Abstract
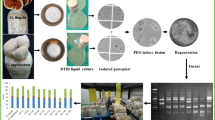
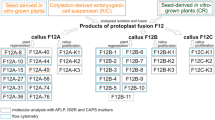
The commercial production of Morchella mushrooms calls for urgent breeding of excellent varieties or strains with appropriate tools, such as protoplast fusion. However, the protoplast fusion in morels has not been studied. In this paper, interspecific hybridization between cultivated morels of M. importuna and M. sextelata by PEG-induced protoplast fusion was conducted. Apart from functional complementation of double inactivated protoplasts, the fusants were characterized by cultural and cultivated characters and molecular markers of random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD). The results suggested that the hybrids and their parents showed significant difference in their inoculum recovery time, mycelial growth rate, yield of cultivation and total amino acid content of ascocarps. Moreover, positive barrage reactions were observed between parental strains as well as between each parent and a hybrid line. A dendrogram created on the basis of RAPD fingerprints exhibited three major clusters, in which morel hybrids showed intra-cluster variations, M. sextelata #6 formed an out group, while M. importuna #4 was phylogenetically closer to morel hybrids. All the results demonstrated that real fusants were obtained in our study. Protoplast fusion may provide an ideal alternative for new strain selection, and thus will promote the healthy development of morel industry.
Graphic Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- CYM:
-
Complete yeast extracts medium
- GB:
-
Guo Biao (Chinese National Standard)
- PEG:
-
Polyethylene glycol
- RAPD:
-
Random amplified polymorphic DNA
- RCYM:
-
CYM supplemented with 0.6 M mannitol
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- UPGMA:
-
Unweighted pair-group method with mathematic averages
References
Anderson FB, Millband JW (1966) Protoplast formation and yeast cell-wall structure. Biochem J 99:682–687
Bok JW, Choi EC, Kim BK (1994) Studies on protoplast fusion between Lentinula edodes and Ganoderma lucidum. Arch Pharm Res 17:492–496
Carris LM, Peever T, McCotter SW (2015) Mitospore stages of Disciotis, Gyromitra and Morchella in the inland Pacific Northwest USA. Mycologia 107:729–744. https://doi.org/10.3852/14-207
Chai H, Chen L, Chen W, Zhao Q, Zhang X, Su K, Zhao Y (2017) Characterization of mating-type idiomorphs suggests that Morchella importuna, Mel-20 and M. sextelata are heterothallic. Mycol Prog 16:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-017-1309-x
Chakraborty U, Sikdar SR (2008) Production and characterization of somatic hybrids raised through protoplast fusion between edible mushroom strains Volvariella volvacea and Pleurotus florida. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:1481–1492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-007-9630-1
Chakraborty U, Sikdar SR (2010) Intergeneric protoplast fusion between Calocybe indica (milky mushroom) and Pleurotus florida aids in the qualitative and quantitative improvement of sporophore of the milky mushroom. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 26:213–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-009-0162-8
Chang ST, Li GSF, Peberdy JF (1985) Isolation of protoplast from edible fungi. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 1:185–193
Chen F, Tan F, Liu X (2007) Preparation and regeneration of protoplasts from Morchella spp. Southwest China J Agric Sci 20:1097–1100
Chen J, Zeng J, Tang S, Pang H (2003) The culture condition and the protoplast preparation of the Morchella angusticeps. Journal of Northwest Normal University (Natural Science) 39(4):74–75,79
Cui Z, Luo X (2003) Protoplast isolation and regeneration of Morchella. Mycosystema 22:498–501
Dhitaphichit P, Pornsuriya C (2005) Protoplast fusion between Pleurotus ostreatus (Jacq.:Fr.) P. Kumm and P. citrinopileatus Singer. Int J Medicinal Mushrooms 7:397
Djajanegara I, Masduki A (2010) Protoplast fusion between white and brown oyster mushrooms. Indones J Agric Sci 11:16–23
Dolgleish HJ, Jacobson KM (2005) A first assessment of genetic variation among Morchella esculenta (Morel) populations. J Heredity 96:396–403. https://doi.org/10.1093/jhered/esi045
