Abstract
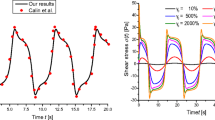
In this paper, the influence of clobetasol propionate and sodium dodecyl sulfate on the viscoelastic modules and gelation transition of aqueous solutions of poloxamer 407 are investigated experimentally. The influence of the polymer volume fraction is also examined. The experimental investigations are carried out with eight different samples of solutions. Four of them are free of additives varying just on macromolecule volume fraction. The other four samples are produced from the previous ones by addition of clobetasol and a surfactant (sodium dodecyl sulfate) in a volume fraction compatible with commercial applications. All samples are sheared in a high-performance rheometer of parallel disks with an automatic control of gap and temperature. The first set of tests are carried out under the condition of steady shear. From these tests, we obtain results for the apparent viscosity of the solutions of shear rate for two different temperatures, 6∘C and 36∘C. While a shear-thinning behavior is verified for the temperature of 36∘C, the viscosity is observed to have a non-shear rate dependence at 6∘C for all samples. The second tests deal with non-isotherm trials under a regime of small amplitude oscillatory shear, in a temperature range from 3.5 to 50∘C. The viscoelastic moduli of storage and loss of energy are obtained as a function of the temperature for fixed values of frequency and angular deflection. The gelation transition of the polymer solution is characterized as a sudden change in the viscoelastic modulus. This interesting finding is directly associated with microstructure transitions induced by increase of the temperature. We show results of the temperature of micellization and the gelation temperature as a function of the polymer volume fraction for a suspension in the absence of additives and with a certain volume fraction of SDS (surfactant) and clobetasol propionate. The presence of additives reinforces the link of micelles making the structure more stable and resistant to breakup. The effect of SDS or clobetasol propionate on gelation is seen to be very important, and there is a lack of systematic research about additives. We also present a result for the shear elastic modulus of the solution as a function of the polymer volume fraction for 6∘C. This shows that the micelles-like chain formation at a given temperature leads to a solid characteristic of the polymer that can be interpreted as a yield stress even at low temperatures. The presence of SDS and clobetasol propionate produces new rheological response of the poloxamer.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akash MSH, Rehman K, Chen S (2014) Pluronic f127-based thermosensitive gels for delivery of therapeutic proteins and peptides. Polym Rev 54(4):573–597
Alexandridis P, Hatton TA (1995) Poly (ethylene oxide)-poly (propylene oxide)-poly (ethylene oxide) block copolymer surfactants in aqueous solutions and at interfaces: thermodynamics, structure, dynamics, and modeling. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 96(1–2):1–46
Alexandridis P, Lindman B (2000) Amphiphilic block copolymers: self-assembly and applications. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Barnes HA, Hutton JF, Walters K (1989) An introduction to rheology, vol 3. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Batchelor GK (2000) An introduction to fluid dynamics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Bazargan V, Stoeber B (2010) Flow control using a thermally actuated microfluidic relay valve. J Microelectromech Syst 19(5):1079–1087
Bird RB, Armstrong RC, Hassager O (1987) Dynamics of polymeric liquids. Vol. 1: Fluid mechanics. Wiley-Interscience, New York
Bird RB, Stewart WE, Lightfoot EN (2007) Transport phenomena. John Wiley & Sons
Cabana A, Aït-Kadi A, Juhász J (1997) Study of the gelation process of polyethylene oxidea–polypropylene oxideb– polyethylene oxidea copolymer (poloxamer 407) aqueous solutions. J Colloid Interface Sci 190(2):307–312
Cox W, Merz E (1958) Correlation of dynamic and steady flow viscosities. J Polym Sci 28(118):619–622
Cruz OA, Zarnegar SR, Myers SE (1995) Treatment of periocular capillary hemangloma with topical clobetasol propionate. Ophthalmology 102(12):2012–2015
Denkova A, Mendes E, Coppens MO (2009) Rheology of worm-like micelles composed of tri-block copolymer in the limit of slow dynamics. J Rheol 53(5):1087–1100
Dumortier G, Grossiord J, Zuber M, Couarraze G, Chaumeil J (1991) Rheological study of a thermoreversible morphine gel. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 17(9):1255–1265
Dumortier G, Grossiord JL, Agnely F, Chaumeil JC (2006) A review of poloxamer 407 pharmaceutical and pharmacological characteristics. Pharm Res 23(12):2709–2728. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-006-9104-4
Escobar-Chávez JJ, López-Cervantes M, Naik A, Kalia Y, Quintanar-Guerrero D, Ganem-Quintanar A (2006) Applications of thermo-reversible pluronic f-127 gels in pharmaceutical formulations. J Pharm Pharm Sci 9(3):339–358
