Abstract
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disease that degenerates the central nervous system (CNS). B cells exacerbate the progression of CNS lesions in MS by producing auto-antibodies, pro-inflammatory cytokines, and presenting auto-antigens to activated T cells. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) play a crucial role in complex biological processes and their stability in body fluids combined with their tissue specificity make these biomolecules promising biomarker candidates for MS diagnosis. In the current study, we investigated memory B cell-specific lncRNAs located, on average, less than 50 kb from differentially expressed protein-coding genes in MS patients compared to healthy individuals. Moreover, we included in our selection criteria lncRNA transcripts predicted to interact with microRNAs with established involvement in MS. To assess the expression levels of lncRNAs and their adjacent protein-coding genes, quantitative reverse transcription PCR was performed on peripheral blood mononuclear cells samples of 50 MS patients compared to 25 controls. Our results showed that in relapsing MS patients, compared to remitting MS patients and healthy controls, lncRNA RP11-530C5.1 was up-regulated while AL928742.12 was down-regulated. Pearson’s correlation tests showed positive correlations between the expression levels of RP11-530C5.1 and AL928742.12 with PAWR and IGHA2, respectively. The results of the ROC curve test demonstrated the potential biomarker roles of AL928742.12 and RP11-530C5.1. We conclude that these lncRNAs are potential markers for detection of relapsing MS patients.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- cDNA:
-
Complementary DNA
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- DNase I:
-
Deoxyribonuclease I
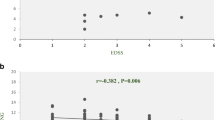
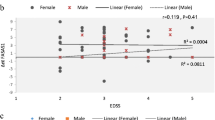
- EDSS:
-
Expanded disability status scale
- GEO:
-
Gene expression omnibus
- GSE:
-
GEO series
- IGHA2 :
-
Immunoglobulin heavy constant alpha 2
- EDTA:
-
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- lncRNA:
-
Long non-coding RNA
- miRNA:
-
microRNA
- MS:
-
Multiple sclerosis
- PAWR :
-
PRKC apoptosis WT1 regulator
- PBMC:
-
Peripheral blood mononuclear cell
- RT-qPCR:
-
Quantitative reverse transcription PCR
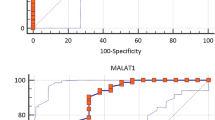
- ROC curve:
-
Receiver operating characteristic
- RRMS:
-
Relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis
References
Baker, D., Marta, M., Pryce, G., Giovannoni, G., & Schmierer, K. (2017). Memory B cells are major targets for effective immunotherapy in relapsing multiple sclerosis. EBioMedicine,16, 41–50.
Bar-Or, A., Calabresi, P. A., Arnold, D., Markowitz, C., Shafer, S., Kasper, L. H., et al. (2008). Rituximab in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: A 72-week, open-label, phase I trial. Annals of Neurology,63(3), 395–400.
Bar-Or, A., Fawaz, L., Fan, B., Darlington, P. J., Rieger, A., Ghorayeb, C., et al. (2010). Abnormal B-cell cytokine responses a trigger of T-cell–mediated disease in MS? Annals of Neurology,67(4), 452–461.
Berger, T., Rubner, P., Schautzer, F., Egg, R., Ulmer, H., Mayringer, I., et al. (2003). Antimyelin antibodies as a predictor of clinically definite multiple sclerosis after a first demyelinating event. New England Journal of Medicine,349(2), 139–145.
Cepok, S., Rosche, B., Grummel, V., Vogel, F., Zhou, D., Sayn, J., et al. (2005). Short-lived plasma blasts are the main B cell effector subset during the course of multiple sclerosis. Brain,128(7), 1667–1676.
Chen, G., Wang, Z., Wang, D., Qiu, C., Liu, M., Chen, X., et al. (2012). LncRNADisease: A database for long-non-coding RNA-associated diseases. Nucleic Acids Research,41(D1), D983–D986.
Comabella, M., Cantó, E., Nurtdinov, R., Río, J., Villar, L. M., Picón, C., et al. (2015). MRI phenotypes with high neurodegeneration are associated with peripheral blood B-cell changes. Human Molecular Genetics,25(2), 308–316.
