Abstract
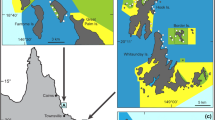
Reef-forming species play a key role creating, modifying and maintaining important habitat and their associated communities. Globally, many of these habitats are extensively fragmented but our understanding of key ecological processes is drawn from older studies performed in less degraded environments with extensive reef habitats. We tested whether proximity to habitat edges affected the persistence and functioning of fragmented intertidal mussel reefs, Mytilus edulis, at three sites in sedimentary habitats in Northern Ireland. Specifically, we quantified and compared key ecological properties in mid-habitat and edges and hypothesised that at the edges, there would be (i) larger individual mussels, (ii) lower recruitment, (iii) lower associated taxon diversity, (iv) lower biodeposition, (v) greater predation intensity and (vi) greater food availability. Additionally, we tested whether rates of functioning (e.g. organic matter accumulation) were greater in mussel patches (edge and mid-habitat) compared to sediment without mussels (vii). We did find larger mussels at the edges of patches, where there was also less organic enrichment of the sediment compared to mid-habitat (but more than areas without mussels). None of the other variables quanitifed differed consistently between the edge and mid-habitat. The lack of strong edge effects identified may be explained by the nature of the mussel habitat in this study, i.e. intrinsically greater proportion of edges compared to more extensive reefs. Our results suggest that at the scale of the reef patches in this study, edge effects were not as strong as previously thought in terms of regulating key ecological processes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, Marti J. 2006. Distance-based tests for homogeneity of multivariate dispersions. Biometrics 62 (1): 245–253. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1541-0420.2005.00440.x.
Anderson, Marti J., and Daniel C.I. Walsh. 2013. PERMANOVA, ANOSIM, and the mantel test in the face of heterogeneous dispersions: What null hypothesis are you testing? Ecological Monographs 83: 557–574. https://doi.org/10.1890/12-2010.1.
Angelini, Christine, and Brian R. Silliman. 2012. Patch size-dependent community recovery after massive disturbance. Ecology. Ecological Society of America 93: 101–110. https://doi.org/10.1890/11-0557.1.
Arribas, Lorena P., Donnarumma Luigia, M. Gabriela Palomo, and Ricardo A. Scrosati. 2014. Intertidal mussels as ecosystem engineers: Their associated invertebrate biodiversity under contrasting wave exposures. Marine Biodiversity 44 (2): 203–211. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-014-0201-z.
Barbier, Pierrick, Tarik Meziane, Martin Forêt, Réjean Tremblay, René Robert, and Frédéric Olivier. 2017. Nursery function of coastal temperate benthic habitats: New insight from the bivalve recruitment perspective. Journal of Sea Research 121: 11–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seares.2016.12.007.
Barrios-O’Neill, Daniel, Camilla Bertolini, and Patrick C. Collins. 2017. Trophic cascades and the transient keystone concept. Biological Conservation 212: 191–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2017.06.011.
Bates, Douglas. 2005. Fitting linear mixed models in R. R News 5: 27–30. https://doi.org/10.1159/000323281.
Beck, Michael W., Robert D. Brumbaugh, Laura Airoldi, Alvar Carranza, Loren D. Coen, Christine Crawford, Omar Defeo, et al. 2009. Shellfish reefs at risk: A global analysis of problems and solutions. Arlington: The nature conservancy.
Bell, Susan S., and Bradley T. Furman. 2017. Seascapes are landscapes after all; comment on Manderson (2016): Seascapes are not landscapes: An analysis performed using Bernhard Riemann’s rules. ICES Journal Of Marine Science 73: 1831–1838. https://doi.org/10.1093/icesjms/fsx070.
Bertolini, Camilla, W.I. Montgomery, and Nessa E. O’Connor. 2018. Habitat with small inter-structural spaces promotes mussel survival and reef generation. Marine Biology 165 (10): 163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-018-3426-8.
Bertolini, C., B. Cornelissen, J.J. Capelle, J. Van de Koppel, and T.J. Bouma. 2019. Putting self organization to the test: Labyrinthine patterns as optimal solution for persistence Oikos. 128(12): 1805–1815.
Bishop, Melanie J., and James E. Byers. 2015. Predation risk predicts use of a novel habitat. Oikos 124: 1225–1231. https://doi.org/10.1111/oik.01967.
