Abstract
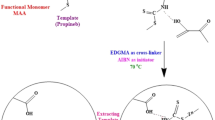
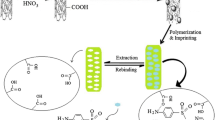
In the present study, sulfamethazine-imprinted polymers have been prepared by bulk polymerization method with a living radical photopolymerization using sulfamethazine (SM2) as the template molecule, methacrylic acid (MAA) as the functional monomer, ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA) as the cross-linker, and azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN) as the initiator in the porogenic solvent of acetonitrile. After estimating the recognition properties, the imprinting factor of the polymer reached up to 9.3779. Then, the polymer particles were incorporated into a solid-phase extraction (SPE) column for the selective separation and purification of the sulfonamides (SAs), including sulfadiazine (SD), sulfamerazine (SM1), and SM2, from edible swine tissues. By using the detection method of high-performance liquid chromatography with the optimum SPE conditions, the limits of detection and limits of quantitation were calculated as 0.7–2.3 μg kg−1 and 3.4–4.6 μg kg−1 in the complex samples, respectively. The recovery of SAs ranged from 85.5 to 88.3%. Compared with the commonly used Waters Oasis HLB® column, the proposed selective SM2-MI-SPE column has opened a promising new approach for trace enrichment of the residues. It will facilitate sulfonamide residue analysis in animal tissues.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdallah H, Arnaudguilhem C, Lobinski R, Jaber F (2015) A multi-residue analysis of sulphonamides in edible animal tissues using QuEChERS extraction and HPLC-MS/MS. Anal Methods 7:1549–1557. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ay01727g
Almeida SAA, Moreira FTC, Heitor AM, Montenegro MCBSM, Aguilar GG, Sales MGF (2011) Sulphonamide-imprinted sol-gel materials as ionophores in potentiometric transduction. Mater Sci Eng C-Mater Biol Appl 31:1784–1790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2011.08.011
Arroyo Manzanares N, Lara FJ, Airado Rodriguez D, Gamiz Gracia L, Garcia Campana AM (2015) Determination of sulfonamides in serum by on-line solid-phase extraction coupled to liquid chromatography with photoinduced fluorescence detection. Talanta 138:258–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.03.012
Chen L, Wang X, Lu W, Wu X, Li J (2016) Molecular imprinting: perspectives and applications. Chem Soc Rev 45:2137–2211. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6cs00061d
Chen X, Li Z, Guo J, Li D, Gao H, Wang Y, Xu C (2017) Simultaneous screening for marbofloxacin and ofloxacin residues in animal-derived foods using an indirect competitive immunoassay. Food Agric Immunol 28:489–499. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540105.2017.1297780
Dibbern DA Jr, Montanaro A (2008) Allergies to sulfonamide antibiotics and sulfur-containing drugs. Ann Allerg Asthma Im 100:91–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1081-1206(10)60415-2
European Commission (2009) Regulation No 37/2010/EC of 22 December 2009 on pharmacologically active substances and their classification regarding maximum residue limits in foodstuffs of animal origin, Off. J Euro Union L15 1–72
FAO (2020) Statistics. http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QL. Accessed 5th March 2020
Fuh MRS, Chu SY (2003) Quantitative determination of sulfonamide in meat by solid-phase extraction and capillary electrophoresis. Anal Chim Acta 499:215–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(03)00721-9
Gao R, Zhang J, He X, Chen L, Zhang Y (2010) Selective extraction of sulfonamides from food by use of silica-coated molecularly imprinted polymer nanospheres. Anal Bioanal Chem 398:451–461. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-3909-z
Haupt K (2003) Imprinted polymers-tailor-made mimics of antibodies and receptors. Chem Commun: 171–178. https://doi.org/10.1039/b207596b
He C, Long Y, Pan J, Li K, Liu F (2007a) Application of molecularly imprinted polymers to solid-phase extraction of analytes from real samples. J Biochem Biophys Methods 70:133–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbbm.2006.07.005
He J, Zhu Q, Deng Q (2007b) Investigation of imprinting parameters and their recognition nature for quinine-molecularly imprinted polymers. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 67:1297–1305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2006.09.040
