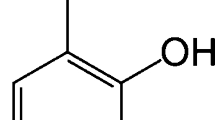
Abstract
Room-temperature ionic liquids (RTILs) have proven to be efficient polar or highly polar stationary phases for GC. Nevertheless, the thermal stability of monocationic RTILs limits their use in high-temperature GC. To improve the thermal stability, an RTIL based on a 1-methylimidazolium derivative was anchored in a three-dimensional network using the sol–gel process. Three different strategies were compared: using the derivative pure, in combination with a polymer or copolymerised with diethoxydimethylsilane. This last method allowed for the preparation of hybrid stationary phases with satisfactory efficiency (3500 plates per meter determined by the injection of n-tetradecane at 80 °C, k = 8.19) and very good thermal stability up to 340 °C using the NTf2 counter ion. The stationary phases demonstrated a good ability to separate positional isomers and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Polarity and molecular interactions with analytes were characterized by calculating the Rohrschneider–McReynolds constants and Abraham system constants. A classification of the polarity of the new stationary phases relative to 44 stationary phases, including commercial and non-commercial ones, was performed based on the RTILs using principal component analysis. Finally, the maximal operating temperature of these new stationary phases was compared with those of the most thermally stable conventional or RTIL-based stationary phases, demonstrating that the sol–gel process is an efficient way to enhance the thermal stability of GC stationary phases.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang D, Chong S, Malik A (1997) Sol-gel column technology for single-step deactivation, coating, and stationary-phase immobilization in high-resolution capillary gas chromatography. Anal Chem 69:4566–4576
Shende C, Kadir A, Malik A (2003) Sol-gel poly(ethylene glycol) stationary phase for high-resolution capillary gas chromatography. Anal Chem 75:3518–3530
Zeng Z, Qiu W, Xing H, Huang Z (2000) Sol-gel-derived crown ether stationary phase for capillary gas chromatography. Anal Sci 16:851–854
Liang M, Qi M, Zhang C, Fu R (2004) Peralkylated-beta-cyclodextrin used as gas chromatographic stationary phase prepared by sol-gel technology for capillary column. J Chromatogr A 1059:111–119
Dong-Xin W, Malik A (2007) Separation of enantiomers of a chiral lactone on sol-gel gas chromatography capillary columns of poly(methydrosiloxane) stationary phase with pendant Permethylated β-Cyclodextrin. Chinese J Anal Chem 35:360–364
Sidelnikov V, Patrushev Y, Belov Y (2006) Sol-gel multicapillary columns for gas-solid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1101:315–318
Malik A , Wang D , PCT WO 00/11463 (2000)
Malik A , Kabir A , Shende C , PCT WO 02/072225 A1 (2002)
Poole CF, Poole SK (2011) Ionic liquid stationary phases for gas chromatography. J Sep Sci 34:888–900
Fanali A, Micalizzi G, Dugo P, Mondello L (2017) Ionic liquids as stationary phases for fatty acid analysis by gas chromatography. Analyst 142:4601–4612
Talebi M, Patil R, Sidisky L, Berthod A, Armstrong DW (2018) Variation of anionic moieties of dicationic ionic liquid GC stationary phases: Effect on stability and selectivity. Anal Chim Acta 1042:155–164
Pojjanapornpun S, Nolvachai Y, Aryusuk K, Kulsing C, Krisnangkura K, Marriott P (2018) Ionic liquid phases with comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography of fatty acid methyl esters. Anal Bioanal Chem 410:4669–4677
Cagliero A, Bicchi C, Cordero C, Liberto E, Rubiolo P, Sgorbini B (2018) Ionic liquids as water-compatible GC stationary phases for the analysis of fragrances and essential oils. Anal Bioanal Chem 410:4657–4668
Mazzucotelli M, Bicchi C, Marengo Z, Rubiolo P, Galli S, Anderson J, Sgorbini B, Cagliero C (2019) Ionic liquids as stationary phases for gas chromatography-Unusual selectivity of ionic liquids with a phosphonium cation and different anions in the flavor, fragrance and essential oil analyses. J Chromatogr A 1583:124–135
Ros M, Escobar-Armanz J, Sanz ML, Ramos L (2018) Evaluation of ionic liquid gas chromatography stationary phases for the separation of polychlorinated biphenyls. J Chromatogr A 1559:156–163
Ho TD, Zhang C, Hantao LW, Anderson JL (2014) Ionic liquids in analytical chemistry: fundamentals, advances, and perspectives. Anal Chem 86:262–285
Poole CF, Lenca N (2014) Gas chromatography on wall-coated open-tubular columns with ionic liquid stationary phases. J Chromatogr A 1357:87–109
Shashkov M, Sidelnikov V (2019) Orthogonality and quality of GC × GC separations for complex samples with ionic liquid stationary phases in first dimension. Chromatographia 82:615–624
Nan H, Anderson J (2018) Ionic liquid stationary phases for multidimensional gas chromatography. Trends Anal Chem 105:367–379
Patil R, Talebi M, Sidisky L, Armstrong DW (2017) Examination of selectivities of thermally stable geminal dicationic ionic liquids by structural modification. Chromatographia 80:1563–1574