Bolker, Benjamin M., Mollie E. Brooks, Connie J. Clark, Shane W. Geange, John R. Poulsen, M. Henry, H. Stevens, and Jada-Simone S. White. 2009. Generalized linear mixed models: a practical guide for ecology and evolution. Trends in Ecology & Evolution 24 (3): 127–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2008.10.008.
Boström, Christoffer. 2006. Seagrass landscapes and their effects on associated fauna: A review. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 68: 383–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2006.01.026.
Boström, Christoffer, Simon J. Pittman, Charles Simenstad, and Ronald T. Kneib. 2011. Seascape ecology of coastal biogenic habitats: Advances , gaps, and challenges. Marine Ecology Progress Series 427: 191–217. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps09051.
Briggs, R.P. 1982. Community structure and growth of Mytilus-Edulis in lough Foyle Northern Ireland Uk. Proceedings of the Royal Irish Academy Section B Biological Geological Chemical Science 82: 245–259.
Burrows, Michael T. 2012. Influences of wave fetch, tidal flow and ocean colour on subtidal rocky communities. Marine Ecology Progress Series 445: 193–207. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps09422.
Byers, James E., Zachary C. Holmes, and Jennafer C. Malek. 2017. Contrasting complexity of adjacent habitats influences the strength of cascading predatory effects. Oecologia 185: 107–117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-017-3928-y.
Calderwood, Julia, Nessa E. O’Connor, and Dai Roberts. 2015. Effects of baited crab pots on cultivated mussel (Mytilus edulis) survival rates. ICES Journal of Marine Science 71: 236–240. https://doi.org/10.1093/icesjms/fst176.
Calderwood, Julia, Nessa E. O’Connor, and Dai Roberts. 2016. Breaking and entering: Examining the role of stress and aerial exposure in predator-prey relationships between the common shore crab (Carcinus maenas) and cultivated blue mussels (Mytilus edulis). Aquaculture 452. Elsevier B.V.: 217–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2015.11.009.
Capelle, Jacob J., Jeroen W.M. Wijsman, Tim Schellekens, Marnix R. van Stralen, Peter M.J. Herman, and Aad C. Smaal. 2014. Spatial organisation and biomass development after relaying of mussel seed. Journal of Sea Research 85: 395–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seares.2013.07.011.
Capelle, Jacob J., Gerard Scheiberlich, Jeroen W.M. Wijsman, and Aad C. Smaal. 2016. The role of shore crabs and mussel density in mussel losses at a commercial intertidal mussel plot after seeding. Aquaculture International 24 (5): 1459–1472. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-016-0005-1.
Capelle, Jacob J., Marnix R. Van Stralen, Jeroen W.M. Wijsman, Peter M.J. Herman, and Aad C. Smaal. 2017. Population dynamics of subtidal blue mussels Mytilus edulis and the impact of cultivation. Aquaculture Environment Interactions 9: 155–168. https://doi.org/10.3354/aei00221.
Carroll, John M., and Bradley J. Peterson. 2013. Ecological trade-offs in seascape ecology: Bay scallop survival and growth across a seagrass seascape. Landscape Ecology 28 (7): 1401–1413. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-013-9893-x.
Clarke, K.R. 1993. Non-parametric multivariate analyses ofchanges in community structure. Australian Journal of Ecology 18: 117–143.
Commito, J.A., and N.M.J.A. Dankers. 2001. Dynamics of spatial and temporal complexity in European and north American soft-bottom mussel beds. In Ecological comparisons of sedimentary shores, 39–59. Berlin: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-56557-1_3.
Commito, John A., Wendy E. Dow, and Benjamin M. Grupe. 2006. Hierarchical spatial structure in soft-bottom mussel beds. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 330: 27–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jembe.2005.12.015.
Commito, John A., Serena Como, Benjamin M. Grupe, and Wendy E. Dow. 2008. Species diversity in the soft-bottom intertidal zone: Biogenic structure, sediment, and macrofauna across mussel bed spatial scales. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 366: 70–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jembe.2008.07.010.
