Abstract
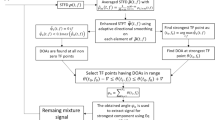
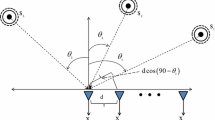
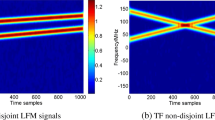
Time–frequency (TF) approaches are frequently employed for source localization at low signal to noise ratio. However, TF approaches fail to achieve the desired performance for sparsely sampled signals or signals corrupted by heavy noise in an under-determined scenario when sources are not TF separable. In this study, we propose a new TF method for direction of arrival (DOA) estimation of sources with closely spaced and overlapping TF signature. The proposed method uses a combination of a high-resolution time–frequency distribution and instantaneous frequency estimation method for extraction of sources with intersecting and closely spaced time–frequency signatures. Once sources are extracted, their DOAs are estimated using a well known multiple signal classification (MUSIC) algorithm. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed source localization method achieves better performance as compared to the conventional time–frequency MUSIC algorithm.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin, M. G., & Zhang, Y. (2000). Direction finding based on spatial time–frequency distribution matrices. Digital Signal Processing, 10(4), 325–339.
Belouchrani, A., & Amin, M. (1999). Time–frequency MUSIC. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 6, 109–110.
Belouchrani, A., Amin, M., Thirion-Moreau, N., & Zhang, Y. (2013). Source separation and localization using time–frequency distributions: An overview. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 30(6), 97–107.
Boashash, B. (2003). Time frequency analysis: A comprehensive reference. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Boashash, B., & Aïssa-El-Bey, A. (2018). Robust multisensor time-frequency signal processing: A tutorial review with illustrations of performance enhancement in selected application areas. Digital Signal Processing, 77, 153–186.
Boashash, B., Khan, N. A., & Ben-Jabeur, T. (2015). Time-frequency features for pattern recognition using high-resolution TFDs: A tutorial review. Digital Signal Processing, 40, 1–30.
Boashash, B., Aïssa-El-Bey, A., & Al-Saad, M. F. (2018) Multisensor time–frequency signal processing matlab package: An analysis tool for multichannel non-stationary data. SoftwareX.
Chabriel, G., Kleinsteuber, M., Moreau, E., Shen, H., Tichavsky, P., & Yeredor, A. (2014). Joint matrices decompositions and blind source separation: A survey of methods, identification, and applications. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 31, 34–43.
Guo, L., Zhang, Y., Wu, Q., & Amin, M. (2015). Doa estimation of sparsely sampled nonstationary signals. In IEEE China summit and international conference on signal and information processing (ChinaSIP), pp. 300–304.
Heidenreich, P., Cirillo, L., & Zoubir, A. (2009). Morphological image processing for FM source detection and localization. Signal Processing, 89(6), 1070–1080.
Kassis, C. E., Picheral, J., & Mokbel, C. (2010). Advantages of nonuniform arrays using root-MUSIC. Signal Processing, 90(2), 689–695.
Khan, N. A., & Ali, S. (2018). Sparsity-aware adaptive directional time–frequency distribution for source localization. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 37(3), 1223–1242.
Khan, N. A., & Mohammadi, M. (2018). Reconstruction of non-stationary signals with missing samples using time–frequency filtering. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 37, 3175–3190.
Khan, N. A., Ali, S., & Jansson, M. (2018). Direction of arrival estimation using adaptive directional time–frequency distributions. Multidimensional Systems and Signal Processing, 29(2), 503–521.
Khan, N. A., Mohammadi, M., & Ali, S. (2019). Instantaneous frequency estimation of intersecting and close multi-component signals with varying amplitudes. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 13(3), 517–524.
Krim, H., & Viberg, M. (1996). Two decades of array signal processing research: The parametric approach. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 13, 67–94.
Matlab code for direction of arrival estimation of close and intersecting sources. https://github.com/mokhtarmohammadi/DOA-estimation-of-intersecting-components. Accessed 21 January 2019.
Mohammadi, M., Pouyan, A. A., Khan, N. A., & Abolghasemi, V. (2018a). Locally optimized adaptive directional time-frequency distributions. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 37, 3154–3174.
Mohammadi, M., Pouyan, A. A., Khan, N. A., & Abolghasemi, V. (2018b). An improved design of adaptive directional time-frequency distributions based on the radon transform. Signal Processing, 150, 85–89.
Mu, W., Amin, M. G., & Zhang, Y. (2003). Bilinear signal synthesis in array processing. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 51(1), 90–100.
Ouelha, S., Aïssa-El-Bey, A., & Boashash, B. (2017). Improving doa estimation algorithms using high-resolution quadratic time–frequency distributions. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 65, 5179–5190.
Sharif, W., Chakhchoukh, Y., & Zoubir, A. (2011). Robust spatial time–frequency distribution matrix estimation with application to direction-of-arrival estimation. Signal Processing, 91(11), 2630–2638.
Swindlehurst, A., & Kailath, T. (1992). A performance analysis of subspace-based methods in the presence of model errors. I. The music algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 40, 1758–1774.
Trees, H. L. V. (2002). Optimum array processing. New York: Wiley Interscience.
Yang, Y., Dong, X., Peng, Z., Zhang, W., & Meng, G. (2015). Component extraction for non-stationary multi-component signal using parameterized de-chirping and band-pass filter. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 22(9), 1373–1377.
Zhang, Y., Ma, W., & Amin, M. (2001). Subspace analysis of spatial time–frequency distribution matrices. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 49, 747–759.
Zhang, Y. D., Amin, M. G., & Himed, B. (2012). Direction-of-arrival estimation of nonstationary signals exploiting signal characteristics. In 11th International conference on information science, signal processing and their applications (ISSPA), IEEE, pp. 1223–1228.
Zhang, Y., Guo, L., Wu, Q., & Amin, M. (2015). Multi-sensor kernel design for time-frequency analysis of sparsely sampled nonstationary signals. In IEEE radar conference (RadarCon), pp. 0896–0900.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, N.A., Ali, S., Mohammadi, M. et al. Direction of arrival estimation of sources with intersecting signature in time–frequency domain using a combination of IF estimation and MUSIC algorithm. Multidim Syst Sign Process 31, 549–567 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11045-019-00676-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11045-019-00676-1