Abstract
Introduction
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is a deadly brain tumor with a short expected median survival, despite current standard-of-care treatment. We explored the combination of intermediate stereotactic dose radiation therapy and immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy as a novel treatment strategy for GBM.
Methods
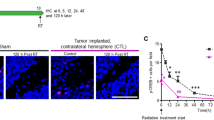
Glioma xenograft-bearing mice were exposed to high dose brain-directed radiation (10 Gy single exposure) as well as mouse anti-PD-1 antibody. The tumor-bearing animals were randomized to four groups: no treatment, radiation alone, anti-PD-1 alone, and radiation + anti-PD-1. Survival was followed, and tumor growth was monitored using MRI. Immunohistochemistry, gene expression arrays, and flow cytometry were used to characterize the treatment-induced effects. Pharmacologic inhibitors of T-lymphocytes, bone marrow derived macrophages, and microglia were used to assess the respective roles of different immune populations in observed treatment effects.
Results
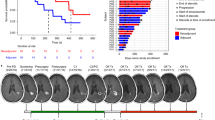
We found the combined treatment with high dose radiation and immunotherapy to be highly effective with a 75% complete pathologic response and dramatically improved survival outcomes. We found both CD8+ T-cells and macrophages to be necessary for the full effect of combined therapy, with T lymphocytes appearing to play a role early on and macrophages mediating a later phase of the combined treatment effect. Radiation treatment appeared to trigger macrophage repolarization, increasing M1/M2 ratio.
Conclusions
These findings point to a novel immunologic mechanism underlying the interaction between radiotherapy and immunotherapy. They also provide the basis for clinical investigation of immunogenic dose radiation in combination with immune checkpoint blockade as a potential treatment approach for newly diagnosed high grade gliomas.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Liao P, Vecchione-Koval T, Wolinsky Y, Kruchko C, Barnholtz-Sloan JS (2017) CBTRUS statistical report: Primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2010–2014. Neuro Oncol 19(suppl_5):v1–v88
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, Curschmann J, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Gorlia T, Allgeier A, Lacombe D, Cairncross JG, Eisenhauer E, Mirimanoff RO (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352:987–996
Patel M, Siddiqui F, Liu M, Scarpace L, Jin JY, Mikkelsen T, Movsas B, Ryu S (2009) Salvage radiosurgery of recurrent high grade glioma: Radiographic tumor control and clinical outcome. J Neuro-Oncol 92:185–191
Kim EY, Yechieli RL, Kim JK, Mikkelsen T, Kalkanis S, Rock JP, Ryu S (2014) Patterns of failure after radiosurgery to two different target volumes of enhancing lesions with and without FLAIR abnormalities in recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. J Neurooncol 116(2):291–297
Modh A, Bergman D, Siddiqui MS, Schultz L, Krozek, E, Scarpace L, Mikkelsen T, Ryu S (2018) Randomized prospective trial of stereotactic radiosurgery versus chemotherapy for recurrent malignant glioma after second-line chemotherapy , Abstract 505376 (RTHP-06), Annual meeting of society of Neurooncology 2018
Holt DE, Bernard ME, Quan K, Clump DA (2016) Salvage stereotactic radiosurgery for recurrent glioblastoma multiforme with prior radiation therapy. J Cancer Res Ther 12(4):1243–1248
Pollom EL, Fujimoto D, Wynne J, Seiger K (2017) Phase 1/2 trial of 5-fraction stereotactic radiosurgery with 5-mm margins with concurrent and adjuvant temozolomide in newly diagnosed supratentorial glioblastoma: health-related quality of life results. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 98(1):123–130
Greer L, Pannullo SC, Smith AW, Taube S (2017) Accelerated hypofractionated radiotherapy in the era of concurrent temozolomide chemotherapy in elderly patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Cureus 9(6):e1388