Commito, John A., Ann E. Commito, Rutherford V. Platt, Benjamin M. Grupe, Wendy E. Dow Piniak, Natasha J.G. Gownaris, Kyle A. Reeves, and Allison M. Vissichelli. 2014. Recruitment facilitation and spatial pattern formation in soft-bottom mussel beds. Ecosphere 5: 1–26.
Commito, John A., Brittany R. Jones, Mitchell A. Jones, Sondra E. Winders, and Serena Como. 2018. What happens after mussels die? Biogenic legacy effects on community structure and ecosystem processes. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 506: 30–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JEMBE.2018.05.004.
Cosser, Phillip R. 1989. Water quality, sediments and the macroinvertebrate community of residential canal estates in south-East Queensland, Australia: A multivariate analysis. Water Research 23: 1087–1097. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(89)90152-8.
Crawford, Thomas W., John A. Commito, and Ann M. Borowik. 2006. Fractal characterization of Mytilus edulis L. spatial structure in intertidal landscapes using GIS methods. Landscape Ecology 21 (7): 1033–1044. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-006-0003-1.
Dean, Walter E., Jr. 1974. Determination of carbonate and organic matter in calcareous sediments and sedimentary rocks by loss on ignition: Comparison with other methods. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology 44: 242–248. https://doi.org/10.1306/74D729D2-2B21-11D7-8648000102C1865D.
Denny, Mark W. 1987. Lift as a mechanism of patch initiation in mussel beds. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 114: 231–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-0981(87)90103-1.
Despland, E. 2003. Fractal index captures the role of vegetation clumping in locust swarming. Functional Ecology 17: 315–322. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2435.2003.00728.x.
Donohue, Ian, Helmut Hillebrand, José M. Montoya, Owen L. Petchey, Stuart L. Pimm, Mike S. Fowler, Kevin Healy, A.L. Jackson, M. Lurgi, D. McClean, N.E. O'Connor, E.J. O'Gorman, and Q. Yang. 2016. Navigating the complexity of ecological stability. Ecology Letters 19 (9): 1172–1185. https://doi.org/10.1111/ele.12648.
Donovan, Therese M., Peter W. Jones, Elizabeth M. Annand, and Frank R. Thompson. 1997. Variation in local-scale edge effects: Mechanisms and landscape context. Ecology 78: 2064–2075. https://doi.org/10.1890/0012-9658(1997)078[2064:VILSEE]2.0.CO;2.
Duffy, J. Emmett, Shelby L. Ziegler, Justin E. Campbell, Paige M. Bippus, and Jonathan S. Lefcheck. 2015. Squidpops: A simple tool to Crowdsource a global map of marine predation intensity. PLoS One 10 (11): e0142994. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0142994.
Ermgassen, Zu, S.E. Philine, Mark D. Spalding, Brady Blake, Loren D. Coen, Brett Dumbauld, Steve Geiger, Jonathan H. Grabowski, et al. 2012. Historical ecology with real numbers: Past and present extent and biomass of an imperilled estuarine habitat. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 279: 3393–3400. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2012.0313.
Fahrig, Lenore. 2003. Effects of habitat fragmentation on biodiversity. Annual Review of Ecology Evolution and Systematics 34: 487–515. https://doi.org/10.1146/132419.
Fegley, Stephen R., Bruce A. MacDonald, and Timothy R. Jacobsen. 1992. Short-term variation in the quantity and quality of seston available to benthic suspension feeders. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 34: 393–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0272-7714(05)80078-2.
Frechette’, Marcel, Cheryl Ann Butman, and W. Rockwell Geyer. 1989. The importance of boundary-layer flows in supplying phytoplankton to the benthic suspension feeder, Mytilus edulis L. Limnology and Oceanography 34: 19–36.
Geraldi, Nathan R., Camilla Bertolini, Mark C. Emmerson, Dai Roberts, Julia D. Sigwart, and Nessa E. O’Connor. 2017. Aggregations of brittle stars can provide similar ecological roles as mussel reefs. Marine Ecology Progress Series 563: 157–167. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps11993.
Gillis, L.G., F.E. Belshe, A.D. Ziegler, and T.J. Bouma. 2017. Driving forces of organic carbon spatial distribution in the tropical seascape. Journal of Sea Research 120: 35–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seares.2016.12.006.
