Abstract
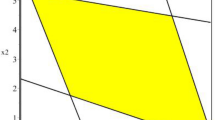
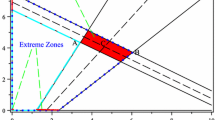
In this paper, we consider interval multi-objective linear programming (IMOLP) models which are used to deal with uncertainties of real-world problems. So far, a variety of approaches for obtaining efficient solutions (ESs) of these problems have been developed. In this paper, we propose a new and two generalized methods. In the new method, converting IMOLP into an interval linear programming (ILP) and then obtaining its optimal solutions (OSs), ESs of the IMOLP are determined. This method has several advantages: (i) This method is the only method which obtains a solution box for IMOLP models. (ii) The solving process is not time consuming. (iii) The number of ESs is higher than for other methods. (V) The method is applicable for large-scale problems. Also, we generalize the \(\varepsilon\)-constraint and lexicographic methods which are used for obtaining ESs of the multi-objective linear programming (MOLP) models which do not have any problems such as lengthy and time-consuming and are applicable for large-scale problems. Some examples were solved to show the efficiency of the proposed methods. Finally, by the proposed method, we solve the IMOLP model corresponding to the problem of the facilities and non-return funds in a bank.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alefeld, G., Herzberger, J.: Introduction to Interval Computations. Academic Press, New York (1983)
Allahdadi, M., Deng, C.: An improved three-step method for solving the interval linear programming problem. Yugoslav J. Oper. Res. 28(4), 435–451 (2018)
Allahdadi, M., Nehi, H.M.: The optimal solutions set of the interval linear programming problems. Optim. Lett. 7, 893–1911 (2013)
Allahdadi, M., Nehi, H.M.: The optimal value bounds of the objective function in the interval linear programming problem. Chiang Mai. J. Sci. 42(2), 501–511 (2015)
Allahdadi, M., Nehi, H.M., Ashayerinasab, H.A., Javanmard, M.: Improving the modified interval linear programming method by new techniques. Inf. Sci. 339, 224–236 (2016)
Ashayerinasab, H.A., Nehi, H.M., Allahdadi, M.: Solving the interval linear programming problem: a new algorithm for a general case. Expert Syst. Appl. 93, 39–49 (2018)
Bottea, M., Schöbel, A.: Dominance for multi-objective robust optimization concepts. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 273(2), 430–440 (2019)
Chinneck, J.W., Ramadan, K.: Linear programming with interval coefficients. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 51, 209–220 (2000)
Dechao Li, L., Leung, Y., Weizhi, W.: Multiobjective interval linear programming in admissible-order vector space. Inf. Sci. 486, 1–19 (2019)
Dourado, A.D.P., Lobato, F.S., Ap Cavalini, A., Steffen, V.: Fuzzy reliability-based optimization for engineering system design. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 21(5), 1418–1429 (2019)
Ehrgott, M.: Multicriteria Optimization. Springer, Berlin (2005)
Garajová, E., Hladík, M., Rada, M.: The effects of transformations on the optimal set in interval linear programming, In: Proceedings of the 14th international symposium on operational research, SOR’17, Bled, Slovenian Society Informatika, Ljubljana, Slovenia, pp. 487–492 (2017)
Hladík, M.: Complexity of necessary efficiency in interval linear programming and multiobjective linear programming. Optim. Lett. 6(5), 893–899 (2012)
Hladík, M.: How to determine basis stability in interval linear programming. Optim. Lett. 8, 375–389 (2014)
Hladík, M.: Interval linear programming: a survey. In: Mann, Z.A. (ed.) Linear Programming, New Frontiers in Theory and Applications, Chapter 2, pp. 85–120. Nova Science Publishers, New York (2012)
Hladík, M.: One necessarily efficient solutions in interval multi objective linear programming, Proceedings of the 25th Mini-EURO Conference Uncertainty and Robustness in Planning and Decision Making URPDM 2010, pp. 1–10. Coimbra, Portugal (2010)
Hladík, M.: Weak and strong solvability of interval linear systems of equations and inequalities. Linear Algebra Appl. 438(11), 4156–4165 (2013)
Huang, G.H., Baetz, B.W., Patry, G.G.: Grey integer programming: an application to waste management planning under uncertainty. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 83, 594–620 (1995)
