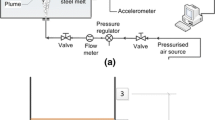
Abstract
When transporting yogurt, vibrations and sharp movements can damage its quality. This study developed a model to connect the changes in yogurt quality with the transportation distance as simulated by the total number of vibrations. Linear regression analysis showed that there was a significant negative correlation between the water holding capacity and hardness of the yogurt over the same transport distance (p < 0.05). The yogurt vibration model was established by combining principal component analysis with a Back-Propagation Artificial Neural Network model. The number of training iterations was 2669, with a correlation coefficient of 0.96611, indicating that the model was reliable. The optimal transportation distance was determined to be within the range from 20 rpm for 8 h to 100 rpm for 4 h.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bringe NA, Kinsella JE. Calcium chloride, temperature, preheat treatments and pH affect the rate of acid-induced aggregation of casein. Food Hydrocolloid. 2: 113-121 (1993)
Cai C. Prediction Model of shelf life of yoghourt to vrious parameters during storage. Huazhong Agricultural University (2012)
Cheng HF. Volatile flavor compounds in yogurt: a review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 50: 938-950 (2010)
Das K, Choudhary R, Thompson-Witrick KA. Effects of new technology on the current manufacturing process of yogurt-to increase the overall marketability of yogurt. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 108: 69-80 (2019)
Devillers J. Neural network in QSAR and drug design. Academic Press, San Diego, CA (1996)
Fu RQ, Xu TW, Pan ZX. Modelling of the adsorption of bovine serum albumin on porous polyethylene membrane by back-propagation artificial neural network. J. Membrane Sci. 251: 137-144 (2005)
Hassan ANR, Ipsen R, Janzen T, Qvist KB. Microstructure and rheology of yogurt made with cultures differing only in their ability to produce exopolysaccharides. J. Dairy Sci. 86: 1632-1638 (2003)
Jaworska DB, Kolanowski WR W, Swiderski F. Relative importance of texture properties in the sensory quality and acceptance of natural yoghurts. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 58: 39-46 (2005)
Karagül-Yüceer Y, Y, Drake MA, Chandan RC, Chandan RC, White CH, Kilara A, Hui YH. Sensory analysis of yogurt. Manufacturing Yogurt and Fermented Milks. Blackwell Publishing, pp 265-278 (2006)
Khanmohammadi M, Garmarudi AB, Ghasemi K, Garrigues S, Guardia MDL. Artificial neural network for quantitative determination of total protein in yogurt by infrared spectrometry. Microchem. J. 91: 47-52 (2009)
Khanmohammadi M, Garmarudi AB, Khoddami N, Shabani K, Khanlari M. A novel technique based on diffuse reflectance near-infrared spectrometry and back-propagation artificial neural network for estimation of partical size in TiO2 nano particle samples. Microchem. J. 95: 337-340 (2010)
Körzendörfer A, Temme P, Schlücker E, Hinrichs J, Nöbel S. Vibration-induced particle formation during yogurt fermentation-effect of frequency and amplitude. J. Dairy Sci. 101: 3866-3877 (2018)
Li C, Song J, Kwok LY, Wang J, Dong Y, Yu H, Hou Q, Zhang H, Chen Y. Influence of Lactobacillus plantarum on yogurt fermentation properties and subsequent changes during postfermentation storage. J. Dairy Sci. 100:2512-2525 (2017)
Lucey JA, Singh H. Formation and physical properties of acid milk gels: a review. Food Res. Int. 30: 529-542 (1997)
Lucey JA. Cultured dairy products: an overview of their gelation and texture properties. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 57: 77-84 (2004)
Mani-López, E, Palou E, López-Malo, A. Probiotic viability and storage stability of yogurts and fermented milks prepared with several mixtures of lactic acid bacteria. J. Dairy Sci. 97: 2578-2590 (2014)
Petchwattana N, Naknaen P. Influence of packaging material and storage time on physical, chemical and microbiological properties of set yogurt: A comparative study between modified biodegradable poly(lactic acid) and polypropylene. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 11: 1437-1449 (2016)
Salvador A, Fiszman SM. Textural and sensory characteristics of whole and skimmed flavored set-type yogurt during long storage. J. Dairy Sci. 87: 4033-4041 (2004)
Shaker RRB, Jumah AJRY, Ibrahim SA. Rheological properties of set yogurt during gelation process: II. Impact of incubation temperature. Milchwissenschaft 56: 622-625 (2001)
Sofu A, Ekinci FY. Estimation of storage time of yogurt with artificial neural network modeling. J. Dairy Sci. 90: 3118-3125 (2007)
Soukoulis C, Panagiotidis P K, Koureli R, Tzia C. Industrial yogurt manufacture: monitoring of fermentation process and improvement of final product quality. J. Dairy Sci. 90: 2641-2654 (2007)
Yang LL. Research on quality evaluation of food cold chain logistics service based on PCA-BP neural networ. Shenzhen University (2016)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31741102) and the Major Science and Technology Projects of Zhejiang Province (No. 2017C02033).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, A., Wei, X., Cai, R. et al. Modeling the effect of vibration on the quality of stirred yogurt during transportation. Food Sci Biotechnol 29, 889–896 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-020-00741-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-020-00741-7