Du X, Zhao Q, Xia E, Gao L, Richard F, Yang Z (2017) Mixed-reproductive strategies, competitive mating-type distribution and life cycle of fourteen black morel species. Sci Rep 7:1493. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-01682-8
Eyini M, Rajkumar K, Balaji P (2006) Isolation, regeneration and PEG-induced fusion of protoplasts of Pleurotus pulmonarius and Pleurotus florida. Mycobiology 34:73–78
Gessner RV, Romano MA, Schultz RW (1987) Allelic variation and segregation in Morchella deliciosa and M. esculenta. Mycologia 79:683–687
Gupta AK, Gautam SP (1995) Improved production of extracellular α-amylase, by the thermophilic fungus Malbranchea sulfurea, following protoplast fusion. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 11:193–195
He P, Cai Y, Liu S, Han L, Huang L, Liu W (2015) Morphological and ultrastructural examination of senescence in Morchella elata. Micron 78:79–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micron.2015.07.010
He P, Wang K, Cai Y, Liu W (2017) Live cell confocal laser imaging studies on the nuclear behavior during meiosis and ascosporogenesis in Morchella importuna under artificial cultivation. Micron 101:108–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micron.2017.06.012
He B, You L, Ye Z, Guo L, Lin J, Wei T, Zheng Q (2018a) Construction of novel cold-tolerant strains of Volvariella volvacea through protoplast fusion between Volvariella volvacea and Pleurotus eryngii. Sci Hortic-Amsterdam 230:161–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2017.12.003
He P, Wang K, Cai Y, Hu X, Zheng Y, Zhang J, Liu W (2018b) Involvement of autophagy and apoptosis and lipid accumulation in sclerotial morphogenesis of Morchella importuna. Micron 109:34–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micron.2018.03.005
He X, Zhao M, Wang Y, Zhang N, Tan R, Wang Y, Zhu W, Chen B (2019) Study on the hyphal fusion and non-fusion phenomena between morels. Edible Med Mushrooms 27:244–252
Kim C, Choi EC, Kim BK (1997) Protoplast fusion between Lentinula edodes and Coriolus versicolor. Arch Pharm Res 20:448–453
Kirimura K, Sato T, Nakanishi N, Terada M, Usami S (1997) Breeding of starch-utilizing and itaconic-acid-producing koji molds by interspecific protoplast fusion between Aspergillus terreus and Aspergillus usamii. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 47:127–131
Kuo M, Dewsbury DR, O'Donnell K et al (2012) Taxonomic revision of true morels (Morchella) in Canada and the United States. Mycologia 104:1159–1177. https://doi.org/10.2307/23488822
Linardi VR, Carvalho CM, Dias AA (1993) Intraspecific protoplast fusion of amylase-producing strains of Candida fennica. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 9:601–602
Liu S, Mao J, You Y, Wu Y, Huang J, Yang Z (2008) Study on protoplast preparation and regeneration of Morchella crassipes. China Brewing 15:16–18
Liu W, Cai Y, He P, Zhang Y, Bian Y (2016) Morphological and structural analysis of mitospore of Morchella importuna. J Fungal Res 14:157–161
Liu W, Zhang Y, He P (2017) The Biology and Cultivation of Morchella Mushrooms. Jilin Science and Technology Press, Changchun
Liu Q, Ma H, Zhang Y, Dong C (2018a) Artificial cultivation of true morels: current state, issues and perspectives. Cri Rev Biotechnol 38:259–271. https://doi.org/10.1080/07388551.2017.1333082
Liu W, Chen L, Cai Y, Zhang Q, Bian Y (2018b) Opposite polarity monospore genome de novo sequencing and comparative analysis reveal the possible heterothallic life cycle of Morchella importuna. Int J Mol Sci 19:2525. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092525
Liu W, Lan A, Zhang Q, Cai Y, Ma X, Bian Y (2018c) Genetic diversity analyses and species specificity RAPD-SCAR marker exploitation of the cultivated Morchella strains. Mycosystema 37:1650–1660
Liu W, Cai Y, He P, Bian Y (2019) Cultivation of monosporic and hybrid populations and polarity analysis of Morchella importuna. J Fungal Res 17:43–49
Menczel L (1984) Inactivation of protoplasts before fusion to facilitate selective recovery of fusion-derived clones. In: Vasil IK (ed) Cell culture and somatic cell genetics of plants. Academic Press, pp 428–432.