Patil R, Talebi M, Armstrong DW (2018) Physicochemical properties of branched-chain dicationic ionic liquids. J Mol Liq 256:247–255
Patil R, Talebi M, Sidisky L, Berthod A, Armstrong DW (2018) Gas chromatography selectivity of new phosphonium-based dicationic ionic liquid stationary phases. J Sep Sci 41:4142–4148
Heydar KT, Pourrahim S, Ghonouei N, Yaghoubnejad S, Sharifi A (2018) Thermodynamic parameters of a new synthesized tricationic ionic liquid stationary phase by inverse gas chromatography. J Chem Eng Data 63:4513–4523
Dai J-L, Zhao L-H, Shi J-H (2017) Preparation and evaluation of a novel bonded imidazolium ionic liquid as stationary phase for gas chromatography. J Sep Sci 40:2769–2778
Zhao X, Tan K, Xing J (2019) Flexible and convenient strategy for synthesis of ionic liquid bonded polysiloxane stationary phases. J Chromatogr A 1587:197–208
Delahousse G, Peulon-Agasse V, Debray J, Vaccaro M, Cravotto G, Jabin I, Cardinael P (2013) The incorporation of calix[6]arene and cyclodextrin derivatives into sol-gels for the preparation of stationary phases for gas chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1318:207–216
Cardinael P, Ndzie E, Petit S, Coquerel G, Combret Y, Combret JC (1997) Enantiomeric separation of 5-alkyl-5-methylhydantoin derivatives by capillary gas chromatography on permethylated β-cyclodextrin and molecular modelling. J High Resolut Chromatogr 20:560–564
Curat A, Tisse S, Andrieu A, Bar N, Villemin D, Cardinael P (2014) Physical ionic liquid/polysiloxane mixtures for tuning the polarity and the selectivity of the polysiloxane stationary phase for GC analysis. Chromatographia 77:1671–1681
Rohrschneider L (1966) A method of characterization of the liquids used for separation in gas chromatography. J Chromatogr 22:6–22
McReynolds WO (1970) Characterization of some liquid phases. J Chromatogr Sci 8:685–691
Grob RL, Barry EF (2004) Modern pratice of gas chromatography, 4th edn. Wiley, Hoboken
Poole A (2012) Gas chromatography. Elsevier, Waltham
Abraham MH, Poole C, Poole SK (1999) Classification of stationary phases and other materials by gas chromatography. J Chromatogr A 842:79–114
Abraham MH, Ibrahim A, Zissimos AM (2004) Determination of sets of solute descriptors from chromatographic measurements. J Chromatogr A 1037:29–47
Grob K, Grob G, Grob K (1978) Comprehensive, standardized quality test for glass capillary columns. J Chromatogr 156:1–20
Grob K, Grob G (1981) Testing capillary gas chromatographic columns. J Chromatogr 219:13–20
Qi M, Armstrong DW (2007) Dicationic ionic liquid stationary phase for GC-MS analysis of volatile compounds in herbal plants. Anal Bioanal Chem 388:889–899
Wei Q, Qi ML, Yang HX, Fu RN (2011) Separation characteristics of ionic liquids grafted polymethylsiloxanes stationary phases for capillary GC. Chromatographia 74:717–724
Gonzalez-Alvarez J, Arias-Abrodo P, Puerto M, Viguri ME, Perez J, Gutierrez-Alvarez MD (2013) Polymerized phosphonium-based ionic liquids as gas chromatography stationary phases. RSC Adv 3:21377–21380
Armstrong DW, He L, Liu YA (1999) Examination of ionic liquids and their interaction with molecules, when used as stationary phases in gas chromatography. Anal Chem 71:3673–3676
Sun X, Wu C, Xing J (2010) Ionic liquid-bonded polysiloxane as stationary phase for capillary gas chromatography. J Sep Sci 33:3159–3167
Sun X, Zhu Y, Wang P, Li J, Wu C, Xing J (2011) High temperature and highly selective stationary phases of ionic liquid bonded polysiloxanes for gas chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1218:833–841
Wang L, Wang X, Qi M, Fu R (2014) High temperature and highly selective stationary phases of ionic liquid bonded polysiloxanes for gas chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1334:112–117
Wang X, Qi M, Fu R (2014) Separation performance of cucurbit[7]uril in ionic liquid-based sol-gel coating as stationary phase for capillary gas chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1371:237–243
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the interregional program ‘Centre Régional Universitaire Normand de Chimie’ (CRUNCh) for its financial support. The authors thank the Conseil Régional de Haute Normandie, France, for a PhD grant awarded to Aurélien Curat. The authors thank Benjamin Schamme (University of Rouen) for the TGA experiments and Emilie Bobo (University of Rouen) for the microscopy experiments. The authors thank the French Ministry for Research and Education, the Region Normandie (Research Grant) and FEDER for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Curat, A., Tisse, S., Agasse-Peulon, V. et al. Incorporation of Imidazolium Ionic Liquids in GC Stationary Phases via the Sol–Gel Process. Chromatographia 83, 439–449 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-020-03854-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-020-03854-7