Gittman, Rachel K., F. Joel Fodrie, Christopher J. Baillie, Michelle C. Brodeur, Carolyn A. Currin, Danielle A. Keller, Matthew D. Kenworthy, Joseph P. Morton, Justin T. Ridge, and Y. Stacy Zhang. 2017. Living on the edge: Increasing patch size enhances the resilience and community Development of a restored salt marsh. Estuaries and Coasts 41 (3): 884–895. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-017-0302-6.
Grabowski, Jonathan H., and David L. Kimbro. 2005. Predator-avoidance behavior extends trophic cascades to refuge habitats. Ecology 86: 1312–1319.
Griffin, John N., Stuart R. Jenkins, Lars Gamfeldt, Douglas Jones, Stephen J. Hawkins, and Richard C. Thompson. 2009. Spatial heterogeneity increases the importance of species richness for an ecosystem process. Oikos 118: 1335–1342. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0706.2009.17572.x.
Guichard, Frédéric, Patti M. Halpin, Gary W. Allison, Jane Lubchenco, and Bruce A. Menge. 2003. Mussel disturbance dynamics: Signatures of oceanographic forcing from local interactions. The American Naturalist 161 (6): 889–904. https://doi.org/10.1086/375300.
Hanke, Marc H., Martin H. Posey, and Troy D. Alphin. 2017. The influence of habitat characteristics on intertidal oyster Crassostrea virginica population. Marine Ecology Progress Series 571: 121–138.
Harwell, Heather D., Martin H. Posey, and Troy D. Alphin. 2011. Landscape aspects of oyster reefs: Effects of fragmentation on habitat utilization. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 409: 30–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jembe.2011.07.036.
Hayward, Peter J., and John S. Ryland. 1995. Handbook of the marine fauna of North-West Europe. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Heath, Michael R., Douglas C. Speirs, and John H. Steele. 2014. Understanding patterns and processes in models of trophic cascades. Ecology Letters 17 (1): 101–114. https://doi.org/10.1111/ele.12200.
Henderson, Christopher J., Ben L. Gilby, Shing Y. Lee, and Tim Stevens. 2017. Contrasting effects of habitat complexity and connectivity on biodiversity in seagrass meadows. Marine Biology 164 (5): 117–119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-017-3149-2.
Humphries, Austin T., Megan K. La Peyre, and Gary a Decossas. 2011. The effect of structural complexity, prey density, and “predator-free space” on prey survivorship at created oyster reef mesocosms. PLoS One 6 (12): e28339. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0028339.
Johnson, Matthew W., and Kenneth L. Heck Jr. 2007. Habitat fragmentation influences survival and growth of transplanted northern quahog (Mercenaria mercenaria) in big lagoon, Florida. Journal of Shellfish Research 26: 1011–1019. https://doi.org/10.2983/0730-8000(2007)26.
Jones, Jess, Tim Lane, Brett Ostby, Braven Beaty, Steven Ahlstedt, Robert Butler, Don Hubbs, and Craig Walker. 2018. Collapse of the Pendleton Island mussel Fauna in the Clinch River, Virginia: Setting baseline conditions to guide recovery and restoration. Freshwater Mollusk Biology And Conservation 21: 36–56. https://doi.org/10.31931/FMBC.V21I2.2018.36-56.
Kahlert, Maria, and Brendan G. McKie. 2014. Comparing new and conventional methods to estimate benthic algal biomass and composition in freshwaters. Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts 16: 2627–2634. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4EM00326H.
Kautsky, Nils, and Sverker Evans. 1987. Role of biodeposition by Mytilus edulis in the circulation of matter and nutrients in a Baltic coastal ecosystem. Marine Ecology Progress Series 38: 201–212.
Kéfi, Sonia, Eric L. Berlow, Evie a Wieters, Sergio a Navarrete, Owen L. Petchey, Spencer a Wood, Alice Boit, et al. 2012. More than a meal… integrating non-feeding interactions into food webs. Ecology Letters 15 (4): 291–300. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2011.01732.x.
Kéfi, Sonia, Milena Holmgren, and Marten Scheffer. 2016. When can positive interactions cause alternative stable states in ecosystems? Functional Ecology 30: 88–97. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.12601.
