Abstract
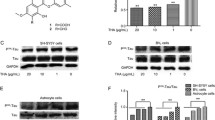
Alzheimer’s disease (AD), one of the most common neurodegenerative diseases, threatens people’s health. Based on the theory of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) efficacy and treatment theory, we first proposed the Alpinia oxyphylla–Schisandra chinensis herb pair (ASHP) for finding a candidate of AD treatment. This study aimed at exploring the effects of ASHP on improving the cognitive function and neurodegeneration, and revealing the possible mechanism. In this study, an amyloid-β (Aβ) induced AD model was established in mice via intracerebroventricular injection. The Y-maze test and Morris water maze test were carried out to observe the behavioral change of mice, which showed that ASHP significantly ameliorated cognitive impairment. In addition, ASHP reduced amyloid-β deposition and downregulated the hyperphosphorylation of tau via immunofluorescence assay and western blot analysis, respectively. Subsequently we focused on the PI3K/Akt pathway that is a classical pathway related to nervous system diseases. It also noticeably ASHP improved the histopathological changes in the hippocampus and cortex. Moreover, it was found that ASHP could upregulate the PI3K/Akt/Gsk-3β/CREB signaling pathway in N2a-SwedAPP cells. Taken together, it suggests that ASHP might reverse cognitive deficits and neurodegeneration via PI3K/Akt/Gsk-3β/CREB pathway.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn, J., Jang, J., Choi, J., Lee, J., Oh, S. H., Lee, J., et al. (2014). GSK3β, but not GSK3α, inhibits the neuronal differentiation of neural progenitor cells as a downstream target of mammalian target of rapamycin complex1. Stem Cells & Development, 23(10), 1121–1133.
Arnes, M., Acebes, A., & Ferrus, A. (2011). Neuroprotective and synaptogenic actions of PI3K in an Alzheimer's model in Drosophila. Alzheimers & Dementia the Journal of the Alzheimers Association, 7(4), e27–e27.
Astort, F., Repetto, E. M., Rochaviegas, L., Mercau, M. E., Puch, S. S., Finkielstein, C. V., et al. (2016). Role of CREB on heme oxygenase-1 induction in adrenal cells: Involvement of the PI3K pathway. Journal of Molecular Endocrinology, 57(2), 113.
Chang, Y. M., Chang, H. H., Tsai, C. C., Lin, H. J., Ho, T. J., Ye, C. X., et al. (2017). Alpinia oxyphylla Miq. fruit extract activates IGFR-PI3K/Akt signaling to induce Schwann cell proliferation and sciatic nerve regeneration. BMC Complementary & Alternative Medicine, 17(1), 184.
Chen, Y., Wang, C., Hu, M., Pan, J., Chen, J., Duan, P., et al. (2012). Effects of ginkgolide A on okadaic acid-induced tau hyperphosphorylation and the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway in N2a cells. Planta Medica, 78(12), 1337–1341.
Crouch, P. J., Harding, S. M. E., White, A. R., Camakaris, J., Bush, A. I., & Masters, C. L. (2008). Mechanisms of Aβ mediated neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease. International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology, 40(2), 181–198.
Desai, A., Konda, V. R., Darland, G., Austin, M., Prabhu, K. S., Bland, J. S., et al. (2009). META060 inhibits multiple kinases in the NF-kappaB pathway and suppresses LPS–mediated inflammation in vitro and ex vivo. Inflammation Research, 58(5), 229–234.
Durairajan, S. S., Liu, L. F., Lu, J. H., Koo, I., Maruyama, K., Chung, S. K., et al. (2011). Stimulation of non-amyloidogenic processing of amyloid-β protein precursor by cryptotanshinone involves activation and translocation of ADAM10 and PKC-α. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 25(2), 245–262.
