Abstract
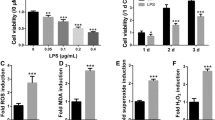
Periodontitis can cause damage to dental support tissue and affect the function of periodontal ligament cells. Rutin, a common flavonoid, plays a key role in anti-inflammatory responses, tissue repair and bone development. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of rutin on the oxidative stress, proliferation, and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells (PDLSCs) in an inflammatory environment and the underlying mechanism. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was used to stimulate PDLSCs to mimic an inflammatory environment model. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels were detected by the dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) probe and the oxidative stress factors were tested by an oxidative stress factor detection kit. Moreover, the proliferation of PDLSCs was evaluated by cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) assay. In addition, the osteogenic differentiation of PDLSCs was determined by alkaline phosphatase (ALP) staining, ALP activity test, alizarin red staining, and alizarin red semi-quantitative analysis. Furthermore, the protein levels of AKT and p-AKT were detected by Western blot. The results showed that rutin inhibited the release of ROS and increased the secretion of oxidative stress factors [superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione (GSH)] and promoted the proliferation of PDLSCs in an inflammatory environment. Moreover, rutin upregulated ALP activity and enhanced the number of mineralized nodules. Conversely, the use of LY294002 (an inhibitor of PI3K) blocked the activation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and prevented the beneficial effects of rutin. In conclusion, rutin promoted the antioxidative stress ability, proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of PDLSCs through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in LPS-induced inflammatory environment.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Naim AB, Alghamdi AA, Algandaby MM, Al-Abbasi FA, Al-Abd AM, Eid BG, Abdallah HM, El-Halawany AM (2018) Rutin Isolated from Chrozophora tinctoria Enhances Bone Cell Proliferation and Ossification Markers. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018:1–10
Bartold PM, McCulloch CA, Narayanan AS, Pitaru S (2010) Tissue engineering: a new paradigm for periodontal regeneration based on molecular and cell biology. Periodontology 24:253–269
Ben Sghaier M, Pagano A, Mousslim M, Ammari Y, Kovacic H, Luis J (2016) Rutin inhibits proliferation, attenuates superoxide production and decreases adhesion and migration of human cancerous cells. Biomed Pharmacother 84:1972–1978
Benqué E, Zahedi S, Brocard D, Oscaby F, Justumus P, Brunel G (2010) Guided tissue regeneration using a collagen membrane in chronic adult and rapidly progressive periodontitis patients in the treatment of 3-wall intrabony defects. J Clin Periodontol 24:544–549
Caglayan C, Kandemir FM, Darendelioğlu E, Yıldırım S, Kucukler S, Dortbudak MB (2019) Rutin ameliorates mercuric chloride-induced hepatotoxicity in rats via interfering with oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. J Trace Elem Med Biol 56:60–68
Chen FM, Sun HH, Lu H, Yu Q (2012) Stem cell-delivery therapeutics for periodontal tissue regeneration. Biomaterials 33:6320–6344
Chen H, Miao Q, Geng M, Liu J, Hu Y, Tian L, Pan J, Yang Y (2013) Anti-tumor effect of rutin on human neuroblastoma cell lines through inducing G2/M cell cycle arrest and promoting apoptosis. Scientific World Journal 2013:269165
Chen X, Hu C, Wang G, Li L, Kong X, Ding Y, Jin Y (2013) Nuclear factor-B modulates osteogenesis of periodontal ligament stem cells through competition with β-catenin signaling in inflammatory microenvironments. Cell Death Dis 4:e510
