Bacterial Immunity: An adaptable defense
Many bacteria use a system known as CRISPR-Cas to defend themselves against infection by viruses called phages. This system protects the bacterial cell by taking a short length of DNA from the phage and inserting this 'spacer' into its own genome. If the bacterial cell becomes re-infected, the spacer allows the cell to recognize the phage and stop it from replicating by cutting and destroying its DNA. Bacteria with these spacers survive infections and pass their spacers on to their progeny, creating a population that is resistant to the phage.
Phage populations, however, can also adapt and evade bacterial CRISPR-Cas systems. For example, if a phage develops a random mutation in the region targeted by the spacer, it may become undetectable by CRISPR-Cas, leaving it free to replicate and infect other cells (Barrangou et al., 2007; Deveau et al., 2008). Bacteria can combat these phages by creating multiple spacers that target different regions of the phage genome (van Houte et al., 2016; Figure 1). However, previous studies have shown that bacteria rarely acquire multiple spacers (Heler et al., 2015). Now, in eLife, Nora Pyenson and Luciano Marraffini from the Rockefeller University report that the number of spacers each bacterial cell acquires depends on its local environment (Pyenson and Marraffini, 2020).
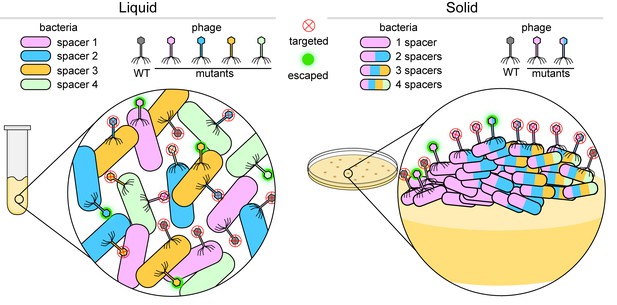
Bacteria versus viruses called phages.
To defend themselves against phages, bacteria (colored capsules) acquire a region of a phage genome and insert it into their own genome as a 'spacer'. When growing in a liquid environment (left), individual bacterial cells usually acquire a single spacer that targets just one region of the wild-type (WT) phage (shown in grey). In the figure, each bacterial cell has one of four different spacers (shown in blue, green, orange and pink). However, phages mutate in an effort to bypass these defenses: a mutation in the region of the phage genome corresponding to, say, a blue spacer means that the phage can attack and escape the defense of bacteria with blue spacers (fuzzy green circle), but not bacteria with green, orange or pink spacers (red X inside a circle). When growing on a solid surface (right), if an individual cell acquires, say, a pink spacer, it will go on to form a colony of phage resistant cells (inset). If a phage gains a mutation in the region targeted by the pink spacer, the phage will escape detection. In order to stay protected, some bacterial cells within the colony acquire multiple spacers (multi-colored bacterial cells) and can fight off various mutant phages.
Image credit: Dipali Sashital (CC BY 4.0)
Bacteria grown in liquid culture rarely have multiple spacers. Pyenson and Marraffini hypothesized that this is because bacterial cells move more freely when in this environment and are thus able to work together to defend themselves (Figure 1, left). This limits the need for individual cells to have multiple spacers in order to be protected. To test this theory, Pyenson and Marraffini investigated what happens to infected bacteria that are grown on a solid medium where cell movement is restricted. They found that most cells died, but those that acquired resistance formed separate colonies. Further experiments showed that compared to bacteria grown in liquid culture, bacterial cells in the resistant colonies had often acquired multiple spacers and were able to fight off phages with other mutations (Figure 1, right).
However, it still remained unclear what drives bacteria to acquire multiple spacers. It was previously shown that acquiring an initial spacer can drive the addition of subsequent spacers through a process called priming (Datsenko et al., 2012; Nussenzweig et al., 2019). Pyenson and Marraffini found that a disproportionate number of second spacers were taken from DNA regions located close to the initial spacer, which is a hallmark of priming. This suggests that priming enables immobile bacteria to survive mutated phages that have escaped detection by allowing the bacteria to create multiple spacers.
Cells in these resistant colonies arranged themselves into unusually shaped sectors, with the number and type of spacers present varying between cells in each sector. It seems that when bacteria are immobilized, individual cells within the colony must acquire more spacers to resist infection by the mutated phage (Figure 1, right). The new multi-spacer cells then outgrow the rest of the colony, forming these unusually shaped sectors. These findings suggest that bacteria cooperate and share the spacer load in a liquid environment. On a solid surface, on the other hand, the bacteria are more independent, and if a cell becomes immune to a mutated phage, it will form a new colony sector with its progeny.
