Abstract
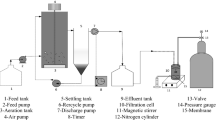
Energy uncoupling is often used for sludge reduction because it is easy to operate and does not require a significant amount of extra equipments (i.e. no additional tank required). However, over time the supernatant extracted using this method can deteriorate, ultimately requiring further treatment. The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of using a low-pressure ultrafiltration membrane process for sludge water recovery after the sludge had undergone an energy uncoupling treatment (using 3,3′,4′,5-tetrachlorosalicylanilide (TCS)). Energy uncoupling was found to break apart sludge floc by reducing extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) content. Analysis of supernatant indicated that when energy uncoupling and membrane filtration were coapplied and the TCS dosage was below 30 mg/L, there was no significant deterioration in organic component removal. However, ammonia and phosphate concentrations were found to increase as the concentration of TCS added increased. Additionally, due to low sludge concentrations and EPS contents, addition of 30-60 mg/LTCS during sludge reduction increased the permeate flux (two times higher than the control) and decreased the hydraulic reversible and cake layer resistances. In contrast, high dosage of TCS aggravated membrane fouling by forming compact fouling layers. In general, this study found that the co-application of energy uncoupling and membrane filtration processes represents an effective alternative method for simultaneous sludge reduction and sludge supernatant recovery.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker A (2001). Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix characterization of some sewage-impacted rivers. Environmental Science & Technology, 35(5): 948–953
Chen G W, Yu H Q, Liu H X, Xu D Q (2006). Response of activated sludge to the presence of 2,4-dichlorophenol in a batch culture system. Process Biochemistry, 41(8): 1758–1763
Chen W, Westerhoff P, Leenheer J A, Booksh K (2003). Fluorescence excitation-emission matrix regional integration to quantify spectra for dissolved organic matter. Environmental Science & Technology, 37(24): 5701–5710
de Oliveira T S, Corsino S F, Di Trapani D, Torregrossa M, Viviani G (2018). Biological minimization of excess sludge in a membrane bioreactor: Effect of plant configuration on sludge production, nutrient removal efficiency and membrane fouling tendency. Bioresource Technology, 259: 146–155
Ding A, Liang H, Li G, Szivak I, Traber J, Pronk W (2017a). A low energy gravity-driven membrane bioreactor system for grey water treatment: Permeability and removal performance of organics. Journal of Membrane Science, 542(11): 408–417
Ding A, Liang H, Qu F, Bai L, Li G, Ngo H H, Guo W (2014). Effect of granular activated carbon addition on the effluent properties and fouling potentials of membrane-coupled expanded granular sludge bed process. Bioresource Technology, 171(1): 240–246
Ding A, Lin D, Zhao Y, Ngo H H, Guo W, Bai L, Luo X, Li G, Ren N, Liang H (2019). Effect of metabolic uncoupler, 2,4-dinitrophenol (DNP) on sludge properties and fouling potential in ultrafiltration membrane process. Science of the Total Environment, 650: 1882–1888
Ding A, Wang J, Lin D, Tang X, Cheng X, Li G, Ren N, Liang H (2017b). In situ coagulation versus pre-coagulation for gravity-driven membrane bioreactor during decentralized sewage treatment: Permeability stabilization, fouling layer formation and biological activity. Water Research, 126: 197–207
Dvořák L, Gómez M, Dvořáková M, Růžičková I, Wanner J (2011). The impact of different operating conditions on membrane fouling and EPS production. Bioresource Technology, 102(13): 6870–6875
Fang F, Hu H L, Qin M M, Xue Z X, Cao J S, Hu Z R (2015). Effects of metabolic uncouplers on excess sludge reduction and microbial products of activated sludge. Bioresource Technology, 185: 1–6
Feng X C, Guo W Q, Yang S S, Zheng H S, Du J S, Wu Q L, Ren N Q (2014). Possible causes of excess sludge reduction adding metabolic uncoupler, 3,3′,4′,5-tetrachlorosalicylanilide (TCS), in sequence batch reactors. Bioresource Technology, 173: 96–103
Ferrer-Polonio E, Fernández-Navarro J, Alonso-Molina J L, Bes-Piá A, Amorós I, Mendoza-Roca J A (2019). Changes in the process performance and microbial community by addition of the metabolic uncoupler 3,3′,4′,5-tetrachlorosalicylanilide in sequencing batch reactors. Science of the Total Environment, 694: 133726