Kent, Flora E.A., Mark J. Gray, Kim S. Last, and William G. Sanderson. 2016. Horse mussel reef ecosystem services: Evidence for a whelk nursery habitat supporting a shellfishery. International Journal of Biodiversity Science, Ecosystem Services & Management 12: 172–180. https://doi.org/10.1080/21513732.2016.1188330.
Kluijer, M.J, and Ingalsuo, S.S. 2000a. Macrobenthos of the North Sea- Crustacea. World Biodiversity Database CD-ROM Series. Expert Center for Taxonomic Identification (ETI): Amsterdam. ISBN 3–540–14808-6. 1.
Kluijer, M.J, and Ingalsuo, S.S. 2000b. Macrobenthos of the North Sea - Miscellaneous worms. World Biodiversity Database CD-ROM Series. Expert Center for Taxonomic Identification (ETI): Amsterdam. ISBN 3–540–14808-6. 1.
Kluijer, M.J, Ingalsuo, S.S., and De Bryne, R.H. 2000a. Mollusca of the north sea. World Biodiversity Database CD-ROM Series. Expert Center for Taxonomic Identification (ETI): Amsterdam. ISBN 3–540–14808-6. 1.
Kluijer, M.J, Ingalsuo, S.S., and van Zanten, H.V. 2000b. Macrobenthos of the North Sea - Polychaeta. World Biodiversity Database CD-ROM Series. Expert Center for Taxonomic Identification (ETI): Amsterdam. ISBN 3–540–14808-6. 1.
Knowlton, N. 2001. The future of coral reefs. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 98 (10): 5419–5425. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.091092998.
Kostylev, V., and J. Erlandsson. 2001. A fractal approach for detecting spatial hierarchy and structure on mussel beds. Marine Biology 139 (3): 497–506. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002270100597.
Kuznetsova, Alexandra, Brockhoff, Per Bruun, and Christensen, Rune Haubo Bojesen. 2014. lmerTest: Tests for random and fixed effects for linear mixed effect models (lmer objects of lme4 package). R package version. https://doi.org/http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=lmerTest.
Lefcheck, Jonathan S., Simon J. Brandl, Pamela L. Reynolds, Ashley R. Smyth, and Sebastian T. Meyer. 2016. Extending rapid ecosystem function assessments to marine ecosystems: A reply to Meyer. Trends in Ecology & Evolution 31 (4): 251–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2016.02.002.
Lindsey, Emily L., Andrew H. Altieri, and Jon D. Witman. 2006. Influence of biogenic habitat on the recruitment and distribution of a subtidal xanthid crab. Marine Ecology Progress Series 306: 223–231. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps306223.
Liu, Quan-Xing, Peter M.J. Herman, Wolf M. Mooij, Jef Huisman, Marten Scheffer, Han Olff, and Johan van de Koppel. 2014. Pattern formation at multiple spatial scales drives the resilience of mussel bed ecosystems. Nature Communications 5: 5234. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms6234.
Loughs Agency, The. 2010. Sanitary Survey Report and Sampling Plan for Lough Foyle The Sea Fisheries Protection Authority.
Macreadie, Peter I., Rod M. Connolly, Gregory P. Jenkins, Jeremy S. Hindell, and Michael J. Keough. 2010. Edge patterns in aquatic invertebrates explained by predictive models. Marine and Freshwater Research 61: 214–218. https://doi.org/10.1071/MF09072.
Macreadie, Peter I., Nathan R. Geraldi, and Charles H. Peterson. 2011. How small-scale variation in oyster reef patchiness influences predation on bivalves. Marine Ecology Progress Series 429: 87–91. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps09115.
Mahoney, Richard D., Matthew D. Kenworthy, Julie K. Geyer, Kevin A. Hovel, and F. Joel Fodrie. 2018. Distribution and relative predation risk of nekton reveal complex edge effects within temperate seagrass habitat. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 503. Elsevier: 52–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JEMBE.2018.02.004.
Maloy, Aaron P., Peter Nelle, Sarah C. Culloty, John W. Slater, and Chris Harrod. 2013. Identifying trophic variation in a marine suspension feeder: DNA- and stable isotope-based dietary analysis in Mytilus spp. Marine Biology 160 (2): 479–490. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-012-2105-4.
