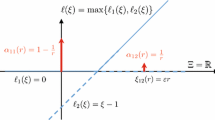
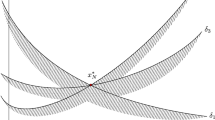
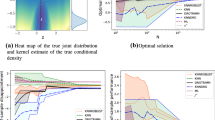
Abstract
As a solution method that not only considers the probability distribution information of data, but also ensures that the results are not too conservative, more and more researches have been made on the distributionally robust optimization method. Based on the minimum cost consensus model, this paper proposes a new minimum cost consensus model with distributionally robust chance constraints (DRO-MCC). Firstly, Conditional Value-at-Risk (CVaR) is used to approximate the chance constraints in the cost model. Secondly, when the information of the first and second moments of random variables affecting the unit adjustment cost are known, the min-max problem is obtained based on the moment method and dual theory, and a tractable semidefinite programming problem can be easily processed through further transformation. Finally, in order to evaluate the robustness of the proposed model, the results of different parameters are compared, and the DRO-MCC is compared with the robust optimization model (RO-MCC) and the minimum cost consensus model (MCC). The example proves that MCC is too optimistic and RO-MCC is too conservative. In contrast, DRO-MCC overcomes the conservatism of robust optimization and considers the probability information of data, so the result is more ideal.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dong, Y.C., Xu, W.J., Xu, W.D.: An automatic method to reach consensus in a local context for AHP group decision making. Eur. J. Ind. Eng. 7(4), 456–474 (2013)
Xu, Z.S., Cai, X.Q.: Deriving weights from interval multiplicative preference relations in group decision making. Group Decis. Negot. 23(4), 695–713 (2014)
Wu, Z.B., Xu, J.P.: An interactive consensus reaching model for decision making under hesitation linguistic environment. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 31(3), 1635–1644 (2016)
Qin, J.D., Liu, X.W., Pedeycz, W.: A multiple attribute interval type-2 fuzzy group decision making and its application to supplier selection with extended LINMAP method. Soft Comput. 21(12), 3207–3226 (2017)
Xu, Y.J., Zhang, Z.Q., Wang, H.M.: A consensus-based method for group decision making with incomplete uncertain linguistic preference relations. Soft Comput. 23(2), 669–682 (2019)
Wu, J., Sun, Q., Fujita, H.: An attitudinal consensus degree to control the feedback mechanism in group decision making with different adjustment cost. Knowl. Based Syst. 164, 265–273 (2019)
Wu, Z.B., Yang, X.Y., Tu, J.C., Chen, X.: Optimal consistency and consensus models for interval additive preference relations: a discrete distribution perspective. J. Oper. Res. Soc. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/01605682.2019.1621219
Gong, Z.W., Xu, X.X., Li, L.S., Xu, C.: Consensus modeling with nonlinear utility and cost constraints: a case study. Knowl. Based Syst. 88, 210–222 (2015)
Gong, Z.W., Xu, C., Chiclana, F., Xu, X.X.: Consensus measure with multi-stage fluctuation utility based on Chinas urban demolition negotiation. Group Decis. Negot. 26(2), 379–407 (2017)
Dong, Y.C., Zhan, M., Kou, G., Ding, Z.G., Liang, H.M.: A survey on the fusion process in opinion dynamics. Inform. Fusion 43, 57–65 (2018)
Zhang, B.W., Dong, Y.C., Xu, Y.F.: Maximum expert consensus models with linear cost function and aggregation operators. Comput. Ind. Eng. 66(1), 147–157 (2013)
Gou, X.J., Xu, Z.S., Herrera, F.: Consensus reaching process for large-scale group decision making with double hierarchy hesitant fuzzy linguistic preference relations. Knowl. Based Syst. 157, 20–33 (2018)
Wu, T., Liu, X.W., Qin, J.D., Herrera, F.: Consensus evolution networks: a consensus reaching tool for managing consensus thresholds in group decision making. Inform. Fusion 52, 375–388 (2019)
Ben-Arieh, D., Easton, T.: Multi-criteria group consensus under linear cost opinion elasticity. Decis. Supp. Syst. 43(3), 713–721 (2007)
Ben-Arieh, D., Easton, T., Evans, B.: Minimum cost consensus with quadratic cost functions. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. Hum. 39(1), 210–217 (2009)
Liu, J., Chan, F.T.S., Li, Y., Zhang, Y.J., Deng, Y.: A new optimal consensus method with minimum cost in fuzzy group decision. Knowl. Based Syst. 35, 357–360 (2012)
Gong, Z.W., Zhang, H.H., Forrest, J., Li, L.S., Xu, X.X.: Two consensus models based on the minimum cost and maximum return regarding either all individuals or one individual. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 240(1), 183–192 (2015)
Dong, Y.C., Xu, Y.F., Li, H., Feng, B.: The OWA-based consensus operator under linguistic representation models using position indexes. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 203(2), 455–463 (2010)
Zhang, G.Q., Dong, Y.C., Xu, Y.F., Li, H.Y.: Minimum-cost consensus models under aggregation operators. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. Hum. 41(6), 1253–1261 (2011)
Zhang, H.H., Kou, G., Peng, Y.: Soft consensus cost models for group decision making and economic interpretations. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 277(3), 964–980 (2019)