Corcione, A., Casazza, S., Ferretti, E., Giunti, D., Zappia, E., Pistorio, A., et al. (2004). Recapitulation of B cell differentiation in the central nervous system of patients with multiple sclerosis. Proceedings of the National academy of Sciences of the United States of America,101(30), 11064–11069.
Dendrou, C. A., Fugger, L., & Friese, M. A. (2015). Immunopathology of multiple sclerosis. Nature Reviews Immunology,15(9), 545.
DiStefano, J. K. (2018). The emerging role of long noncoding RNAs in human disease. Methods in Molecular Biology, 1706, 91–110.
Duddy, M., Niino, M., Adatia, F., Hebert, S., Freedman, M., Atkins, H., et al. (2007). Distinct effector cytokine profiles of memory and naive human B cell subsets and implication in multiple sclerosis. The Journal of Immunology,178(10), 6092–6099.
Fatica, A., & Bozzoni, I. (2014). Long non-coding RNAs: New players in cell differentiation and development. Nature Reviews Genetics,15(1), 7.
Fillatreau, S., Sweenie, C. H., McGeachy, M. J., Gray, D., & Anderton, S. M. (2002). B cells regulate autoimmunity by provision of IL-10. Nature Immunology,3(10), 944.
Geisler, S., & Coller, J. (2013). RNA in unexpected places: Long non-coding RNA functions in diverse cellular contexts. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology,14(11), 699.
Heward, J. A., & Lindsay, M. A. (2014). Long non-coding RNAs in the regulation of the immune response. Trends in Immunology,35(9), 408–419.
Hosseini, A., Teimuri, S., Ehsani, M., Rasa, S. M. M., Etemadifar, M., Nasr Esfahani, M. H., et al. (2019). LncRNAs associated with multiple sclerosis expressed in the Th1 cell lineage. Journal of Cellular Physiology,1, 1. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.28779.
Ignacio, R. J., Liliana, P., & Edgardo, C. (2010). Oligoclonal bands and MRI in clinically isolated syndromes: Predicting conversion time to multiple sclerosis. Journal of Neurology,257(7), 1188–1191.
Krumbholz, M., Derfuss, T., Hohlfeld, R., & Meinl, E. (2012). B cells and antibodies in multiple sclerosis pathogenesis and therapy. Nature Reviews Neurology,8(11), 613.
Kurtzke, J. F. (1983). Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: An expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology,33(11), 1444.
Lee, J. T. (2012). Epigenetic regulation by long noncoding RNAs. Science,338(6113), 1435–1439.
Li, J.-H., Liu, S., Zhou, H., Qu, L.-H., & Yang, J.-H. (2013). starBase v2. 0: Decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein–RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Research,42(D1), D92–D97.
Liao, Q., Liu, C., Yuan, X., Kang, S., Miao, R., Xiao, H., et al. (2011). Large-scale prediction of long non-coding RNA functions in a coding–non-coding gene co-expression network. Nucleic Acids Research,39(9), 3864–3878.
Lisak, R. P., Nedelkoska, L., Benjamins, J. A., Schalk, D., Bealmear, B., Touil, H., et al. (2017). B cells from patients with multiple sclerosis induce cell death via apoptosis in neurons in vitro. Journal of Neuroimmunology,309, 88–99.
McFarland, H. F., & Martin, R. (2007). Multiple sclerosis: A complicated picture of autoimmunity. Nature Immunology,8(9), 913.
McHeyzer-Williams, M., Okitsu, S., Wang, N., & McHeyzer-Williams, L. (2012). Molecular programming of B cell memory. Nature Reviews Immunology,12(1), 24.
Mirza, A. H., Berthelsen, C. H., Seemann, S. E., Pan, X., Frederiksen, K. S., Vilien, M., et al. (2015). Transcriptomic landscape of lncRNAs in inflammatory bowel disease. Genome Medicine,7(1), 39.
Olsson, T., Barcellos, L. F., & Alfredsson, L. (2017). Interactions between genetic, lifestyle and environmental risk factors for multiple sclerosis. Nature Reviews Neurology,13(1), 25.
Oturai, D. B., Søndergaard, H., Börnsen, L., Sellebjerg, F., & Romme Christensen, J. (2016). Identification of suitable reference genes for peripheral blood mononuclear cell subset studies in multiple sclerosis. Scandinavian Journal of Immunology,83(1), 72–80.