Manderson, John Pilling. 2016. Seascapes are not landscapes: An analysis performed using Bernhard Riemann’s rules. ICES Journal of Marine Science 73: 1831–1838. https://doi.org/10.1093/icesjms/fss023.
Martins, G.M., M.G. Matias, I. Moniz, C. Rius, J. Sanderson, A.I. Neto, and S.R. Jenkins. 2017. Post-settlement dispersal ability determines structure of marine benthic metacommunities. Marine Ecology Progress Series 569: 15–23. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps12108.
Matias, Miguel G., Ross A. Coleman, Dieter F. Hochuli, Antony J. Underwood, and S.P. Lawler. 2013. Macrofaunal responses to edges are independent of habitat-heterogeneity in experimental landscapes. PLoS One 8. Public library of science: e61349. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0061349.
Maxwell, Paul S., Johan S. Eklöf, Marieke M. van Katwijk, Katherine R. O’Brien, Maricela de la Torre-Castro, Christoffer Boström, Tjeerd J. Bouma, et al. 2016. The fundamental role of ecological feedback mechanisms for the adaptive management of seagrass ecosystems - a review. Biological Reviews 92 (3): 1521–1538. https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12294.
McLeod, Ian M., Darren M. Parsons, Mark A. Morrison, Agǹs Agnès Le Port, and Richard B. Taylor. 2012. Factors affecting the recovery of soft-sediment mussel reefs in the firth of Thames, New Zealand. Marine and Freshwater Research 63: 78–83. https://doi.org/10.1071/MF11083.
McLeod, I.M., D.M. Parsons, M.A. Morrison, S.G. Van Dijken, and R.B. Taylor. 2014. Mussel reefs on soft sediments: a severely reduced but important habitat for macroinvertebrates and fishes in New Zealand. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 48: 48–59. https://doi.org/10.1080/00288330.2013.834831.
Mees, J., Boxshall, G.A., Costello, M.J., Hernandez, F., Bailly, N., Boury-Esnault, N., Gofas, S., et al. 2015. World register of marine species.
Menge, B.A., B.A. Daley, P.A. Wheeler, E. Dahlhoff, E. Sanford, and P.T. Strub. 1997. Benthic-pelagic links and rocky intertidal communities: Bottom-up effects on top-down control? Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 94: 14530–14535.
Menge, Bruce a., Francis Chan, Karina J. Nielsen, Emanuele Di Lorenzo, and Jane Lubchenco. 2009. Climatic variation alters supply-side ecology: Impact of climate patterns on phytoplankton and mussel recruitment. Ecological Monographs 79: 379–395. https://doi.org/10.1890/08-2086.1.
Menge, Bruce A., Tarik C. Gouhier, Tess L. Freidenburg, and Jane Lubchenco. 2011. Linking long-term, large-scale climatic and environmental variability to patterns of marine invertebrate recruitment: Toward explaining “unexplained” variation. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 400: 236–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jembe.2011.02.003.
Minchinton, Todd E. 1997. Life on the edge : Conspecific attraction and recruitment of populations to disturbed habitats. Oecologia 111: 45–52.
Moksnes, P.-O., L. Pihll, and Jacques van Montfrans. 1998. Predation on postlarvae and juveniles of the shore crab Carcinus maenas: Importance of shelter, size and cannibalism. Marine Ecology Progress Series 166: 211–225.
Mrowicki, Robert J., Christine A. Maggs, and Nessa E. O’Connor. 2014. Does wave exposure determine the interactive effects of losing key grazers and ecosystem engineers? Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 461: 416–424. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jembe.2014.09.007.
Navarro, J.M., and R.J. Thompson. 1997. Biodeposition by the horse mussel Modiolus modiolus (Dillwyn) during the spring diatom bloom. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 209: 1–13.
Newell, R.C. 1990. The effects of mussel (Mytilus edulis, linnaeus, 1758) position in seeded bottom patches on growth at subtidal lease sites in Maine. Journal of Shellfish Research 9: 113–118.
Nicastro, Katy R., Gerardo I. Zardi, Christopher D. McQuaid, Gareth a Pearson, and Ester a Serrão. 2012. Love thy neighbour: Group properties of gaping behaviour in mussel aggregations. PLoS One 7: e47382. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0047382.