Fan, W., Li, X., Huang, L., He, S., Xie, Z., Fu, Y., et al. (2018). S-oxiracetam ameliorates ischemic stroke induced neuronal apoptosis through up-regulating α7 nAChR and PI3K/Akt/GSK3β signal pathway in rats. Neurochemistry International, 115, 50–60.
Gong, R., Rifai, A., Ge, Y., Chen, S., & Dworkin, L. D. (2008). Hepatocyte growth factor suppresses proinflammatory NFκB activation through GSK3β inactivation in renal tubular epithelial cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 283(12), 7401.
Hu, D., Cao, Y., He, R., Han, N., Liu, Z., Miao, L., et al. (2012). Schizandrin, an antioxidant lignan from Schisandra chinensis, ameliorates Aβ1-42-induced memory impairment in mice. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/721721.
Hu, Z. Y., Liu, G., Yuan, H., Yang, S., Zhou, W. X., Zhang, Y. X., et al. (2010). Danggui-Shaoyao-San and its active fraction JD-30 improve Abeta-induced spatial recognition deficits in mice. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 128(2), 365–372.
Kamat, P. K., Kalani, A., Rai, S., Swarnkar, S., Tota, S., Nath, C., et al. (2016). Mechanism of oxidative stress and synapse dysfunction in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease: Understanding the therapeutics strategies. Molecular Neurobiology, 53(1), 648.
Kirouac, L., Rajic, A. J., Cribbs, D. H., & Padmanabhan, J. (2017). Activation of Ras-ERK signaling and GSK-3 by amyloid precursor protein and amyloid beta facilitates neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Eneuro. https://doi.org/10.1523/ENEURO.0149-16.2017.
Lee, C. C., Chiu, C. C., Liao, W. T., Wu, P. F., Chen, Y. T., Huang, K. C., et al. (2013). Alpinia oxyphylla Miq. bioactive extracts from supercritical fluid carbon dioxide extraction. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 78(6), 101–107.
Li, X., Zhao, X., Xu, X., Mao, X., Liu, Z., Li, H., et al. (2014). Schisantherin A recovers Abeta-induced neurodegeneration with cognitive decline in mice. Physiology & Behavior, 132, 10–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2014.04.046.
Li, Y. Z., Ren, S., Yan, X. T., Sun, Y. S., Li, H. P., Li, W., et al. (2018a). Improvement of cisplatin-induced renal dysfunction by Schisandra chinensis stems via anti-inflammation and anti-apoptosis effects. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 217, 228–237.
Li, Z., He, X., Liu, F., Wang, J., & Feng, J. (2018b). A review of polysaccharides from Schisandra chinensis and Schisandra sphenanthera: Properties, functions and applications. Carbohydrate Polymers, 184, 178.
Liu, A., Zhao, X., Li, H., Liu, Z., Liu, B., Mao, X., et al. (2014). 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural, an antioxidant agent from Alpinia oxyphylla Miq. improves cognitive impairment in Abeta 1–42 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. International Immunopharmacology, 23(2), 719–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2014.10.028.
Manna, P., & Jain, S. K. (2011). Hydrogen sulfide and L-cysteine increase phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP3) and glucose utilization by inhibiting phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) protein and activating phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/serine/threonine protein kinase (AK). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 286(46), 39848–39859.
Mao, X., Liao, Z., Guo, L., Xu, X., Wu, B., Xu, M., et al. (2015). Schisandrin C ameliorates learning and memory deficits by Abeta1-42-induced oxidative stress and neurotoxicity in mice. Phytotherapy Research, 29(9), 1373–1380. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.5390.
Murphy, J., Mcgreevy, P. D., & Murphy, J. (2009). Assessing equine prospective memory in a Y-maze apparatus. Veterinary Journal, 181(1), 24–28.
Noel, A., Barrier, L., & Ingrand, S. (2016). The Tyr216 phosphorylated form of GSK3β contributes to tau phosphorylation at PHF-1 epitope in response to Aβ in the nucleus of SH-SY5Y cells. Life Sciences, 158, 14–21.