Ding, Z.G., Liang, H.M., Dong, Y.C., Chiclana, F., Herrera CViedma, E., Cabrerizo, F.J.: An opinion control rule with minimum adjustments to support the consensus reaching in bounded confidence model. Proc. Comput. Sci. 91, 617–624 (2016)
Wu, J., Dai, L., Chiclana, F., Fujita, H., Herrera-Viedma, E.: A minimum adjustment cost feedback mechanism based consensus model for group decision making under social network with distributed linguistic trust. Inform. Fusion 41, 232–242 (2018)
Zhang, B.W., Dong, Y.C., Xu, Y.F.: Multiple attribute consensus rules with minimum adjustments to support consensus reaching. Knowl. Based Syst. 67, 35–48 (2014)
Kwok, P.K., Lau, H.Y.K.: A modified consensus-building methodology for reaching a group decision using minimum costs. IEEE Acess 6, 3509–3523 (2018)
Li, Y., Zhang, H.J., Dong, Y.C.: The interactive consensus reaching process with the minimum and uncertain cost in group decision making. Appl. Soft Comput. 60, 202–212 (2017)
Cheng, D., Zhou, Z.L., Cheng, F.X., Zhou, Y.F., Xie, Y.J.: Modeling the minimum cost consensus problem in an asymmetric costs context. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 270(3), 1122–1137 (2018)
Heravi, G., Faeghi, S.: Group decision making for stochastic optimization of time, cost, and quality in construction projects. J. Comput. Civil Eng. 28(2), 275–283 (2014)
Chu, T.C., Nguyen, H.T.: Ranking alternatives with relative maximizing and minimizing sets in a fuzzy MCDM model. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 21(4), 1170–1186 (2019)
Li, S., Wei, C.P.: Modeling the social influence in consensus reaching process with interval fuzzy preference relations. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 21(6), 1755–1770 (2019)
Zhang, N., Gong, Z.W., Chiclana, F.: Minimum cost consensus models based on random opinions. Expert Syst. Appl. 89, 149–159 (2017)
Tan, X., Gong, Z.W., Chiclana, F., Zhang, N.: Consensus modeling with cost chance constraint under uncertainty opinions. Appl. Soft Comput. 67, 721–727 (2018)
Aounia, B., Abdelazizb, F.B., Martelc, J.-M.: Decision-maker’s preferences modeling in the stochastic goal programming. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 162(3), 610–618 (2005)
Zhang, J.Q., Jin, Z.Y., An, Y.B.: Dynamic portfolio optimization with ambiguity aversion. J. Bank. Financ. 79, 95–109 (2017)
Zhang, Z.H., Jiang, H.: A robust counterpart approach to the bi-objective emergency medical service design problem. Appl. Math. Model. 38(3), 1033–1040 (2014)
Jabbarzadeh, A., Haughton, M., Pourmehdi, F.: A robust optimization model for efficient and green supply chain planning with postponement strategy. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 214, 266–283 (2019)
Han, Y.F., Qu, S.J., Wu, Z., Huang, R.P.: Robust consensus models based on minimum cost with an application to marketing plan. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. (2019). https://doi.org/10.3233/JIFS-190863
Scarf, H.: A min–max solution of an inventory problems. In: Arrow, K.S., Karlin, S., Scarf, H.E. (eds.) Studies in mathematical theory of inventory and production, pp. 201–209. Stanford University Press, Stanford (1958)
Qu, S.J., Meng, D.H., Zhou, Y.Y., Dai, Y.M.: Distributionally robust games with an application to supply chain. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 33(5), 2749–2762 (2017)
Ding, K.W., Wang, M.H., Huang, N.J.: Distributionally robust chance constrained problem under interval distribution information. Optim. Lett. 12(6), 1315–1328 (2018)
Liu, J., Chen, Z.P., Lisser, A., Xu, Z.J.: Closed-form optimal portfolios of distributionally robust mean-CVaR problems with unknown mean and variance. Appl. Math. Opt. 79(3), 671–693 (2019)
Huang, R.P., Qu, S.J., Yang, X.G., Liu, Z.M.: Multi-stage distributionally robust optimization with risk aversion. J. Ind. Manag. Optim. (2019). https://doi.org/10.3934/jimo.2019109
Rockafellar, R.T., Uryasev, S.: Optimization of conditional value-at-risk. J. Risk 2, 21–41 (2002)
Zymler, S., Kuhn, D., Rustem, B.: Distributionally robust joint chance constraints with second-order moment information. Math. Program. 137(1–2), 167–198 (2013)
Shapiro, A., Kleywegt, A.J.: Minimax analysis of stochastic problems. Optim. Methods Softw. 17(3), 523–542 (2002)
Isii, K.: The extrema of probability determined by generalized moments (i) bounded random variables. Ann. Inst. Stat. Math. 12(2), 119–134 (1960)
Bertsimas, D., Brown, D.B., Caramanis, C.: Theory and applications of robust optimization. Soc. Ind. Appl. Math. 53(3), 464–501 (2011)
Bertsimas, D., Sim, M.: The price of robustness. Oper. Res. 52(1), 35–53 (2004)
Acknowledgements
The work is supported by Natural Scientific Foundation of China (No. 71571055). We are very grateful to the editors and referees for their careful reading and constructive suggestions on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, Y., Qu, S. & Wu, Z. Distributionally Robust Chance Constrained Optimization Model for the Minimum Cost Consensus. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 22, 2041–2054 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-019-00791-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-019-00791-y