Abstract
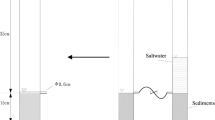
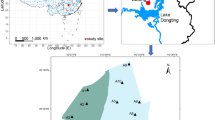
The contents and forms of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and organic carbon (C) were determined with 40 cm (approximately 1600 s) core sediments from Erhai Lake on the Yungui Plateau of China as the sample. The vertical distribution characteristics, coupling relationships and ecological indicator significance of C–N–P were studied and identified. The results showed that the total organic carbon (TOC), total nitrogen (TN), and total phosphorus (TP) contents were in the ranges of 1436–8255 mg·kg−1, 1287–5462 mg·kg−1, and 870.26–1507.74 mg·kg−1, respectively. In the Erhai Lake sediments, the main forms of TOC, organic nitrogen (ON) and organic phosphorus (OP) were humus, TN, and TP, respectively. The deposition of C, N, and P in the Erhai Lake sediments was divided into four periods. In the initial development period (from 40 to 23 cm), C, N and P were deposited and released synchronously; the main form of N was nontransferable total nitrogen (NTN), and that of P was inorganic phosphorus (IP). In the ecological recovery period (from 22 to 14 cm), C and N were deposited synchronously, and their deposition amounts were more than that of P. C, N and P were released synchronously. The main form of N was transferable total nitrogen (TTN), and that of P was IP. In the rapid economic growth period (from 13 to 0 cm), C, N, and P were deposited and released synchronously; the main form of N was NTN, and that of P was OP. In comparison to the other periods, this period was a period of higher active soil organic carbon (ASOC). In the integrated management period (surface sediment), C and N were deposited and released synchronously, and their deposition amounts were greater than that of P. The main form of N was NTN, that of P was OP, and the ASOC content was high. When exogenous inputs were the main sources of C, N, and P, the deposition forms of P and N were mainly OP and NTN, respectively, and those of IP and TTN were calcium-bound P (Ca–P) and ion-exchange form N (IEF–N), respectively. When endogenous inputs were the main sources of C, N and P, the deposition forms of P and N were mainly IP and TTN, respectively, and those of IP and TTN were Fe/Al–P and weak acid extractable form (WAEF–N), respectively. The content ratio of Ca–P and Fe/Al–P, as well as that of IEF–N and WAEF–N, could reflect the changes in the contribution of endogenous and exogenous sources to the Erhai Lake sediments.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Public Health Association (APHA), American Water Work Association (AWWA), Water Environment Federation (WEF) (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 18th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC, pp 134–458
Christensen BT (1992) Physical fractionation of soil and organic matter in primary particle size and density separates. Adu Soil Sci 20:2–90
Curtin D, Mccallum FM, Williams PH (2003) Phosphorus in light fraction organic matter separated from soils receiving long-term applications of superphosphate [J]. Biol Fertil Soils 37(5):280–287
Fu YQ, Zhou YY, Li JQ (2000) Sequential fractionation of reactive phosphorus in the sediment of a shallow eutrophic lake–Donghu lake. China J Environ Sci 12:57–62
Gao L, Zhou JM, Yang H et al (2005) Phosphorus fractions in sediment profiles and their potential contributions to eutrophication in Dianchi Lake [J]. Environ Geol 2005(48):835–844
Hupfer M, Gachter R, Giovanoli R (1995) Transformation of phosphorus species in settling section and during early sediment diagenesis [J]. Aquat Sci 57:305–324
Janzen HH, Campbell CA, Brabdts A (1992) Light-fraction organic matter in soils from long-term crop rotations [J]. Soil Sci Soc Am J 56:1799–1806
Jin XC, Wang SR, Pang Y (2004) The influence of phosphorus forms and pH on release of phosphorus from sediments in Taihu Lake [J]. China Environ Sci 24(6):707–711 (in Chinese)
Jin XC, Wang SR, Zhao HC, Yan CZ (2005) Effects of phosphorus form on the distribution of the phosphorus in water-sediment-submerge plant ecosystem [J]. Ecol Environ 14(5):631–635 (in Chinese)
Lefroy RDB, Blair GJ (1993) Changes in soil organic matter with cropping as measured by organic carbon fractions and 13C natural isotope abundance [J]. Plant Soil 155/156:399–402
Logninow W, Wisniewski W, Strony W et al (1987) Fractionation of organic carbon based on suscep tibility to oxidation. Polish J Soil Sci 20:47–52
Luo SS, Wan GJ, Huang RG (2000) Characteristics of distribution and removal of Fe and Mn at the sediment-water interface of Erhai lake, Yunnan province [J]. Chongqing environmental. Science 22(6):19–21 (in Chinese)
Lv XX, Song JM (2004) The effect of circumstance on the formation and release of transferable nitrogen in different grain size surface sedimetns of the southern yellow sea [J]. Environ Chem 23(3):314–320 (in Chinese)
Ma HB, Song JM, Lv XX et al (2003) Nitrogen forms and their functions in recycling of the Bohai Sea sediments [J]. Geochimca. 23(1):48–54 (in Chinese)
Michael PE, Koprivnjak JF (2007) Using the C/N ratio to estimate terrigenous inputs of organic matter to aquatic environments [J]. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 73:65–72