Dabrowski FA, Burdzinska A, Kulesza A, Sladowska A, Zolocinska A, Gala K, Paczek L, Wielgos M (2017) Comparison of the paracrine activity of mesenchymal stem cells derived from human umbilical cord, amniotic membrane and adipose tissue. J Obst Gynaecol Res 43:1758–1768
Djordjevic A, Spasic S, Jovanovic-Galovic A, Djordjevic R, Grubor-Lajsic G (2004) Oxidative stress in diabetic pregnancy: SOD, CAT and GSH-Px activity and lipid peroxidation products. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 16:367–372
Donahue HJ, Li Z, Zhou Z, Yellowley CE (2000) Differentiation of human fetal osteoblastic cells and gap junctional intercellular communication. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 278:C315–C322
Etienne D (2010) Locally delivered antimicrobials for the treatment of chronic periodontitis. Oral Dis 9:45–50
Feissner RF, Skalska J, Gaum WE, Sheu SS (2011) Crosstalk signaling between mitochondrial Ca2+ and ROS. Front Biosci 14:1197–1218
Grenier D, Mayrand D (1987) Functional characterization of extracellular vesicles produced by Bacteroides gingivalis. Infect Immun 55:111–117
Guardia T, Rotelli AE, Juarez AO, Pelzer LE (2001) Anti-inflammatory properties of plant flavonoids. Effects of rutin, quercetin and hesperidin on adjuvant arthritis in rat. Farmaco 56:683–687
Hessle L, Johnson KA, Anderson HC, Narisawa S, Sali A, Goding JW, Terkeltaub R, Millan JL (2002) Tissue-nonspecific alkaline phosphatase and plasma cell membrane glycoprotein-1 are central antagonistic regulators of bone mineralization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:9445–9449
Huang J, Cai X, Ou Y, Fan L, Zhou Y, Wang Y (2019) Protective roles of FICZ and aryl hydrocarbon receptor axis on alveolar bone loss and inflammation in experimental periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol 46:882–893
Hyun H, Park H, Jeong J, Kim J, Kim H, Oh HI, Hwang HS, Kim HH (2014) Effects of watercress containing rutin and rutin alone on the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human osteoblast-like MG-63 cells. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 18:347–352
Ip YT, Davis RJ (1998) Signal transduction by the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) -- from inflammation to development. Curr Opin Cell Biol 10:205–219
Ji RR, Samad TA, Jin SX, Schmoll R, Woolf CJ (2002) p38 MAPK activation by NGF in primary sensory neurons after inflammation increases TRPV1 levels and maintains heat hyperalgesia. Neuron 36:57–68
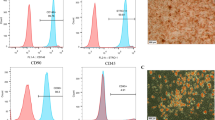
Kim K, Yi T, Yun JH (2016) Maintained stemness of human periodontal ligament stem cells isolated following prolonged storage of extracted teeth. J Periodontol 87:1–16
Langer R (2000) Tissue engineering. Science 260:920–926
Layman DL, Diedrich DL (1987) Growth inhibitory effects of endotoxins from Bacteroides gingivalis and intermedius on human gingival fibroblasts in vitro. J Periodontol 58:387–392
Lee JH, Choi JK, Kim SH, Cho KH, Kim YT, Choi SH, Jung UW (2017) Association between periodontal flap surgery for periodontitis and vasculogenic erectile dysfunction in Koreans. J Periodontal Implant Sci 47:96–105
Li C, Li B, Dong Z, Gao L, He X, Liao L, Hu C, Wang Q, Jin Y (2014) Lipopolysaccharide differentially affects the osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells through Toll-like receptor 4 mediated nuclear factor κB pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther 5:67
Li L, Sun W, Wu T, Lu R, Shi B (2016) Caffeic acid phenethyl ester attenuates lipopolysaccharide-stimulated proinflammatory responses in human gingival fibroblasts via NF-κB and PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol 794:61–68
Liu L, Liu Y, Cui J, Liu H, Liu YB, Qiao WL, Sun H, Yan CD (2013) Oxidative stress induces gastric submucosal arteriolar dysfunction in the elderly. World J Gastroenterol 19:9439–9446
Lv L, Yao Y, Zhao G, Zhu G (2018) Rutin inhibits coronary heart disease through ERK1/2 and Akt signaling in a porcine model. Exp Ther Med 15:506–512
