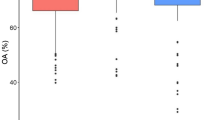
This study utilized hyperspectral imaging technology to identify eight tree species at the leaf level. The successive projections algorithm (SPA), information gain (IG), and Gini index (Gini) were used to select the feature bands. Furthermore, the binary particle swarm optimization (BPSO) algorithm was used to optimize the feature bands selected by SPA, IG, and Gini. The particle swarm optimization–extreme learning machine (PSO–ELM), linear Bayes normal classifi er (LBNC), and k-nearest neighbor (KNN) recognition models for tree species were established based on all bands, feature bands, and optimized feature bands, respectively. The experimental results show that the recognition rates of the PSO–ELM, LBNC, and KNN models based on all bands were 98.45, 99.10, and 83.67%, respectively. The SPA, IG, and Gini models can all effectively select spectral bands on tree species discrimination and greatly reduce the dimension of spectral data, in which the recognition effects of the models based on the feature bands selected by Gini were the best, and the recognition rates of the PSO–ELM, LBNC, and KNN models reached 97.55, 96.53, and 80.5%, respectively. Additionally, BPSO–SPA, BPSO–IG, and BPSO–Gini models can all further reduce the dimension of spectral data on the basis of ensuring the recognition accuracy of models, in which the models established based on the optimized feature bands selected by BPSO–Gini achieved the best recognition effect and the recognition rates of the PSO–ELM, LBNC, and KNN models reached 96.53, 96.68, and 81.05%, respectively. In general, the recognition performance of the PSO–ELM model was better than those of the LBNC and KNN models.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. S. Liu and X. L. Zhang, Forest Res. Manage., 1, 61–64 (2004).
O. Nevalainen, E. Honkavaara, S. Tuominen, N. Viljanen, T. Hakala, and X. Yu, Remote Sens., 9, 185 (2017).
L. C. Plourde, S. V. Ollinger, M. L. Smith, and M. E. Martin, Photogram. Eng. Remote Sens., 73, No. 7, 829–840 (2007).
B. X. Ma, Y. B. Ying, X. Q. Rao, and J. S. Gui, Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal., 29, No. 6, 1611–1615 (2009).
J. B. Feret and G. P. Asner, IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens., 51, No. 1, 73–84 (2012).
R. George, H. Padalia, and S. P. S. Kushwaha, Int. J. Appl. Earth Observ. Geoinform., 28, No. 1, 140–149 (2014).
M. Jia, Y. Zhang, Z. Wang, K. Song, and C. Ren, Int. J. Appl. Earth Observ. Geoinform., 33, No. 1, 226–231 (2014).
H. P. La, D. E. Yang, A. Chang, and C. Kim, KSCE J. Civil Eng., 19, No. 4, 1078–1087 (2015).
Z. Zhang, A. Kazakova, L. Moskal, and D. Styers, Forests, 7, No. 6, 122 (2016).
J. Cao, W. Leng, K. Liu, L. Liu, Z. He, and Y. Zhu, Remote Sens., 10, No. 1, 89 (2018).
A. Ghosh, F. E. Fassnacht, P. K. Joshi, and B. Koch, Int. J. Appl. Earth Observ. Geoinform., 26, No. 2, 49–63 (2014).
R. D. Jackson, P. M. Teillet, P. N. Slater, G. Fedosejevs, M. F. Jasinski, and J. K. Aase, Remote Sens. Environ., 32, No. 2, 189–202 (1990).
X. Li and A. H. Strahler, IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens., 30, No. 2, 276–292 (1992).
P. Pellikka, D. J. King, and S. G. Leblanc, Remote Sens. Rev., 19, No. 1–4, 259–291 (2000).
S. Tuominen, R. Nasi, E. Honkavaara, A. Balazs, T. Hakala, N. Viljanen, I. Polonen, H. Saari, and H. Ojanen, Remote Sens., 10, No. 5, 714 (2018).
M. A. Cochrane, Int. J. Remote Sens., 21, No. 10, 2075–2087 (2000).
Z. H. Wang and L. X. Ding, Spectrosc. Spectr. Analys., 30, No. 7, 1825–1829 (2010).
H. J. Lin, H. F. Zhang, Y. Q. Gao, X. Li, F. Yang, and Y. F. Zhou, Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal., 34, No. 12, 3358–3362 (2014).
X. R. Geng, K. Sun, L. Y. Ji, and Y. C. Zhao, IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens., 52, No. 11, 7111–7119 (2014).
Y. Liu, H. Xie, L. G. Wang, and K. Z. Tan, Appl. Opt., 55, No. 3, 462–472 (2016).
G. K. Zhu, Y. C. Huang, S. Y. Li, J. Tang, and D. Liang, IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett., 14, No. 12, 2320–2324 (2017).
S. Jia, G. H. Tang, J. S. Zhu, and Q. Q. Li, IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens., 54, No. 1, 88–102 (2016).
M. Huang, J. Tang, B. Yang, and Q. Zhu, Comput. Electron. Agric., 122, 139–145 (2016).
M. C. U. Araujo, T. C. B. Saldanha, R. K. H. Galvao, T. Yoneyama, H. C. Chame, and V. Visani, Chemometrics Intell. Lab. Syst., 57, No. 2, 65–73 (2001).
Q. Dai, Cheng, J. H. Sun, and X. A. Zeng, J. Food Eng., 136, 64–72 (2014).
Y. He, C. Zhang, F. Liu, W. W. Kong, P. Cui, and W. J. Zhou, Appl. Eng. Agric., 31, No. 1, 23–30 (2015).
Z. Y. Huang, J. Shandong Agric. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.), 44(2), 252–256 (2013).
W. Q. Shang, H. K. Huang, Y. L. Liu, Y. M. Lin, Y. L. Qu, and H. B. Dong, J. Comput. Res. Dev., 43(10), 1688–1694 (2006).
G. B. Huang, Q. Y. Zhu, and C. K. Siew, Neurocomputing, 70, No. 1/2/3, 489–501 (2006).
J. Wang, L. Zhang, J. J. Cao, and D. Han, Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cyber., 9, No. 1, 21–35 (2018).
A. Kadir, Proc. 3rd Int. Symp. "Leaf Identifi cation Using Polar Fourier Transform and Linear Bayes Normal Classifi - er", 40–49 (2015).
T. Cover and P. Hart, IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory, 13, No. 1, 21–27 (1967).
W. Sun, C. F. Wang, and C. C. Zhang, J. Clean Prod., 162, 1095–1101 (2017).
J. Kennedy and R. Eberhart, IEEE Int. Conf. Neural Networks, 4, 1942–1948 (1995).
J. Kennedy and R. C. Eberhart, IEEE Int. Conf. Systems, Man, Cybern. Comput. Cybern. Simul., 5, 4104–4108 (1997).
X. T. Zhao, S. J. Zhang, J. L. Liu, and H. X. Sun, Food Sci. Technol., 33, No. 10, 281–287 (2017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Abstract of article is published in Zhurnal Prikladnoi Spektroskopii, Vol. 87, No. 1, p. 175, January–February, 2020.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, R., Kan, J. Classification of Tree Species at the Leaf Level based on Hyperspectral Imaging Technology. J Appl Spectrosc 87, 184–193 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-020-00981-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-020-00981-9