterial-induced toxicity. Toxicol Sci 171:303–314
Zhou Q, Tang P, Liu S, Pan J, Yan Q, Zhang SC (2018) Learning atoms for materials discovery. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115:E6411–E6417
Acknowledgements
We thank Catherine Perfect, MA (Cantab), from Liwen Bianji, Edanz Editing China (www.liwenbianji.cn/ac), for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the Outstanding Youth Research Training Program of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (Grant No. xjq201818), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81502091).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by Stefan Hohmann.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, L., Wan, L., He, H. et al. Drug vector representation: a tool for drug similarity analysis. Mol Genet Genomics 295, 1055–1062 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-020-01665-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-020-01665-x