Maeda H, Tomokiyo A, Fujii S, Wada N, Akamine A (2011) Promise of periodontal ligament stem cells in regeneration of periodontium. Stem Cell Res Ther 2:1–3
Nafees S, Rashid S, Ali N, Hasan SK, Sultana S (2015) Rutin ameliorates cyclophosphamide induced oxidative stress and inflammation in Wistar rats: role of NFκB/MAPK pathway. Chem Biol Interact 231:98–107
Noh MK, Jung M, Kim SH, Lee SR, Park KH, Kim DH, Kim HH, Park YG (2013) Assessment of IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α levels in the gingival tissue of patients with periodontitis. Exp Ther Med 6:847–851
Pastore S, Lulli D, Fidanza P, Potapovich AI, Kostyuk VA, De Luca C, Mikhal’chik E, Korkina LG (2012) Plant polyphenols regulate chemokine expression and tissue repair in human keratinocytes through interaction with cytoplasmic and nuclear components of epidermal growth factor receptor system. Antioxid Redox Signal 16:314–328
Pihlstrom BL, Michalowicz BS, Johnson NW (2005) Periodontal diseases. Lancet 366:1809–1820
Porta C, Paglino C, Mosca A (2014) Targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling in cancer. Front Oncol 4:64
Rong R, Xijun X (2015) Erythropoietin pretreatment suppresses inflammation by activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Exp Ther Med 10:413–418
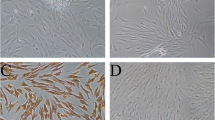
Seo BM, Miura M, Gronthos S, Mark Bartold P, Batouli S, Brahim J, Young M, Robey PG, Wang CY, Shi S (2004) Investigation of multipotent postnatal stem cells from human periodontal ligament. Lancet 364:149–155
Srivastava KC, Austin RD, Shrivastava D, Sethupathy S, Rajesh S (2012) A case control study to evaluate oxidative stress in plasma samples of oral malignancy. Contemp Clin Dent 3:271–276
Srivastava S, Bankar R, Roy P (2013) Assessment of the role of flavonoids for inducing osteoblast differentiation in isolated mouse bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells. Phytomedicine 20:683–690
Sun J, Wang H, Liu B, Shi W, Shi J, Zhang Z, Xing J (2017) Rutin attenuates H2O2-induced oxidation damage and apoptosis in Leydig cells by activating PI3K/Akt signal pathways. Biomed Pharmacother 88:500–506
Wang H, Mao Y, Zhang B, Wang T, Li F, Fu S, Xue Y, Yang T, Wen X, Ding Y, Duan X (2010) Chloride channel clc-3 promotion of osteogenic differentiation through runx2. J Cell Biochem 111:49–58
Węglarz L, Wawszczyk J, Orchel A, Jaworska-Kik M, Dzierżewicz Z (2007) Phytic acid modulates in vitro IL-8 and IL-6 release from colonic epithelial cells stimulated with LPS and IL-1β. Dig Dis Sci 52:93–102
Xiao Y, Wei R, Yuan Z, Lan X, Kuang J, Hu D, Song Y, Luo J (2019) Rutin suppresses FNDC1 expression in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to inhibit postmenopausal osteoporosis. Am J Transl Res 11:6680–6690
Xu XY, He XT, Wang J, Li X, Xia Y, Tan YZ, Chen FM (2019) Role of the P2 × 7 receptor in inflammation-mediated changes in the osteogenesis of periodontal ligament stem cells. Cell Death Dis 10:20
Zhang Y, Xing Y, Jia L, Ji Y, Zhao B, Wen Y, Xu X (2018) An in vitro comparative study of multisource derived human mesenchymal stem cells for bone tissue engineering. Stem Cells Dev 27:1634–1635
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Construction Engineering Special Fund of Taishan Scholars (Grant Number ts201511106), Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (Grant Number ZR2017MH031), and Fundamental Research Funds of Shandong University (Grant Number 2018GN024).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, B., Zhang, W., Xiong, Y. et al. Effects of rutin on the oxidative stress, proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells in LPS-induced inflammatory environment and the underlying mechanism. J Mol Hist 51, 161–171 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-020-09866-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-020-09866-9