He J, Wang S, Fang G, Zhu H, Zhang Y (2008) Molecularly imprinted polymer online solid-phase extraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography-UV for the determination of three sulfonamides in pork and chicken. J Agric Food Chem 56:2919–2925. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf703680q
He X, Tan L, Wu W, Wang J (2016) Determination of sulfadiazine in eggs using molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography. J Sep Sci 39:2204–2212. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201600233
Huang YH, Xu Y, He QH, Cao YS, Du BB (2012) Determination of sulfadiazine residues in pork by molecular imprinted column coupling with high performance liquid chromatography. Chin J Anal Chem 40:1011–1016. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1872-2040(11)60558-6
Kechagia M, Samanidou V, Kabir A, Furton KG (2018) One-pot synthesis of a multi-template molecularly imprinted polymer for the extraction of six sulfonamide residues from milk before high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection. J Sep Sci 41:723–731. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201701205
Kim HJ, Jeong MH, Park HJ, Kim WC, Kim JE (2016) Development of an immunoaffinity chromatography and HPLC-UV method for determination of 16 sulfonamides in feed. Food Chem 196:1144–1149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.10.014
Kugimiya A, Takei H (2008) Selectivity and recovery performance of phosphate-selective molecularly imprinted polymer. Anal Chim Acta 606:252–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2007.11.025
Littlefield NA, Sheldon WG, Allen R, Gaylor DW (1990) Chronic toxicity/carcinogenicity studies of sulphamethazine in Fischer 344/N rats: two-generation exposure. Food Chem Toxicol 28:157–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/0278-6915(90)90004-7
Liu Y, Liu X, Wang J (2003) The adsorption property of nicotine-imprinted polymer. Chin J Anal Chem 31:1202–1206. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02974893
Liu J, Jiang M, Li G, Xu L, Xie M (2010) Miniaturized salting-out liquid-liquid extraction of sulfonamides from different matrices. Anal Chim Acta 679:74–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2010.09.013
Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China (2002) Announcement NO. 235. Maximum residue limit of veterinary drugs in animal food. http://www.moa.gov.cn/zwllm/tzgg/gg/200302/t 20030226_59300.htm. Accessed 27 Aug 2019
Neu HC (1992) The crisis in antibiotic resistance. Science 257:1064–1073. https://doi.org/10.1126/science 257.5073. 1064
Shi X, Meng Y, Liu J, Sun A, Li D, Yao C, Lu Y, Chen J (2011) Group-selective molecularly imprinted polymer solid-phase extraction for the simultaneous determination of six sulfonamides in aquaculture products. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 879:1071–1076. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2011.03.019
Sun H, Ai L, Wang F (2007) Quantitative analysis of sulfonamide residues in natural animal casings by HPLC. Chromatographia 66:333–337. https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-007-0329-0
Tian J, Bai J, Peng Y, Qie Z, Zhao Y, Ning B, Xiao D, Gao Z (2015) A core-shell-structured molecularly imprinted polymer on upconverting nanoparticles for selective and sensitive fluorescence sensing of sulfamethazine. Analyst 140:5301–5307. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5an00579e
United States (2019) Electronic Code of Federal Regulations. Tolerances for residues of new animal drugs in food. https://www.ecfr.gov/cgi-bin/text-idx?SID=2073af19efe77450247d95b9fa53f5bd&mc=true&node=20190711y1.26. Accessed 27 Aug 2019
Wang Y et al (2019) Development of an immunochromatographic strip test for the rapid detection of soybean Bowman-Birk inhibitor. Food Agric Immunol 30:1202–1211. https://doi.org/10.1080/09540105.2019.1680613
Xie X, Liu X, Pan X, Chen L, Wang S (2016) Surface-imprinted magnetic particles for highly selective sulfonamides recognition prepared by reversible addition fragmentation chain transfer polymerization. Anal Bioanal Chem 408:963–970. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-9190-4
