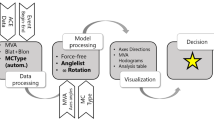
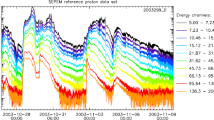
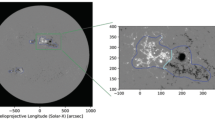
Abstract
The aim of this article is to study the minimum variance analysis (MVA) degeneration problem based on the variance space geometry. We propose a mathematical metric to evaluate the separation of the eigenvalues. In the MVA method, a variance space is obtained geometrically using an ellipsoid where the axes are equal to the square root of the eigenvalues of the covariance matrix. The metric is defined as the product between the geometric flattening of the ellipsoid with respect to the three axes. In this article, we present a statistical analysis applied to the distribution of the eigenvalue ratios and the mathematical metric focussed on the study of several interplanetary coronal mass ejections with and without magnetic clouds (MCs). The results show the non-applicability of the ratio between the intermediate and minimum eigenvalues, as well as that around \(90\%\) of MC events have values in the \([4.5,19.5]\) range for the defined metric. Our metric is compared with others and we show its robustness in indicating the usefulness of the MVA method to identify the axes of MCs.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
http://www.srl.caltech.edu/ACE/ASC/level2/index.html accessed on May 20, 2019.
http://www.srl.caltech.edu/ACE/ASC/DATA/level3/icmetable2.htm accessed on May 20, 2019.
https://wind.gsfc.nasa.gov/mfi/mag_cloud_pub1.html accessed on October 01, 2019.
https://cdaweb.gsfc.nasa.gov/istp_public/ accessed on October 01, 2019.
References
Abdi, H., Williams, L.J.: 2010, Principal component analysis. Wires Comput. Stat.2(4), 433. DOI .
Bothmer, V., Rust, D.M.: 1997, The field configuration of magnetic clouds and the solar cycle. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union99, 139. DOI . ADS .
Bothmer, V., Schwenn, R.: 1998, The structure and origin of magnetic clouds in the solar wind. Ann. Geophys.16, 1. DOI . ADS .
Burlaga, L.F.: 1988, Magnetic clouds and force-free fields with constant alpha. J. Geophys. Res.93, 7217. DOI . ADS .
Burlaga, L.F.E.: 1991, Magnetic clouds. In: Schwenn, R., Marsch, E. (eds.) Physics of the Inner Heliosphere II21, 152. DOI . ADS .
Burlaga, L., Sittler, E., Mariani, F., Schwenn, R.: 1981, Magnetic loop behind an interplanetary shock - Voyager, Helios, and IMP 8 observations. J. Geophys. Res.86, 6673. DOI . ADS .
Cid, C., Hidalgo, M.A., Nieves-Chinchilla, T., Sequeiros, J., Viñas, A.F.: 2002, Plasma and magnetic field inside magnetic clouds: A global study. Solar Phys.207(1), 187. DOI . ADS .
Dal Lago, A., Gonzalez, W.D., de Gonzalez, A.L.C., Vieira, L.E.A.: 2001, Compression of magnetic clouds in interplanetary space and increase in their geoeffectiveness. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys.63(5), 451. DOI . ADS .
Démoulin, P., Dasso, S., Janvier, M.: 2018, Exploring the biases of a new method based on minimum variance for interplanetary magnetic clouds. Astron. Astrophys.619, A139. DOI . ADS .
Dong, D., Fang, P., Bock, Y., Webb, F., Prawirodirdjo, L., Kedar, S., Jamason, P.: 2006, Spatiotemporal filtering using principal component analysis and Karhunen-Loeve expansion approaches for regional GPS network analysis. J. Geophys. Res.111(B3), B03405. DOI . ADS .
Echer, E., Alves, M.V., Gonzalez, W.D.: 2005, A statistical study of magnetic cloud parameters and geoeffectiveness. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys.67(10), 839. DOI . ADS .
Farrugia, C.J., Osherovich, V.A., Burlaga, L.F.: 1995, Magnetic flux rope versus the spheromak as models for interplanetary magnetic clouds. J. Geophys. Res.100(A7), 12293. DOI . ADS .
Goldstein, H.: 1983, On the field configuration in magnetic clouds. In: NASA Conf. Pub.228. ADS .
Gonzalez, W.D., Tsurutani, B.T.: 1987, Criteria of interplanetary parameters causing intense magnetic storms (D\(_{st}<\)-100 nT). Planet. Space Sci.35(9), 1101. DOI . ADS .
Gulisano, A.M., Dasso, S., Mandrini, C.H., Démoulin, P.: 2007, Estimation of the bias of the minimum variance technique in the determination of magnetic clouds global quantities and orientation. Adv. Space Res.40, 1881. DOI . ADS .
Hunter, J.D.: 2007, Matplotlib: A 2D graphics environment. Comput. Sci. Eng.9(3), 90. DOI . ADS .
Huttunen, K.E.J., Schwenn, R., Bothmer, V., Koskinen, H.E.J.: 2005, Properties and geoeffectiveness of magnetic clouds in the rising, maximum and early declining phases of solar cycle 23. Ann. Geophys.23, 625. DOI . ADS .
Karney, C.F.F., Deakin, R.E.: 2010, F.W. Bessel (1825): The calculation of longitude and latitude from geodesic measurements. Astron. Nachr.331, 852. DOI . ADS .
Kelly, P.M.: 1977, Solar influence on North Atlantic mean sea level pressure. Nature269(5626), 320. DOI . ADS .