In nature, bacteria are often attached to surfaces. For example, some bacteria live at the bottom of bodies of water, and these bacterial communities may be regularly targeted by phages (Tuson and Weibel, 2013). Bacteria also gather on biological surfaces when preparing to invade other organisms. For example, the bacteria Streptococcus preferentially bind and form colonies on mucus membrane surfaces in the human body before infecting epithelial cells (Beachey, 1981). The study by Pyenson and Marraffini reveals how different types of environments may influence the way that bacteria and phages respond to each other and synchronously evolve over time.
CRISPR-Cas systems are exceptionally diverse and use a variety of mechanisms to defend bacteria against infection. Further experiments studying these systems in a variety of environmental contexts will be important to help explain the diverse mechanisms of CRISPR-Cas systems.
References
-
Bacterial adherence: adhesin-receptor interactions mediating the attachment of bacteria to mucosal surfaceJournal of Infectious Diseases 143:325–345.https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/143.3.325
-
Phage response to CRISPR-encoded resistance in Streptococcus thermophilusJournal of Bacteriology 190:1390–1400.https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.01412-07
Article and author information
Author details
Publication history
- Version of Record published: March 30, 2020 (version 1)
Copyright
© 2020, Schelling and Sashital
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use and redistribution provided that the original author and source are credited.
Metrics
-
- 5,864
- views
-
- 297
- downloads
-
- 2
- citations
Views, downloads and citations are aggregated across all versions of this paper published by eLife.
Download links
Downloads (link to download the article as PDF)
Open citations (links to open the citations from this article in various online reference manager services)
Cite this article (links to download the citations from this article in formats compatible with various reference manager tools)
Further reading
-
- Microbiology and Infectious Disease
In the Firmicutes phylum, GpsB is a membrane associated protein that coordinates peptidoglycan synthesis with cell growth and division. Although GpsB has been studied in several bacteria, the structure, function, and interactome of Staphylococcus aureus GpsB is largely uncharacterized. To address this knowledge gap, we solved the crystal structure of the N-terminal domain of S. aureus GpsB, which adopts an atypical, asymmetric dimer, and demonstrates major conformational flexibility that can be mapped to a hinge region formed by a three-residue insertion exclusive to Staphylococci. When this three-residue insertion is excised, its thermal stability increases, and the mutant no longer produces a previously reported lethal phenotype when overexpressed in Bacillus subtilis. In S. aureus, we show that these hinge mutants are less functional and speculate that the conformational flexibility imparted by the hinge region may serve as a dynamic switch to finetune the function of the GpsB complex and/or to promote interaction with its various partners. Furthermore, we provide the first biochemical, biophysical, and crystallographic evidence that the N-terminal domain of GpsB binds not only PBP4, but also FtsZ, through a conserved recognition motif located on their C-termini, thus coupling peptidoglycan synthesis to cell division. Taken together, the unique structure of S. aureus GpsB and its direct interaction with FtsZ/PBP4 provide deeper insight into the central role of GpsB in S. aureus cell division.
-
- Microbiology and Infectious Disease
Mechanisms by which Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) evades pathogen recognition receptor activation during infection may offer insights for the development of improved tuberculosis (TB) vaccines. Whilst Mtb elicits NOD-2 activation through host recognition of its peptidoglycan-derived muramyl dipeptide (MDP), it masks the endogenous NOD-1 ligand through amidation of glutamate at the second position in peptidoglycan side-chains. As the current BCG vaccine is derived from pathogenic mycobacteria, a similar situation prevails. To alleviate this masking ability and to potentially improve efficacy of the BCG vaccine, we used CRISPRi to inhibit expression of the essential enzyme pair, MurT-GatD, implicated in amidation of peptidoglycan side-chains. We demonstrate that depletion of these enzymes results in reduced growth, cell wall defects, increased susceptibility to antibiotics, altered spatial localization of new peptidoglycan and increased NOD-1 expression in macrophages. In cell culture experiments, training of a human monocyte cell line with this recombinant BCG yielded improved control of Mtb growth. In the murine model of TB infection, we demonstrate that depletion of MurT-GatD in BCG, which is expected to unmask the D-glutamate diaminopimelate (iE-DAP) NOD-1 ligand, yields superior prevention of TB disease compared to the standard BCG vaccine. In vitro and in vivo experiments in this study demonstrate the feasibility of gene regulation platforms such as CRISPRi to alter antigen presentation in BCG in a bespoke manner that tunes immunity towards more effective protection against TB disease.