Qi, Y., Cheng, X., Jing, H., Yan, T., Xiao, F., Wu, B., et al. (2019a). Combination of schisandrin and nootkatone exerts neuroprotective effect in Alzheimer's disease mice model. Metabolic Brain Disease. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-019-00475-4.
Qi, Y., Cheng, X., Jing, H., Yan, T., Xiao, F., Wu, B., et al. (2019b). Effect of Alpinia oxyphylla-Schisandra chinensis herb pair on inflammation and apoptosis in Alzheimer's disease mice model. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 237, 28–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2019.03.029.
Rangaraju, S., Dammer, E. B., Raza, S. A., Rathakrishnan, P., Xiao, H., Gao, T., et al. (2018). Identification and therapeutic modulation of a pro-inflammatory subset of disease-associated-microglia in Alzheimer's disease. Molecular Neurodegeneration, 13(1), 24.
Ringman, J. M. (2017). Alzheimer and the dementias. Neurologic Clinics, 35(2), ix–x.
Rojas-Gutierrez, E., Muñoz-Arenas, G., Treviño, S., Espinosa, B., Chavez, R., Rojas, K., et al. (2017). Alzheimer's disease and metabolic syndrome: A link from oxidative stress and inflammation to neurodegeneration. Synapse (New York, N. Y.), 71, e21990.
Sankaranarayanan, S., Meredith, J., Guss, V., Xu-Lin, A., Soares, H., Blennow, K., et al. (2012). Novel human CSF tau-fragment and pTau assays for distinguishing Alzheimer's from control subjects. Alzheimers & Dementia the Journal of the Alzheimers Association, 8(4), P110–P110.
Saura, C. A., & Cardinaux, J. R. (2017). Emerging roles of CREB-regulated transcription coactivators in brain physiology and pathology. Trends in Neurosciences, 40(12), 720–733.
Shi, S. H., Zhao, X., Liu, A. J., Liu, B., Li, H., Wu, B., et al. (2015). Protective effect of n-butanol extract from Alpinia oxyphylla on learning and memory impairments. Physiology & Behavior, 139, 13–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2014.11.016.
Shi, S. H., Zhao, X., Liu, B., Li, H., Liu, A. J., Wu, B., et al. (2014). The effects of sesquiterpenes-rich extract of Alpinia oxyphylla Miq. on amyloid-beta-induced cognitive impairment and neuronal abnormalities in the cortex and hippocampus of mice. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/451802.
Shi, X., Cai, X., Di, W., Li, J., Xu, X., Zhang, A., et al. (2016). MFG-E8 Selectively inhibited Aβ-induced microglial M1 polarization via NF-κB and PI3K-Akt pathways. Molecular Neurobiology, 54, 1–12.
Storozheva, Z. I., Gruden, M. A., Proshin, A. T., & Sewell, R. (2015). Learning ability is a key outcome determinant of GSK-3 inhibition on visuospatial memory in rats. Journal of Psychopharmacology, 29(7), 822.
Tang, M., Shi, S., Guo, Y., Xu, W., Wang, L., Chen, Y., et al. (2014). GSK-3/CREB pathway involved in the gx-50's effect on Alzheimer's disease. Neuropharmacology, 81, 256–266.
Tian, N., Kanno, T., Jin, Y., & Nishizaki, T. (2014). Lithium potentiates GSK-3β activity by inhibiting phosphoinositide 3-kinase-mediated Akt phosphorylation. Biochemical & Biophysical Research Communications, 450(1), 746–749.
Thinakaran, G., Teplow, D. B., Siman, R., Greenberg, B., & Sisodia, S. S. (1996). Metabolism of the Swedish amyloid precursor protein variant in neuro2a (N2a) cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 271(16), 9390–9396.