Klein, L.W., Burlaga, L.F.: 1982, Interplanetary magnetic clouds at 1 AU. J. Geophys. Res.87(A2), 613. DOI . ADS .
Lepping, R.P., Behannon, K.W.: 1980, Magnetic field directional discontinuities: 1. Minimum variance errors. J. Geophys. Res.85(A9), 4695. DOI . ADS .
Lepping, R.P., Burlaga, L.F., Jones, J.A.: 1990, Magnetic field structure of interplanetary magnetic clouds at 1 AU. J. Geophys. Res.95, 11957. DOI . ADS .
Lugaz, N., Farrugia, C.J.: 2014, A new class of complex ejecta resulting from the interaction of two CMEs and its expected geoeffectiveness. Geophys. Res. Lett.41, 769. DOI . ADS .
Lui, A.T.Y.: 2011, Grad-Shafranov reconstruction of magnetic flux ropes in the near-Earth space. Space Sci. Rev.158, 43. DOI . ADS .
Marubashi, K.: 1986, Structure of the interplanetary magnetic clouds and their solar origins. Adv. Space Res.6, 335. DOI . ADS .
Marubashi, K., Lepping, R.P.: 2007, Long-duration magnetic clouds: A comparison of analyses using torus- and cylinder-shaped flux rope models. Ann. Geophys.25, 2453. DOI . ADS .
McKinney, W.: 2010, Data structures for statistical computing in python. In: van der Walt, S., Millman, J. (eds.) Proc. 9th Python Sci. Conf., 51.
Mulligan, T., Russell, C.T.: 2001, Multispacecraft modeling of the flux rope structure of interplanetary coronal mass ejections: Cylindrically symmetric versus nonsymmetric topologies. J. Geophys. Res.106(A6), 10581. DOI . ADS .
Nieves-Chinchilla, T., Hidalgo, M.A., Sequeiros, J.: 2005, Magnetic clouds observed at 1 Au during the period 2000-2003. Solar Phys.232, 105. DOI . ADS .
Ojeda González, A., Mendes, O., Calzadilla, M.A., Domingues, M.O.: 2013, Spatio-temporal entropy analysis of the magnetic field to help magnetic cloud characterization. J. Geophys. Res.118(9), 5403. DOI . ADS .
Ojeda, A., Calzadilla, A., Lazo, B., Alazo, K., Savio, S.: 2005, Analysis of behavior of solar wind parameters under different IMF conditions using nonlinear dynamics techniques. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys.67, 1859. DOI . ADS .
Ojeda-González, A., Klausner, V., Mendes, O., Domingues, M.O., Prestes, A.: 2017a, Characterization of the complex ejecta measured in situ on 19 – 22 March 2001 by six different methods, Solar Phys.292, 160. DOI . ADS .
Ojeda-González, A., Mendes, O., Calzadilla, A., Domingues, M.O., Prestes, A., Klausner, V.: 2017b, An alternative method for identifying interplanetary magnetic cloud regions. Astrophys. J.837(2), 156. DOI . ADS .
Pearson, K.: 1901, On lines and planes of closest fit to systems of points in space. Phil. Mag.2(11), 559. DOI .
Richardson, I.G., Cane, H.V.: 2010, Near-Earth interplanetary coronal mass ejections during solar cycle 23 (1996 - 2009): Catalog and summary of properties. Solar Phys.264, 189. DOI . ADS .
Schwenn, R.: 2006, Space weather: The solar perspective. Living Rev. Solar Phys.3, 2. DOI . ADS .
Schwenn, R., Marsch, E., Jackson, B.V.: 1993, Book-Review - Physics of the inner heliosphere - Part two - Particles waves and turbulence. Solar Phys.145, 405. ADS .
Siscoe, G.L., Suey, R.W.: 1972, Significance criteria for variance matrix applications. J. Geophys. Res.77, 1321. DOI . ADS .
Smith, C.W., L’Heureux, J., Ness, N.F., Acuña, M.H., Burlaga, L.F., Scheifele, J.: 1998, The ACE magnetic fields experiment. Space Sci. Rev.86, 613. DOI . ADS .
Sonnerup, B.U.O., Cahill, J.L.J.: 1967, Magnetopause structure and attitude from explorer 12 observations. J. Geophys. Res.72, 171. DOI . ADS .
Sonnerup, B.U.Ö., Scheible, M.: 1998, Minimum and Maximum Variance Analysis, ISSI Scientific Rep. Ser.1, 185. ADS .
Van der Walt, S., Colbert, S.C., Varoquaux, G.: 2011, The NumPy array: A structure for efficient numerical computation. Comput. Sci. Eng.13(2), 22. DOI . ADS .
Vandas, M., OdstrčIl, D., Watari, S.: 2002, Three-dimensional MHD simulation of a loop-like magnetic cloud in the solar wind. J. Geophys. Res.107(A9), 1236. DOI . ADS .
Acknowledgements
R.A. Rosa Oliveira thanks PROSUC-CAPES for the PhD scholarship in the Physics and Astronomy course at UNIVAP. A. Ojeda-González wishes to thank CNPq for financial support (grant 431396/2018-3). In addition, the authors would like to thank the ACE and Wind science team members for the data sets used in this work. V. De la Luz thanks to CONACyT Ciencia Básica (254497) support. We also wish to thank the anonymous referee.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosa Oliveira, R.A., da Silva Oliveira, M.W., Ojeda-González, A. et al. New Metric for Minimum Variance Analysis Validation in the Study of Interplanetary Magnetic Clouds. Sol Phys 295, 45 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-020-01610-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-020-01610-6