Abstract
Solder joints can experience fatigue cracking at the interface between the solder and substrate during thermal cycling due to the difference in thermal expansion between joined components. In order to strengthen the interfacial region and prevent cracking, two Cu pad surface treatments were studied on Sn-3Ag-0.5Cu solder, and on matte Sn plate and Ni plate coatings. The resulting intermetallic microstructures were characterized using scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive spectroscopy. Mechanical testing was performed using nano-indentation on the solder joints. The matte Sn plate on Cu sample formed an uneven distribution of Ag3Sn particles and a planar Cu6Sn5 interfacial intermetallic. The Ni-plated sample formed a needle-like Ni-rich interfacial intermetallic and uniform dispersion of Ag3Sn particles. The rough intermetallic compound (IMC)/solder interface and even IMC particle distribution cause the Ni-plated sample to experience reduced damage under board-level thermomechanical cycling because the interfacial structure reduces the Sn matrix recrystallization that contributes to fatigue cracking. In contrast, the matte Sn-plated sample exhibited an Ag3Sn particle-free zone adjacent to a planar Cu6Sn5 IMC layer which allows for rapid Sn recrystallization and fatigue crack propagation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
09 May 2020
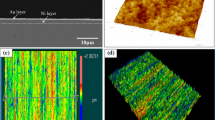
In the original article, there is an error in Fig.��1. Following is the corrected Fig.��1.
References
D.R. Frear, JOM 48, 49 (1996).
C. Chen and S.W. Liang, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 18, 259 (2007).
N. Chawla, Int. Mater. Rev. 54, 368 (2009).
W.Z. Hsieh, M.A. Rahman, T.H. Yang, T.T. Kuo, and C.E. Ho, Surf. Coat. Technol. 303, 112 (2016).
J. Han, F. Guo, and J.P. Liu, J. Alloys Compd. 704, 574 (2017).
L. Yin, L. Wentlent, L. Yang, B. Arfaei, A. Oasaimeh, and P. Borgesen, J. Electron. Mater. 41, 241 (2012).
Y. Zhu, X. Li, R. Gao, and C. Wang, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 25, 3863 (2014).
N.M. Shaffiar, A.F.M. Yamin, W.K. Loh and M.N. Tamin, in IEEE 14th Electronic Packaging Technology Conference (2012).
A.R. Fix, W. Nuchter, and J. Wilde, Solder. Surf. MT. Tech. 20, 13 (2008).
P.L. Liu and J.K. Shang, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 31A, 2867 (2000).
K.N. Subramanian and J.G. Lee, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 421, 46 (2006).
T. Bieler, B. Zhou, L. Blair, A. Zamiri, P. Darbandi, F. Pourboghrat, T.-K. Lee, and K.-C. Liu, J. Electron. Mater. 41, 2 (2012).
A.U. Telang, T.R. Bieler, D.E. Mason, and K.N. Subramanian, J. Electron. Mater. 32, 1455 (2003).
J.K. Shang and D. Yao, Trans. ASME 118, 41 (1996).
H.-T. Lee, M.-H. Chen, H.-M. Jao, and T.-L. Liao, Mater. Eng. A A358, 134 (2003).
F.X. Che and J.H.L. Pang, J. Alloys Compd. 541, 6 (2012).
T. An and F. Qin, Microelectron. Reliab. 54, 932 (2014).
J. Shen, D. Zhai, Z. Cao, M. Zhao, and Y. Pu, J. Electron. Mater. 43, 2 (2014).
J. Zhao, Y. Miyashita, and Y. Mutoh, Int. J. Fat. 23, 723 (2001).
R.M. Shalaby, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26, 6625 (2015).
M. Kerr and N. Chawla, Acta Mater. 52, 4527 (2004).
R.S. Sidhu and N. Chawla, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 39A, 799 (2008).
R.D. Doherty, D.A. Hughes, F.J. Humphreys, J.J. Jonas, D. Juul Jensen, M.E. Kassner, W.E. King, T.R. McNelley, H.J. McQueen, and A.D. Rollett, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 238, 219 (1997).
R.S. Sidhu, S.V. Madge, X. Deng, and N. Chawla, J. Electron. Mater. 36, 12 (2007).
D. Mu, H. Yasuda, H. Huang, and K. Nogita, J. Alloys Compd. 536, 38 (2012).
X. Deng, R.S. Sidhu, P. Johnson, and N. Chawla, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 36A, 55 (2005).
Y.-H. Baek, B.-M. Chung, Y.-S. Choi, J. Choi, and J.-Y. Huh, J. Alloys Compd. 579, 75 (2013).
M. Sona and K.N. Prabhu, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 24, 3149 (2013).
D.C. Yeh and H.B. Huntington, Phys. Rev. Lett. 53, 15 (1984).
M. He, A. Kumar, P.T. Yeo, G.J. Qi, and Z. Chen, Thin Solid Films 462, 387 (2004).
W.H. Chen, C.-F. Yu, H.-C. Cheng, Y.M. Tsai, and S.-T. Lu, Microelectron. Reliab. 53, 30 (2013).
C. Schmetterer, H. Flandorfer, K.W. Richter, and H. Ipser, J. Electron. Mater. 36, 11 (2007).
J. Gorlich, D. Baither, and G. Schmitz, Acta Mater. 58, 3187 (2010).
H. Gao, F. Wei, Y. Sui, Y. He, and Q. Meng, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30, 2186 (2019).
C.-M. Chuang and K.-L. Lin, J. Electron. Mater. 32, 12 (2003).
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr, J. Mater. Res. 7, 1564 (1992).
A.K. Gain and L. Zhang, Materialia 5, 100234 (2019).
L. Jiang, H. Jiang, and N. Chawla, J. Electron. Mater. 41, 2083 (2012).
D. Kim, J.-H. Chang, J. Park, and J.J. Pak, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 22, 703 (2011).
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge funding for this research from NXP, as well as the use of facilities at the Center for 4D Materials Science at Arizona State University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kelly, M.B., Maity, T., Nazmus Sakib, A.R. et al. Influence of Substrate Surface Finish Metallurgy on Lead-Free Solder Joint Microstructure with Implications for Board-Level Reliability. J. Electron. Mater. 49, 3251–3258 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-020-08013-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-020-08013-0