Ulep, M. G., Saraon, S. K., & Mclea, S. (2018). Alzheimer disease. Journal for Nurse Practitioners, 14(3), 129–135.
Wang Fang, Y. W. (1994). The experimental research on the effect of Jiannaowan to the learning and memory of rats. Acta Academiae Medicinae Shandong, 32, 118–122.
Wang, M., Bi, W., Fan, K., Li, T., Yan, T., Xiao, F., et al. (2018). Ameliorating effect of Alpinia oxyphylla-Schisandra chinensis herb pair on cognitive impairment in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 97, 128–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.10.088.
Wang, Y., Yang, R., Gu, J., Yin, X., Jin, N., Xie, S., et al. (2015). Cross talk between PI3K-AKT-GSK-3 beta and PP2A pathways determines tau hyperphosphorylation. Neurobiology of Aging, 36(1), 188–200.
Wei, B., Liu, M., Chen, Z., & Wei, M. (2018). Schisandrin ameliorates cognitive impairment and attenuates Aβ deposition in APP/PS1 transgenic mice: Involvement of adjusting neurotransmitters and their metabolite changes in the brain. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 39, 616–625.
Wong, K. K., Wan, C. C., & Shaw, P. C. (2004). P4–427 Ethanol extract of Alpinia oxyphylla fructus shows inhibition of tau protein phosphorylation in cell culture. Neurobiology of Aging, 25(2), S595–S595.
Yi, J. H., Baek, S. J., Heo, S., Park, H. J., Kwon, H., Lee, S., et al. (2017). Direct pharmacological Akt activation rescues Alzheimer's disease like memory impairments and aberrant synaptic plasticity. Neuropharmacology, 128, 282–292.
Yu, X. W., Oh, M. M., & Disterhoft, J. F. (2017). CREB, cellular excitability, and cognition: Implications for aging. Behavioural Brain Research, 322(Pt B), 206–211.
Zeitlin, R., Patel, S., Burgess, S., Arendash, G. W., & Echeverria, V. (2011). Caffeine induces beneficial changes in PKA signaling and JNK and ERK activities in the striatum and cortex of Alzheimer's transgenic mice. Brain Research, 1417, 127–136.
Zhang, W., Song, J., Yan, R., Li, L., Xiao, Z., Zhou, W., et al. (2018). Diterpene ginkgolides protect against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion damage in rats by activating Nrf2 and CREB through PI3K/Akt signaling. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 39, 1259–1272.
Zheng, R., Zhang, Z. H., Chen, C., Chen, Y., Jia, S. Z., Liu, Q., et al. (2017). Selenomethionine promoted hippocampal neurogenesis via the PI3K-Akt-GSK3 beta-Wnt pathway in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 485(1), 6–15.
Zhuang, P., Zhang, J., Wang, Y., Zhang, M., Song, L., Lu, Z., et al. (2016). Reversal of muscle atrophy by Zhimu and Huangbai herb pair via activation of IGF-1/Akt and autophagy signal in cancer cachexia. Supportive Care in Cancer, 24(3), 1–10.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81573580). Key Laboratory of polysaccharide bioactivity evaluation of TCM of Liaoning Province. Key techniques study of consistency evaluation of drug quality and therapeutic effect (18-400-4-08) and Liaoning Distinguished Professor Project for Ying Jia (2017). The Doctoral Scientific Research Foundation of Liaoning Province (2019-BS-233)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Hereby the authors confirm that there are no conflicts of interest in the present research. All the authors read and confirmed the final paper.
Ethical Approval
All the experimental protocols were approved by the Animal Research Ethics Committee at Shenyang Pharmaceutical University.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, Y., Jing, H., Cheng, X. et al. Alpinia oxyphylla–Schisandra chinensis Herb Pair Alleviates Amyloid-β Induced Cognitive Deficits via PI3K/Akt/Gsk-3β/CREB Pathway. Neuromol Med 22, 370–383 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-020-08595-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-020-08595-2