Guo W Q, Yang S S, Xiang W S, Wang X J, Ren N Q (2013). Minimization of excess sludge production by in-situ activated sludge treatment processes: A comprehensive review. Biotechnology Advances, 31(8): 1386–1396
Jiang B, Liu Y (2010). Energy uncoupling inhibits aerobic granulation. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 85(3): 589–595
Jiang B, Liu Y (2013). Dependence of structure stability and integrity of aerobic granules on ATP and cell communication. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 97(11): 5105–5112
Li X Y, Yang S F (2007). Influence of loosely bound extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on the flocculation, sedimentation and dewaterability of activated sludge. Water Research, 41(5): 1022–1030
Li Y, Li A M, Xu J, Liu B, Fu L C, Li W W, Yu H Q (2012). SMP production by activated sludge in the presence of a metabolic uncoupler, 3,3′,4′,5-tetrachlorosalicylanilide (TCS). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 95(5): 1313–1321
Liu Y (2000). Effect of chemical uncoupler on the observed growth yield in batch culture of activated sludge. Water Research, 34(7): 2025–2030
Maqbool T, Quang V L, Cho J, Hur J (2016). Characterizing fluorescent dissolved organic matter in a membrane bioreactor via excitation-emission matrix combined with parallel factor analysis. Bioresource Technology, 209: 31–39
Meng F, Zhang H, Yang F, Zhang S, Li Y, Zhang X (2006). Identification of activated sludge properties affecting membrane fouling in submerged membrane bioreactors. Separation and Purification Technology, 51(1): 95–103
Meng F, Zhang S, Oh Y, Zhou Z, Shin H S, Chae S R (2017). Fouling in membrane bioreactors: An updated review. Water Research, 114: 151–180
Meng F, Zhou Z, Ni B J, Zheng X, Huang G, Jia X, Li S, Xiong Y, Kraume M (2011). Characterization of the size-fractionated biomacromolecules: Tracking their role and fate in a membrane bioreactor. Water Research, 45(15): 4661–4671
Peter-Varbanets M, Hammes F, Vital M, Pronk W (2010). Stabilization of flux during dead-end ultra-low pressure ultrafiltration. Water Research, 44(12): 3607–3616
Pons M N, Le Bonte S, Potier O (2004). Spectral analysis and fingerprinting for biomedia characterisation. Journal of Biotechnology, 113(1-3): 211–230
Tian Y, Zhang J, Wu D, Li Z, Cui Y (2013). Distribution variation of a metabolic uncoupler, 2,6-dichlorophenol (2,6-DCP) in long-term sludge culture and their effects on sludge reduction and biological inhibition. Water Research, 47(1): 279–288
Wang Z, Yu H, Ma J, Zheng X, Wu Z (2013). Recent advances in membrane bio-technologies for sludge reduction and treatment. Biotechnology Advances, 31(8): 1187–1199
Wei Y, Van Houten R T, Borger A R, Eikelboom D H, Fan Y (2003). Minimization of excess sludge production for biological wastewater treatment. Water Research, 37(18): 4453–4467
Xu H, Liu Y (2011). Control and cleaning of membrane biofouling by energy uncoupling and cellular communication. Environmental Science & Technology, 45(2): 595–601
Acknowledgments
This work was jointly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51608150), Open Project of State Key Laboratory of Urban Water Resource and Environment, Harbin Institute of Technology (No. ES201810-02), Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (No. E2017042), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation Grant (Nos. 2018T110303 and 2017M610210); and Heilongjiang Province Postdoctoral Science Foundation Grant (LBH-TZ14 and LBHZ16070).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Highlights
• Effects of metabolic uncouplers addition on sludge reduction were carried out.
• TCS addition effectively inhibited ATP synthesis and reduced sludge yield.
• The effluent quality such as TOC and ammonia deteriorated but not significantly.
• Suitable dosage retarded biofouling during sludge water recovery by UF membrane.
Electronic supplementary material
11783_2020_1238_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Co-application of energy uncoupling and ultrafiltration in sludge treatment: Evaluations of sludge reduction, supernatant recovery and membrane fouling control
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, A., Zhao, Y., Yan, Z. et al. Co-application of energy uncoupling and ultrafiltration in sludge treatment: Evaluations of sludge reduction, supernatant recovery and membrane fouling control. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 14, 59 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-020-1238-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-020-1238-9