O’Connor, Nessa E. 2010. Shore exposure affects mussel population structure and mediates the effect of epibiotic algae on mussel survival in SW Ireland. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 87: 83–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2009.12.011.
O’Connor, Nessa E., and Tasman P. Crowe. 2007. Biodiversity among mussels: Separating the influence of sizes of mussels from the ages of patches. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the UK 87: 551–557. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0025315407050503.
O’Connor, Nessa E., Tasman P. Crowe, and David McGrath. 2006. Effects of epibiotic algae on the survival, biomass and recruitment of mussels, Mytilus L. (Bivalvia: Mollusca). Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 328. Elsevier: 265–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JEMBE.2005.07.013.
O’Connor, N.E., I. Donohue, T.P. Crowe, and M.C. Emmerson. 2011. Importance of consumers on exposed and sheltered rocky shores. Marine Ecology Progress Series 443: 65–75. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps09412.
O’Connor, Nessa E., Mark C. Emmerson, Tasman P. Crowe, and Ian Donohue. 2013. Distinguishing between direct and indirect effects of predators in complex ecosystems. The Journal of Animal Ecology 82 (2): 438–448. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2656.12001.
Okamura, B. 1986. Group living and the effects of spatial position in aggregations of Mytilus edulis. Oecologia 69 (3): 341–347. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00377054.
Oksanen, Jari, F.G. Blanchet, Roeland Kindt, Pierre Legendre, and R.B. O’Hara. 2016. Vegan: Community ecology package. R Package 2: 3–3. https://doi.org/10.4135/9781412971874.n145.
Paine, Robert T. 1976. Size-limited predation: An observational and experimental approach with the Mytilus-Pisaster interaction. Ecology 57: 858–873.
Paine, Robert T., and Simon A. Levin. 1981. Intertidal landscapes : Disturbance and the dynamics of pattern. Ecological Monographs 51: 145–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/0198-0254(81)91582-X.
Palomo, M.G., J. People, M.G. Chapman, and Antony J. Underwood. 2007. Separating the effects of physical and biological aspects of mussel beds on their associated assemblages. Marine Ecology Progress Series 344: 131–142. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps07002.
R Development Core Team, R. 2015. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74686-7.
Reynolds, Pamela L., John J. Stachowicz, Kevin Hovel, Christoffer Boström, Katharyn Boyer, Mathieu Cusson, Johan S. Eklöf, et al. 2018. Latitude, temperature, and habitat complexity predict predation pressure in eelgrass beds across the northern hemisphere. Ecology 99 (1): 29–35. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecy.2064.
Ries, Leslie, Robert J. Fletcher, James Battin, and Thomas D. Sisk. 2004. Ecological responses to habitat edges: Mechanisms, models, and variability explained. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics 35: 491–522. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.35.112202.130148.
Ritchie, Raymond J. 2006. Consistent sets of spectrophotometric chlorophyll equations for acetone, methanol and ethanol solvents. Photosynthesis Research 89 (1): 27–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-006-9065-9.
Ryer, Clifford H. 1987. Temporal patterns of feeding by blue crabs (Callinectes sapidus) in a tidal-Marsh Creek and adjacent Seagrass meadow in the lower Chesapeake Bay. Estuaries 10: 136–140. https://doi.org/10.2307/1352178.
Satterthwaite, F.E. 1946. An approximate distribution of estimates of variance components. Biometrics 2 (6): 110–114. https://doi.org/10.2307/3002019.
Seed, Ray, and R. a Brown. 1977. A comparison of the reproductive cycles of Modiolus modiolus (L.), Cerastoderma (=Cardium) edule (L.), and Mytilus edulis L. in Strangford lough, Northern Ireland. Oecologia 30 (2): 173–188. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00345419.
Seiderer, L.J., and R.C. Newell. 1999. Analysis of the relationship between sediment composition and benthic community structure in coastal deposits: Implications for marine aggregate dredging. ICES Journal of Marine Science. 56: 757–765. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmsc.1999.0495.
Smith, Timothy M., Jeremy S. Hindell, Gregory P. Jenkins, Rod M. Connolly, and Michael J. Keough. 2011. Edge effects in patchy seagrass landscapes: The role of predation in determining fish distribution. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 399: 8–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jembe.2011.01.010.