Habas JP, Pavie E, Lapp A, Peyrelasse J (2004) Understanding the complex rheological behavior of peo–ppo–peo copolymers in aqueous solution. J Rheol 48(1):1–21
Hopkins CC, de Bruyn JR (2019) Gelation and long-time relaxation of aqueous solutions of pluronic f127. J Rheol 63(1):191–201
Hvidt S, Joergensen EB, Brown W, Schillen K (1994) Micellization and gelation of aqueous solutions of a triblock copolymer studied by rheological techniques and scanning calorimetry. J Phys Chem 98(47):12320–12328
Hyun K, Nam JG, Wilhellm M, Ahn KH, Lee SJ (2006) Large amplitude oscillatory shear behavior of peo-ppo-peo triblock copolymer solutions. Rheol Acta 45(3):239–249
Jalaal M, Stoeber B (2014) Controlled spreading of thermo-responsive droplets. Soft Matter 10(6):808–812
Jalaal M, Cottrell G, Balmforth N, Stoeber B (2017) On the rheology of pluronic f127 aqueous solutions. J Rheol 61(1):139–146
Jegasothy B, Jacobson C, Levine N, Millikan L, Olsen E, Pinnell S, Cole G, Weinstein G, Porter M (1985) Clobetasol propionate versus fluocinonide creams in psoriasis and eczema. Int J Dermatol 24(7):461–465
Juhasz J, Lenaerts V, Raymond P, Ong H (1989) Diffusion of rat atrial natriuretic factor in thermoreversible poloxamer gels. Biomaterials 10(4):265–268
Liu T, Chu B (2000) Formation of homogeneous gel-like phases by mixed triblock copolymer micelles in aqueous solution: Fcc to bcc phase transition. J Appl Crystallogr 33(3):727–730
Luckham PF, Ukeje MA (1999) Effect of particle size distribution on the rheology of dispersed systems. J Colloid Interface Sci 220(2):347–356
Miller SC, Drabik BR (1984) Rheological properties of poloxamer vehicles. Int J Pharm 18(3):269–276
Moore T, Croy S, Mallapragada S, Pandit N (2000) Experimental investigation and mathematical modeling of pluronic® f127 gel dissolution: drug release in stirred systems. J Control Release 67(2–3):191–202
Patel HK, Barot BS, Parejiya PB, Shelat PK, Shukla A (2013) Topical delivery of clobetasol propionate loaded microemulsion based gel for effective treatment of vitiligo: ex vivo permeation and skin irritation studies. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 102:86–94
Pitto-Barry A, Barry NP (2014) Pluronic® block-copolymers in medicine: from chemical and biological versatility to rationalisation and clinical advances. Polym Chem 5(10):3291–3297
Prud’homme RK, Wu G, Schneider DK (1996) Structure and rheology studies of poly (oxyethylene- oxypropylene- oxyethylene) aqueous solution. Langmuir 12(20):4651–4659
Smith JG (2010) Topical formulation of low level clobetasol propionate for treating disorders of the skin and mucous membranes. US Patent App. 12/660,181
Steinleitner A, Lambert H, Kazensky C, Cantor B (1991) Poloxamer 407 as an intraperitoneal barrier material for the prevention of postsurgical adhesion formation and reformation in rodent models for reproductive surgery. Obstet Gynecol 77(1):48–52
Stoeber B, Yang Z, Liepmann D, Muller SJ (2005) Flow control in microdevices using thermally responsive triblock copolymers. J Microelectromech Syst 14(2):207–213
Stoeber B, Hu CMJ, Liepmann D, Muller SJ (2006) Passive flow control in microdevices using thermally responsive polymer solutions. Phys Fluids 18(5):053103
Takats Z, Vekey K, Hegedüs L (2001) Qualitative and quantitative determination of poloxamer surfactants by mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 15(10):805–810
Tanner RI (2000) Engineering rheology, vol 52. OUP Oxford
Tung CYM, Dynes PJ (1982) Relationship between viscoelastic properties and gelation in thermosetting systems. J Appl Polym Sci 27(2):569–574
Wanka G, Hoffmann H, Ulbricht W (1990) The aggregation behavior of poly-(oxyethylene)-poly-(oxypropylene)-poly-(oxyethylene)-block-copolymers in aqueous solution. Colloid Polym Sci 268(2):101–117
Winter HH, Chambon F (1986) Analysis of linear viscoelasticity of a crosslinking polymer at the gel point. J Rheol 30(2):367–382
Yelles MHB, Tan VT, Danede F, Willart J, Siepmann J (2017) Plga implants: how poloxamer/peo addition slows down or accelerates polymer degradation and drug release. J Control Release 253:19–29
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank T. Ângelo and T. Gratieri from the Department of Pharmacy (UnB) for kindly providing all the samples of polymer liquid tested and for helpful discussions during this work.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the grants 441340/2014-8, 402371/2013-5, and 305764/2015-2 from the Council of the Ministry of Science and Technology (CNPq-Brazil). I.D.P acknowledges the fellowship supported by the Foundation of the Ministry of Science and Technology (CAPES-Brazil).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pereira, I.D.O., Cunha, F.R. Rheological response in shear flows of a thermosensitive elastic liquid in the presence of some additives. Rheol Acta 59, 307–316 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-020-01194-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-020-01194-9