Norton SA, Coolidge K, Amirbahman A et al (2008) Speciation of Al, Fe, and P in recent sediment from three lakes in Maine, USA [J]. Sci Total Environ 404:276–283
Oades JM, Ladd JN (1977) Biochemical properties: carbon and nitrogen metabolism. In: Tussell JS, Green EL (eds) Soil factors in crop production in a semi-arid environment. University of Queensland Press, St.Lucia, pp 127–160
Ruban V, Brigault S, Demare D (1999) An investigation of the origin and mobility of phosphorus in freshwater sediments from Bort-les-Orgues reservoir, France. J Environ Monit 1:403
Ruttenburg KC (1992) Development of a sequential extraction method for different forms of phosphorus in marine sediments [J]. Limnol Oceanogr 37:1460–1482
Shen J, Yang LY, Yang XD et al (2004) Lacustrine records of climatic change and human activities in the catchment of Erhai lake, Yunnan province since the past new century [J]. Sci China Ser: D Earth Sci 34(2):130–138 (in Chinese)
Shen MJ, Cui ZJ, Yi CL (2005) Research on relationship between environmental changes of Erhai lake and urban development of Dali city [J]. Yunnan Geogr Environ Res 17(6):63–68 (in Chinese)
Song JM, Ma HB, Lv XX (2002) Nitrogen forms and decomposition of organic carbon in the southern Bohai Sea core sediments (in Chinese). Acta Oceanol Sin 21(l):125–133
Wang QK, Wang SL, Feng ZW et al (2005) Active soil organic matter and its relation ship with soil quality [J]. Acta Ecol Sin 25(3):513–519 (in Chinese)
Wang SR, Jin XC, Zhao HC et al (2006) Phosphorus fractions and its release in the sediments from the shallow lakes in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River area in China. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 273:109–116
Wang SR, Jin XC, Jiao LX et al (2008) Nitrogen fractions and release in the sediments from the Shallow Lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River area, China [J]. Water Air Soil Pollut 187:5–14
Wei ZQ, Liu CQ, Liang XB et al (2004) Characteristics of organic matter and DNA in sediments of lake Erhai[J]. Acta Sedimentol Sin 22(4):672–675 (in Chinese)
Whitbread AM, Lefroy RDB, Graeme BJ (1998) A survey of the impact of cropping on soil physical and chemical properties in North-Western New South Wales[J]. Aust J Soil Res 36(4):669–681
Wu TY, Jeff JS, Li FM et al (2004) Concepts and relative analytical techniques of soil organic matter [J]. Chin J Appl Ecol 15(4):717–722 (in Chinese)
Xiang SL, Zhou WB (2011) Phosphorus forms and distribution in the sediments of Poyang Lake, China [J]. Int J Sediment Res 26:230–238
Xie LQ, Xie P, Tang HJ (2003) Enhancement of dissolved phosphorus release from sediment to lake water by Microcystis blooms-an enclosure experiment in a hyper-eutrophic, subtropical Chinese lake [J]. Environ Pollut 122:391–399
Zhang S, Xu CH, Zhong ZZ et al (1993) Determination of sedimentation rate and dating of sediment in Erhai lake with 210Pb and 137Cs dating methods [J]. Radiat Protect 13(6):453–457
Zhang ZK, Wu RJ, Wang SM et al (2000a) Environmental evolution recorded by lake sediments from Erhai lake, Yunnan province in Holocene megathermal [J]. Oceanologiaet Limnol Sin 31(2):210–214 in Chinese
Zhang ZK, Wu RJ, Zhu YX et al (2000b) Lacustrine records of human activities in the catchment of Erhai lake, Yunnan Province [J]. Acta Geograph Sin 55(1):66–74 (in Chinese)
Zhao HC, Wang SR, Jin XC et al (2008a) Availability and transferring of phosphorus forms by Hydrilla verticillata in the sediment and soil [J]. J Lake Sci 20(3):315–322 (in Chinese)
Zhao HC, Zhao HX, Wang SR et al (2008b) Effect of inorganic phosphorus forms in the sediment and soil by submerged plant [J]. Ecol Environ 17(1):74–80 (in Chinese)
Zhao HC, Wang SR, Zhao M et al (2011) Relationship between the DO and the environmental factors of the water body in Lake Erhai [J]. Environ Sci 32(7):1952–1959 (in Chinese)
Zhao HC, Wang SR, Jiao LX et al (2013a) Characteristics of temporal and spatial distribution of different forms of phosphorus in the sediments of Erhai lake [J]. Res Environ Sci 26(3):227–234
Zhao HC, Wang SR, Jiao LX et al (2013b) Characteristics of temporal and spatial distribution of the nitrogen forms in the sediments of Erhai lake [J]. Res Environ Sci 26(3):235–242
Zhao HC, Wang SR, Jiao LX et al (2013c) Characteristics of temporal and spatial distribution of organic matter in the sediments of Erhai lake[J]. Res Environ Sci 26(3):243–249
Zheng GQ, Yu XX, Jiang N et al (2004) The cause for chang of wster quality of Erhai lake and prediction of water quality [J]. J Northeast Forest Univ 32(1):99–102 (in Chinese)
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41503113), Beijing Major Science and Technology Projects (Z181100005318001) and Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment (2012ZX07102-004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Baojing Gu
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, H., Zhao, H., Wang, S. et al. Coupling characteristics and environmental significance of nitrogen, phosphorus and organic carbon in the sediments of Erhai Lake. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 19901–19914 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08120-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-08120-9