Huang, G.H., Moore, R.D.: Grey linear programming, its solving approach, and its application. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 24, 159–172 (1993)
Inuiguchi, M.: Necessary efficiency is partitioned into possible an necessary optimalities, IFSA World Congress and NAFIPS Annual Meeting (IFSA/NAFIPS), pp. 209–214. Edmonton, AB, Canada (2013)
Inuiguchi, M., Kume, Y.: Goal programming approach for solving IMOLP problems. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 52, 345–360 (1991)
Inuiguchi, M., Sakawa, M.: An achievement rate approach to linear programming problems with an interval objective function. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 48, 25–33 (1997)
Inuiguchi, M., Sakawa, M.: Minimax regret solution to multi objective linear programming problems with interval objective function coefficients. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 86, 526–536 (1995)
Inuiguchi, M., Sakawa, M.: Possible and necessary efficiency in possibilistic multiobjective linear programming problems and possible efficiency test. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 78, 321–341 (1996)
Koníčková, J.: Sufficient condition of basis stability of an interval linear programming problem. ZAMM. Z. Angew. Math. Mech. 81(3), 677–678 (2001)
Mishmast Nehi, H., Ashayerinasab, H.A., Allahdadi, M.: Solving methods for interval linear programming problem: a review and an improved method. Oper. Res. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12351-018-0383-4
Oliveira, C., Antunes, C.H.: Multiple objective linear programming models with interval coefficient-an illustrated overview. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 181, 1434–1463 (2007)
Razavi Hajiagha, S.H.: Programming with interval multi-objective linear coefficients: a fuzzy set based approach. Kybernetes 42(3), 482–496 (2013)
Rex, J., Rohn, J.: Sufficient conditions for regularity and singularity of interval matrices. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 20(2), 437–445 (1998)
Rivaz, S., Yaghoobi, M.A.: Minimax regret solution to linear programming problems with an interval objective function. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 21(3), 625–649 (2013)
Rivaz, S., Yaghoobi, M.A.: Weighted sum of maximum regrets in an interval MOLP problem. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 25(5), 1659–1676 (2015)
Rivaz, S., Yaghoobi, M.A., Hladík, M.: Using modified maximum regret for finding a necessarily efficient solution in an interval MOLP problem. Fuzzy Optim. Decis. Mak. 15(3), 237–253 (2016)
Rohn, J.: Cheap and tight bound: the recent result by E. Hansen can be made more efficient. Interval Comput. 4, 13–21 (1993)
Rohn, J.: Forty necessary and sufficient conditions for regularity of interval matrices: a survey. Electron J. Linear Algebra 18, 500–512 (2009)
Steuer, R.E.: Multiple criteria optimization: theory, computation and application. Wiley, New York (1989)
Tong, S.C.: Interval number, fuzzy number linear programming. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 66, 301–306 (1994)
Wang, X., Huang, G.: Violation analysis on two-step method for interval linear programming. Inf. Sci. 281, 85–96 (2014)
Xu, J., Fang, H., Zeng, F., Chen, Y.H., Guo, H.: Robust observer design and fuzzy optimization for uncertain dynamic systems. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 21(5), 1511–1523 (2019).
Yang, Y., Zhao, J., Xia, J., Zhuang, G., Zhang, W.: Multiobjective optimization control for uncertain nonlinear stochastic system with state-delay. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 21(1), 72–83 (2019).
Zhou, F., Huang, G.H., Chen, G., Guo, H.: Enhanced-interval linear programming. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 199, 323–333 (2009)
Acknowledgements
M. Hladík was supported by the Czech Science Foundation Grant P403-19-02773S.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Batamiz, A., Allahdadi, M. & Hladík, M. Obtaining Efficient Solutions of Interval Multi-objective Linear Programming Problems. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 22, 873–890 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-020-00800-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-020-00800-5