Abstract
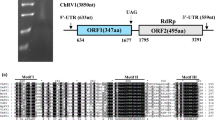
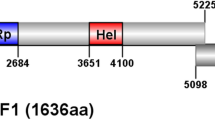
A novel positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus was isolated from strain CCMJ1271 of the fungus Auricularia heimuer, and the complete genome sequence of the virus was determined. Database searching, sequence alignment, and phylogenetic analysis revealed that this fungal virus and some viruses of family Virgaviridae clustered into a single branch of a phylogenetic tree, and we thus tentatively named the virus "Auricularia heimuer mycovirgavirus 1" (AhMV1). The AhMV1 genome consists of 9,934 nucleotides and contains a short poly(A) tail and three open reading frames (ORFs). ORF1 encodes an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), ORF2 encodes a protein that is homologous to movement proteins of plant virgaviruses, and ORF3 encodes a coat protein (CP). AhMV1 is the first virus to be discovered in A. heimuer.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xie J, Jiang D (2014) New insights into mycoviruses and exploration for the biological control of crop fungal diseases. Annu Rev Phytopathol 52(1):45–68
Hollings M (1962) Viruses associated with a die-back disease of cultivated mushroom. Nature 196:962–965
Hollings M, Stone OM (1971) Viruses that infect fungi. Annu Rev Phytopathol 9:93–118
Pearson MN, Beever RE, Boine B, Arthur K (2009) Mycoviruses of filamentous fungi and their relevance to plant pathology. Mol Plant Pathol 10:115–128
Zaayen ADV (1972) Intracellular appearance of mushroom virus in fruiting bodies and basidiospores of Agaricus bisporus. Virology 47(1):94–104
Ghabrial SA, Suzuki N (2009) Viruses of plant pathogenic fungi. Annu Rev Phytopathol 47:353–384
Ghabrial SA, Castón JR, Jiang D (2015) 50-plus years of fungal viruses. Virology 479–480:356–368
Yu X, Li B, Fu Y et al (2010) A geminivirus-related DNA mycovirus that confers hypovirulence to a plant pathogenic fungus. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107(18):8387–8392
Barroso G, Labarère J (1990) Evidence for viral and naked double-stranded RNAs in the basidiomycete Agrocybe aegerita. Curr Genet 18(3):231–237
Guo M, Bian Y, Wang J et al (2017) Biological and molecular characteristics of a novel partitivirus infecting the edible fungus Lentinula edodes. Plant Dis 101(5):726–733
Won HK, Park SJ, Kim DK et al (2013) Isolation and characterization of a mycovirus in Lentinula edodes. J Microbiol 51(1):118–122
Akiko K, Hideki K, Masayuki S, Atsushi K, Kozo N, Nobuhiro S, Fumihiro F (2019) Isolation and characterization of a novel mycovirus infecting an edible mushroom, Grifola frondose. Mycoscience 60(4):211–220
Magae Y, Sunagawa M (2010) Characterization of a mycovirus associated with the brown discoloration of edible mushroom, Flammulina velutipes. Virol J 7(1):342
Yu HJ, Lim D, Lee HS (2003) Characterization of a novel single-stranded RNA mycovirus in Pleurotus ostreatus. Virology 314(1):9–15
International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Virus taxonomy: the classification and nomenclature of viruses [EB/OL]. https://talk.ictvonline.org/ictv-reports/ictv_online_report/
Yuan Y, Wu F, Si J, et al (2017) Whole genome sequence of, Auricularia heimuer, (Basidiomycota, Fungi), the third most important cultivated mushroom worldwide. Genomics 2017:S0888754317301830
China Industry Information Network (2019) Analysis of the development status and development direction of China's edible fungus industry in 2019 [EB/OL]. https://www.chyxx.com/industry/201911/801785.html
China Edible Fungi Association (2019) Letter from China edible fungi association on printing and distributing the results of 2017 National Edible Fungi Statistical Survey [EB/OL]. https://hz.cefa.org.cn/2019/03/18/10498.html
Adams MJ, Antoniw JF, Kreuze J (2009) Virgaviridae: a new family of rod-shaped plant viruses. Adv Virol 154(12):1967–1972
Cock PJA, Fields CJ, Goto N et al (2009) The Sanger FASTQ file format for sequences with quality scores, and the Solexa/Illumina FASTQ variants. Nucleic Acids Res 38(6):1767–1771
Jiang L, Schlesinger F, Davis CA et al (2011) Synthetic spike-in standards for RNA-seq experiments. Genome Res 21(9):1543–1551
Fan X, Zhou Y, Xiao Y et al (2014) Cloning, expression and phylogenetic analysis of a divergent laccase multigene family in Auricularia auricula-judae. Microbiol Res 169(5–6):453–462
Darissa O, Willingmann P, Günter A (2010) Optimized approaches for the sequence determination of double-stranded RNA templates. J Virol Methods 169(2):397–403
Lee M, Shin Y, Nelson BD, Ajayi O et al (2016) Identification of diverse mycoviruses through metatranscriptomics characterization of the viromes of five major fungal plant pathogens. J Virol 2016:JVI.00357-16
Chiba S, Salaipeth L, Lin YH et al (2009) A novel bipartite double-stranded RNA Mycovirus from the white root rot Fungus Rosellinia necatrix: molecular and biological characterization, taxonomic considerations, and potential for biological control. J Virol 83(24):12801–12812
Xiao X, Cheng J, Tang J, Fu Y, Jiang D, Baker TS, Ghabrial SA, Xie J (2014) A novel partitivirus that confershypovirulence on plant pathogenic fungi. J Virol 88:10120–10133
Xie J, Xiao X, Fu Y, Liu H, Cheng J, Ghabrial SA, Li G, Jiang D (2011) A novel mycovirus closely related to hypoviruses that infects the plantpathogenic fungus Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Virology 418:49–56
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Frédéric P (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 1997:25
Guindon S, Dufayard JF, Lefort V et al (2010) New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: assessing the performance of PhyML 30. Syst Biol 59(3):307–321
Stéphane G, Frédéric D, Jean-François D et al (2009) Estimating maximum likelihood phylogenies with PhyML. Methods Mol Biol 537:113–137
Acknowledgements
We thank Frederick Leo Sossah for providing excellent technical assistance in the use of the English language.
Funding
The National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFD1001000, 2017YFD0601002), the Special Fund for Agro-Scientific Research in the Public Interest (201503137), the Jilin Provincial Department of Education (JJKH20180670KJ), and the Program of Introducing Talents of Discipline to Universities (D17014) supported this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies involving human participants or animals.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Robert H. A. Coutts.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.




Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Xie, J., Hai, D. et al. Molecular characteristics of a novel ssRNA virus isolated from Auricularia heimuer in China. Arch Virol 165, 1495–1499 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-020-04615-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-020-04615-5