Xu W, Su S, Jiang P, Wang H, Dong X, Zhang M (2010) Determination of sulfonamides in bovine milk with column-switching high performance liquid chromatography using surface imprinted silica with hydrophilic external layer as restricted access and selective extraction material. J Chromatogr A 1217:7198–7207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2010.09.035
Yan S, Gao Z, Fang Y (2006) Preparation and affinity assessment of monocrotophos molecularly imprinted polymers. Acta Polym Sin: 160-163. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1105.2006.00160
Yang F, Huang XH, Li GH, Ni HJ, Zhao YD, Ding HZ, Zeng ZL (2013) Estimating tulathromycin withdrawal time in pigs using a physiologically based pharmacokinetics model. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess 30:1255–1263. https://doi.org/10.1080/19440049.2013.797113
Yang F, Yang F, Wang G, Kong T, Wang H, Zhang C (2020) Effects of water temperature on tissue depletion of florfenicol and its metabolite florfenicol amine in crucian carp (Carassius auratus gibelio) following multiple oral doses. Aquaculture 515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2019.734542
Yavuz H, Karakoc V, Turkmen D, Say R, Denizli A (2007) Synthesis of cholesterol imprinted polymeric particles. Int J Biol Macromol 41:8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2006.11.011
Yu H, Tao Y, Chen D, Wang Y, Huang L, Peng D, Dai M, Liu Z, Wang X, Yang Z (2011) Development of a high performance liquid chromatography method and a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method with the pressurized liquid extraction for the quantification and confirmation of sulfonamides in the foods of animal origin. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 879:2653–2662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2011.07.032
Zhang Y, Na Q, Chen N, Chen J, Zhou X, Bai L (2013) Preparation and evaluation of melamine molecularly imprinted polymers by thermal-and photo-initiation methods. J Chin Chem Soc (Taipei, Taiwan) 60:204–211. https://doi.org/10.1002/jccs.201200382
Zhao X, Wang J, Wang J, Wang S (2018) Development of water-compatible molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction coupled with high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the detection of six sulfonamides in animal-derived foods. J Chromatogr A 1574:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.08.044
Zheng N, Fu Q, Li Y, Chang W, Wang Z, Li T (2001) Chromatographic characterization of sulfonamide imprinted polymers. Microchem J 69:55–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0026-265X(01)00076-5
Zhu X, Cao Q, Hou N, Wang G, Ding Z (2006) The preparation and the recognition property of molecularly imprinted polymer of podophyllotoxin. Anal Chim Acta 561:171–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2006.01.009
Acknowledgments
Special thanks to Dr. Shoulei Yan for his enthusiastic support in the preparation and characterization of the MIPs.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31772074) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2662017PY049, 2017BC010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Zhaozhou Li declare that he has no conflict of interest. Yulian Wang declare that she has no conflict of interest. Zhenli Liu declare that he has no conflict of interest. Changqing Xie declare that he has no conflict of interest. Dapeng Peng declare that he has no conflict of interest. Zonghui Yuan declare that he has no conflict of interest. There is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service, and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in, or the review of, the manuscript entitled “Selective solid-phase extraction of sulphonamides from edible swine tissues using high-performance imprinted polymers.”
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human subjects. All animal experiments that described in the present study were performed in adherence to Huazhong Agricultural University animal experiment center guidelines and approved by Animal Ethics Committee.
Informed Consent
Informed consent not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Wang, Y., Liu, Z. et al. Selective Solid-Phase Extraction of Sulfonamides from Edible Swine Tissues Using High-Performance Imprinted Polymers. Food Anal. Methods 13, 1304–1313 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-020-01751-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-020-01751-1