Vanpouille-Box C, Alard A, Aryankalayil MJ, Sarfraz Y (2017) DNA exonuclease Trex1 regulates radiotherapy-induced tumour immunogenicity. Nat Commun 8:15618
Motani K, Ito S, Nagata S (2015) DNA-mediated cyclic GMP-AMP synthase-dependent and -independent regulation of innate immune responses. J Immunol 194(10):4914–4923
Wang F, Alain T, Szretter KJ, Stephenson K (2016) S6K-STING interaction regulates cytosolic DNA-mediated activation of the transcription factor IRF3. Nat Immunol 17(5):514–522
Pépin G, Gantier MP (2017) cGAS-STING activation in the tumor microenvironment and its role in cancer immunity. Adv Exp Med Biol 1024:175–194
Zagzag D, Miller DC, Chiriboga L, Yee H, Newcomb EW (2003) Green fluorescent protein immunohistochemistry as a novel experimental tool for the detection of glioma cell invasion in vivo. Brain Pathol 13(1):34–37
Patel MA, Kim JE, Theodros D, Tam A, Velarde E, Kochel CM, Francica B, Nirschl TR, Ghasemzadeh A, Mathios D, Harris-Bookman S, Jackson CC, Jackson C, Ye X, Tran PT, Tyler B, Coric V, Selby M, Brem H, Drake CG, Pardoll DM, Lim M (2016) Agonist anti-GITR monoclonal antibody and stereotactic radiation induce immune-mediated survival advantage in murine intracranial glioma. J Immunother Cancer 4:28
Kim JE, Patel MA, Mangraviti A, Kim ES, Theodros D, Velarde E, Liu A, Sankey EW, Tam A, Xu H, Mathios D, Jackson CM, Harris-Bookman S, Garzon-Muvdi T, Sheu M, Martin AM, Tyler BM, Tran PT, Ye X, Olivi A, Taube JM, Burger PC, Drake CG, Brem H, Pardoll DM, Lim M (2017) Combination therapy with Anti-PD-1, Anti-TIM-3, and focal radiation results in regression of murine gliomas. Clin Cancer Res 23(1):124–136
Acharya MM, Green KN, Allen BD, Najafi AR, Syage A, Minasyan H, Le MT, Kawashita T, Giedzinski E, Parihar VK, West BL, Baulch JE, Limoli CL (2016) Elimination of microglia improves cognitive function following cranial irradiation. Sci Rep 6:31545
Brockmann MA, Ulmer S, Leppert J, Nadrowitz R, Wuestenberg R, Nolte I, Petersen D, Groden C, Giese A, Gottschalk S (2006) Analysis of mouse brain using a clinical 1.5 T scanner and a standard small loop surface coil. Brain Res 1068(1):138–142
Mitsuda M, Yamaguchi M, Furuta T, Nabetani A, Hirayama A, Nozaki A, Niitsu M, Fujii H (2011) Multiple-animal MR imaging using a 3T clinical scanner and multi-channel coil for volumetric analysis in a mouse tumor model. Magn Reson Med Sci 10(4):229–237
Wang F, Alain T, Szretter KJ, Stephenson K, Pol JG, Atherton MJ, Hoang HD, Fonseca BD, Zakaria C, Chen L, Rangwala Z, Hesch A, Chan ESY, Tuinman C, Suthar MS, Jiang Z, Ashkar AA, Thomas G, Kozma SC, Gale M Jr, Fitzgerald KA, Diamond MS, Mossman K, Sonenberg N, Wan Y, Lichty BD (2016) S6K-STING interaction regulates cytosolic DNA-mediated activation of the transcription factorIRF3. Nat Immunol 17(5):514–522
Stessin AM, Banu MA, Clausi MG, Berry N, Boockvar JA, Ryu S (2017) FTY720/fingolimod, an oral S1PR modulator, mitigates radiation induced cognitive deficits. Neurosci Lett 658:1–5
Priceman SJ, Sung JL, Shaposhnik Z, Burton JB, Torres-Collado AX, Moughon DL, Johnson M, Lusis AJ, Cohen DA, Iruela-Arispe ML, Wu L (2010) Targeting distinct tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells by inhibiting CSF-1 receptor: combating tumor evasion of antiangiogenic therapy. Blood 115(7):1461–1471
Zeng J, See AP, Phallen J, Jackson CM, Belcaid Z, Ruzevick J, Durham N, Meyer C, Harris TJ, Albesiano E, Pradilla G, Ford E, Wong J, Hammers HJ, Mathios D, Tyler B, Brem H, Tran PT, Pardoll D, Drake CG, Lim M (2013) Anti-PD-1 blockade and stereotactic radiation produce long-term survival in mice with intracranial gliomas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 86(2):343–349
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stessin, A.M., Clausi, M.G., Zhao, Z. et al. Repolarized macrophages, induced by intermediate stereotactic dose radiotherapy and immune checkpoint blockade, contribute to long-term survival in glioma-bearing mice. J Neurooncol 147, 547–555 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-020-03459-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-020-03459-y