Mendoza CG (1992) Cell wall structure and protoplast reversion in basidiomycetes. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 8(Supplement 1):36–38
Moriguchi M, Kotegawa S (1985) Preparation and regeneration of protoplasts from mycelia of Morchella esculenta. Agric Biol Chem 49:2791–2793
Okamura T, Takeno T, Dohi M et al (2000) Development of mushrooms for thrombosis prevention by protoplast fusion. J Biosci Bioeng 89:474–478
Pagliaccia D, Douhan GW, Douhan L, Peever TL, Carris LM, Kerrigan JL (2011) Development of molecular markers and preliminary investigation of the population structure and mating system in one lineage of black morel (Morchella elata) in the Pacific Northwestern USA. Mycologia 103:969–982. https://doi.org/10.3852/10-384
Peberdy JF (1989) Fungi without coats—protoplasts as tools for mycological research. Mycol Res 93:1–20
Pilz D, McLain R, Alexander S et al (2007) Ecology and management of morels harvested from the forests of western North America. Gen. Tech. Rep. PNW-GTR-710. USDA Forest Service, Pacific Northwest Research Station, Portland, Oregon, p 161
Qiu J, Liao H, Wu Y (1982) Preparation of an enzyme for lysing the cell wall of higher Basidiomycetes. Hereditas (Beijing) 4(4):13–14
Rayner ADM (1991) The challenge of the individualistic mycelium. Mycologia 83:48–71
Richard F, Bellanger JM, Clowez P et al (2015) True morels (Morchella Pezizales) of Europe and North America: evolutionary relationships inferred from multilocus data and a unified taxonomy. Mycologia 107:359–382. https://doi.org/10.3852/14-166
Ruíz-Herrera J, Osorio U (1974) Isolation and chemical analysis of the cell wall of Morchella sp. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 40:57–64
Selvakumar P, Rajasekar S, Babu AG, Periasamy K, Raaman N, Reddy MS (2015) Improving biological efficiency of Pleurotus strain through protoplast fusion between P. ostreatus var. florida and P. djamor var. roseus. Food Sci Biotechnol 24:1741–1748. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-015-0226-5
Singh RI, Aarti K, Singh SS (2007) Formation of interspecies fusants of Agaricus bisporus and Agaricus bitorquis mushroom by protoplast fusion. Indian J Microbiol 47:369–372
Tietel Z, Masaphy S (2018) True morels (Morchella)—nutritional and phytochemical composition, health benefits and flavor: a review. Crit Rev Food Sci 58:1888–1901. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2017.1285269
Volk TJ, Leonard TJ (1989) Experimental studies on the Morel. I. Heterokaryon formation between monoascosporus strains of Morchella. Mycologia 81:523–531
Volk TJ, Leonard TJ (1990) Cytology of the life-cycle of Morchella. Mycol Res 94:399–406
Yan P, Hui J, Shan C (2004) Characterization of protoplasts prepared from the edible fungus, Stropharia rugosoannulata. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 20:173–177
Yoo YB, Lee HS (1994) Interspecific hybridization between Pleurotus ostreatus and Pleurotus sajor-caju by protoplast fusion. Kor J Mycol 22:378–385
Yoo YB, Lee KH, Kim BG (2002) Characterization of somatic hybrids with compatible and incompatible species by protoplast fusion in genera Pleurotus (Fr.) P. Karst. and Ganoderma P. Karst. by RAPD-PCR analysis. Int J Med Mushrooms 4:147–157
Yoo YB, You CH, Shin PG, Park YH, Chang KY (1987) Transfer of isolated nuclei from Pleurotus florida into protoplasts of Pleurotus ostreatus. Kor J Mycol 15:250–253
Zhang J, Zheng Y, Chen M, Ji A (1989) Protoplast isolation and its regeneration of Morchella conica. Acta Botanica Yunnanica 11:449–452
Zhao D, Wu B, Zhang Y, Jia H, Zhang X, Cheng S (2009) Identification of protoplast fusion strain Fhhh by randomly amplified polymorphic DNA. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:1181–1188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-009-9999-0
Zhao J, Chang ST (1993) Monokaryotization by protoplasting heterothallic species of edible mushrooms. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 9:538–543
Zhao J, Chang ST (1995) Intraspecific hybridization between Coprinus cinereus and Schizophyllum commune by PEG-induced protoplast fusion and electrofusion. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 11:585–590
Zhao J, Chang ST (1996) Intergeneric hybridization between Pleurotus ostreatus and Schizophyllum commune by PEG-induced protoplast fusion. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 12:573–578
Zhao J, Chang ST (1997) Interspecific hybridization between Volvariella volvacea and V. bombycina by PEG-induced protoplast fusion. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 13:145–151
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, P., Yu, M., Wang, K. et al. Interspecific hybridization between cultivated morels Morchella importuna and Morchella sextelata by PEG-induced double inactivated protoplast fusion. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 36, 58 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-020-02835-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-020-02835-0