Staveley, Thomas A.B., Diana Perry, Regina Lindborg, and Martin Gullström. 2016. Seascape structure and complexity influence temperate seagrass fish assemblage composition. Ecography: 936–946. https://doi.org/10.1111/ecog.02745.
Strain, E.M.A., R.L. Morris, R.A. Coleman, W.F. Figueira, P.D. Steinberg, E.L. Johnston, and M.J. Bishop. 2017. Increasing microhabitat complexity on seawalls can reduce fish predation on native oysters. Ecological Engineering 120: 637–644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2017.05.030.
Svane, I., and M. Ompi. 1993. Patch dynamics in beds of the blue mussel Mytilus edulis L.: Effects of site, patch size, and position within a patch. Ophelia 37: 187–202.
Svane, I., and I. Setyobudiandi. 1996. Diversity of associated fauna in beds of the blue mussel Mytilus edulis L.: Effects of location, patch size, and position within a patch. Ophelia 45: 39–53. https://doi.org/10.1080/00785326.1996.10432461.
Tanner, Jason E. 2005. Edge effects on fauna in fragmented seagrass meadows. Austral Ecology 30: 210–218. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-9993.2005.01438.x.
Thrush, Simon F., and Paul K. Dayton. 2002. Disturbance to marine benthic habitats by trawling and dredging: Implications for marine biodiversity. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 33: 449–473. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.33.010802.150515.
Underwood, A.J., and M.G. Chapman. 1996. Scales of spatial patterns of distribution of intertidal invertebrates. Oecologia 107 (2): 212–224. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00327905.
Underwood, G.J.C., and J.C. Kromkamp. 1999. Primary production by phytoplankton and microphytobenthos in estuaries. Advances in Ecological Research 29: 93–153.
Underwood, A.J., M.G. Chapman, and S.D. Connell. 2000. Observations in ecology: You can’t make progress on processes without understanding the patterns. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 250: 97–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0981(00)00181-7.
Waser, Andreas M., Rob Dekker, Johannes I.J. Witte, Niamh McSweeney, Bruno J. Ens, and Jaap van der Meer. 2017. Quantifying tidal movements of the shore crab Carcinus maenas on to complex Epibenthic bivalve habitats. Estuaries and Coasts 41 (2): 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-017-0297-z.
Whitlach, Robert B. 1981. Animal-sediment relationships in intertidal marine benthic habitats: Some determinants of deposit feeding species diversity. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 53: 31–45.
Widdows, John, Nick D. Pope, Mary D. Brinsley, Jo Gascoigne, and Michel J. Kaiser. 2009. Influence of self-organised structures on near-bed hydrodynamics and sediment dynamics within a mussel (Mytilus edulis) bed in the Menai Strait. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 379: 92–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jembe.2009.08.017.
Wimp, Gina M., Shannon M. Murphy, Danny Lewis, and Leslie Ries. 2011. Do edge responses cascade up or down a multi-trophic food web? Ecology Letters 14 (9): 863–870. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2011.01656.x.
Witman, Jon D. 1985. Refuges , Biological Disturbance , and Rocky Subtidal Community Structure in New England. Ecological Monographs 55: 421–445. https://doi.org/10.2307/2937130.
Witman, Jon D., Robert W. Lamb, and Jarrett E.K. Byrnes. 2015. Towards an integration of scale and complexity in marine ecology. Ecological Monographs 85: 475–504.
Zuur, A.F., Elena N. Ieno, Neil J. Walker, Anatoly A. Saveliev, and Graham M. Smith. 2009. Mixed effects models and extensions in ecology with R. Vol. 1. Berlin: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107415324.004.
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to Ciarán McGonigle and his team at the Lough’s Agency for field support in Lough Foyle and to Lydia White for field support at Strangford and Belfast Loughs. We thank Prof Mark Emmerson and Prof Steven Widdicombe for useful discussion on this chapter.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Funding
The study was funded by the Northern Ireland Environment Agency and Queen’s University Belfast as part of Camilla Bertolini PhD studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Patricia Ramey-Balci
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bertolini, C., Montgomery, W.I. & O’Connor, N.E. Edge Effects Are Not Linked to Key Ecological Processes in a Fragmented Biogenic Reef. Estuaries and Coasts 43, 708–721 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-020-00705-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-020-00705-4