Paraskevopoulou, M. D., Georgakilas, G., Kostoulas, N., Reczko, M., Maragkakis, M., Dalamagas, T. M., et al. (2012). DIANA-LncBase: Experimentally verified and computationally predicted microRNA targets on long non-coding RNAs. Nucleic Acids Research,41(D1), D239–D245.
Polman, C. H., Reingold, S. C., Banwell, B., Clanet, M., Cohen, J. A., Filippi, M., et al. (2011). Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2010 revisions to the McDonald criteria. Annals of Neurology,69(2), 292–302.
Ranzani, V., Rossetti, G., Panzeri, I., Arrigoni, A., Bonnal, R. J., Curti, S., et al. (2015). The long intergenic noncoding RNA landscape of human lymphocytes highlights the regulation of T cell differentiation by linc-MAF-4. Nature Immunology,16(3), 318.
Schroeder, H. W., & Cavacini, L. (2010). Structure and function of immunoglobulins. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology,125(2), S41–S52.
Sellebjerg, F., Börnsen, L., Khademi, M., Krakauer, M., Olsson, T., Frederiksen, J., et al. (2009). Increased cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of the chemokine CXCL13 in active MS. Neurology,73(23), 2003–2010.
Spurlock, C. F., III, Tossberg, J. T., Guo, Y., Collier, S. P., Crooke, P. S., III, & Aune, T. M. (2015). Expression and functions of long noncoding RNAs during human T helper cell differentiation. Nature Communications,6, 6932.
Taft, R. J., Pang, K. C., Mercer, T. R., Dinger, M., & Mattick, J. S. (2010). Non-coding RNAs: Regulators of disease. The Journal of Pathology: A Journal of the Pathological Society of Great Britain and Ireland,220(2), 126–139.
Teimuri, S., Hosseini, A., Rezaenasab, A., Ghaedi, K., Ghoveud, E., Etemadifar, M., et al. (2018). Integrative analysis of lncRNAs in Th17 cell lineage to discover new potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets in autoimmune diseases. Molecular Therapy-Nucleic Acids,12, 393–404.
Tintore, M., Rovira, A., Rio, J., Tur, C., Pelayo, R., Nos, C., et al. (2008). Do oligoclonal bands add information to MRI in first attacks of multiple sclerosis? Neurology,70(13 Part 2), 1079–1083.
Tong, Y.-K., & Lo, Y. D. (2006). Diagnostic developments involving cell-free (circulating) nucleic acids. Clinica Chimica Acta,363(1–2), 187–196.
Tufekci, K. U., Oner, M. G., Genc, S., & Genc, K. (2011). MicroRNAs and multiple sclerosis. Autoimmune Diseases,1, 1. https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/807426.
Ulitsky, I., & Bartel, D. P. (2013). lincRNAs: Genomics, evolution, and mechanisms. Cell,154(1), 26–46.
Wang, J., Ma, R., Ma, W., Chen, J., Yang, J., Xi, Y., et al. (2016). LncDisease: A sequence based bioinformatics tool for predicting lncRNA-disease associations. Nucleic Acids Research,44(9), e90. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw093.
Wilusz, J. E., Sunwoo, H., & Spector, D. L. (2009). Long noncoding RNAs: Functional surprises from the RNA world. Genes & Development,23(13), 1494–1504.
Yap, K. L., Li, S., Muñoz-Cabello, A. M., Raguz, S., Zeng, L., Mujtaba, S., et al. (2010). Molecular interplay of the noncoding RNA ANRIL and methylated histone H3 lysine 27 by polycomb CBX7 in transcriptional silencing of INK4a. Molecular Cell,38(5), 662–674.
Yoon, J.-H., Abdelmohsen, K., & Gorospe, M. (2014). Functional interactions among microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs. Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology, 34, 9–14.
Zhang, Y., & Cao, X. (2016). Long noncoding RNAs in innate immunity. Cellular & Molecular Immunology,13(2), 138.
Acknowledgements
The authors declare that they have no competing interests. A part of this project was supported by the National Institute for Medical Research Development (NIMAD’s Project No. 942792) and also partly by Royan Institute for Biotechnology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghoveud, E., Teimuri, S., Vatandoost, J. et al. Potential Biomarker and Therapeutic LncRNAs in Multiple Sclerosis Through Targeting Memory B Cells. Neuromol Med 22, 111–120 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-019-08570-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-019-08570-6