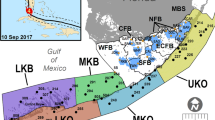
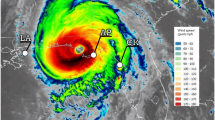
Abstract
Hurricanes are important ecological disturbances that maintain biodiversity. We investigated the short-term impacts of Hurricane Irma, a category 4 storm that passed through south Florida on September 10, 2017, on fish and macroinvertebrate communities of western and north-central Florida Bay, FL, USA. Spatiotemporal trends in physical water conditions (temperature, salinity, water depth, dissolved oxygen, chlorophyll a, and turbidity) as well as rainfall and coastal discharge were assessed to characterize hurricane-induced habitat changes. Dramatic but ephemeral changes in water depth and rainfall were observed. Longer lasting reductions of salinity regime and increases in turbidity and chlorophyll a were also observed. The prevailing hypersalinity (≥ 40 ppt) conditions, ongoing since March 2017, were abruptly ended by the storm. Hurricane Irma significantly altered fish and macroinvertebrate communities. Analysis of community spatiotemporal trends revealed spatially distinct temporal community shifts. Cluster analysis distinguished four groups among nine highly abundant species identified as exerting the most influence on pre- and post-hurricane total community differences. Reductions in relative abundance of two groups were coincident with Irma’s passage while a third group, comprised solely of pelagic, zooplanktivorous Anchoa mitchilli, exhibited rapid population growth that started 2 months after the passage of the storm. These faunal disruptions are reminiscent of a prior Florida Bay community shift that followed a similar sequence of consecutive disturbances: hypersalinity, seagrass die-off, and a category-5 hurricane. Recovery from this prior community shift cascade took many years.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abele, L.G., and W. Kim. 1986. An illustrated guide to the marine decapod crustaceans of Florida (Vol. 8). Tallahassee: Department of Environmental Regulation.
Anderson, M.J. 2001. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecology 26: 32–46.
Anderson, M.J., and T.J. Willis. 2003. Canonical analysis of principal coordinates: a useful method of constrained ordination for ecology. Ecology 84 (2): 511–525.
Anderson, M.J., K.E. Ellingsen, and B.H. McArdle. 2006. Multivariate dispersion as a measure of beta diversity. Ecology Letters 9 (6): 683–693.
Anderson, M.J. 2008. Animal-sediment relationships re-visited: Characterising species' distributions along an environmental gradient using canonical analysis and quantile regression splines. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 366 (1–2): 16–27.
Anderson, M.J., T.O. Crist, J.M. Chase, M. Vellend, B.D. Inouye, A.L. Freestone, N.J. Sanders, H.V. Cornell, L.S. Comita, K.F. Davies, S.P. Harrison, N.J.B. Kraft, J.C. Stegen, and N.G. Swenson. 2011. Navigating the multiple meanings of β diversity: a roadmap for the practicing ecologist. Ecology Letters 14 (1): 19–28.
Bailey, H., and D.H. Secor. 2016. Coastal evacuations by fish during extreme weather events. Nature Scientific Reports 6: 30280. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep30280.
Biggs, C.R., S.K. Lowerre-Barbieri, and B. Erisman. 2018. Reproductive resilience of an estuarine fish in the eye of a hurricane. Biology Letters 14. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsbl.2018.0579.
Burkholder, J., D. Eggleston, H. Glasgow, C. Brownie, R. Reed, G. Janowitz, Ma. Posey, G. Melta, C. Kinder, R. Corbett, D. Toms, T. Alphin, N. Deamer, and J. Springer. 2004. Comparative impacts of two major hurricane seasons on the Neuse River and western Pamlico sound ecosystems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 101 (25): 9291–9296.
Cangialosi, J.P., A.S. Latto, and R. Berg. 2018. National Hurricane Center Tropical Cyclone.
Carlson, D.F., L.A. Yarbro, S. Scolaro, M. Poniatowski, V. McGee-Absten, and P.R. Carlson Jr. 2018. Sea surface temperatures and seagrass mortality in Florida bay: Spatial and temporal patterns discerned from MODIS and AVHRR data. Remote Sensing of Environment 208: 171–188.
Carter, M., L. Burns, T. Cavinder, K. Dugger, P. Fore, D. Hicks, L. Revells, and T.W. Schmidt. 1973. Ecosystems analysis of the Big Cypress Swamp and estuaries. Atlanta: U.S.E.P.A., Reg. IV EPA 904/9-74-002 N.P.
Clarke, K.R. 1993. Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Austalian Journal of Ecology 18: 117–143.
Clarke, K.R., P.J. Somerfield, and R.N. Gorley. 2008. Testing of null hypotheses in exploratory community analyses: similarity profiles and biota-environment linkage. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 366: 56–69.
Clarke, K.R., R.N. Gorley, P.J. Somerfield, and R.M. Warwick. 2014. Change in marine communities: An approach to statistical analysis and interpretation. 3rd ed. Plymouth: PRIMER-E Ltd..
Cole, A.M., M.J. Durako, and M.O. Hall. 2018. Multivariate analysis of water quality and benthic macrophyte communities in Florida Bay, USA reveals hurricane effects and susceptibility to seagrass die-off. Frontiers in Plant Science 9: 630. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00630.
Emanuel, K. 2005. Increasing destructiveness of tropical cyclones over the past 30 years. Nature 436 (4): 686–688.
Fives, J.M., S.M. Warlen, and D.E. Hoss. 1986. Aging and growth of larval bay anchovy, Anchoa mitchilli, from the Newport River Estuary, North Carolina. Estuaries 9 (4B): 362–367.
Flaherty, K.E., R.E. Matheson, R.H. McMichael, and W.B. Perry. 2013. The influence of freshwater on nekton community structure in hydrologically distinct basins in Northeast Florida Bay, FL, USA. Estuaries and Coasts 36 (5): 918–939.
Fourqurean, J.W., and M.B. Robblee. 1999. Florida Bay: a history of recent ecological changes. Estuaries 22: 345–357.
Greening, Holly, Peter Doering, and Catherine Corbett. 2006. Hurricane impacts on coastal ecosystems. Estuaries and Coasts 29 (6): 877–879.
Greenwood, M.F.D., P.W. Stevens, and R.E. Matheson Jr. 2006. Effects of the 2004 hurricanes on the fish assemblages in two proximate southwest Florida estuaries: change in the context of interannual variability. Estuaries and Coasts 29 (6A): 985c996.
Hall, M.O., M.J. Durako, J.W. Fourqurean, and J.C. Zieman. 1999. Decadal changes in seagrass distribution and abundance in Florida Bay. Estuaries 22 (2B): 445–459.
Hall, M.O., B.T. Furman, M. Merello, and M.J. Durako. 2016. Recurrence of Thalassia testudinum seagrass die-off in Florida Bay, USA: initial observations. Marine Ecology Progress Series 560: 243–249.
Haynes, K., I.A. Eckley, and P. Fearnhead. 2017. Computational efficient changepoint detection for a range of penalties. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics 26 (1): 134.143.
Humann, P., and N. Deloach. 2002. Reef fish identification: Florida, Caribbean, Bahamas. Jacksonville: New World Publications.
Johnson, C.R., M.S. Koch, O. Pedersen, and C.J. Madden. 2018. Hypersalinity as a trigger of seagrass (Thalassia testudinum) die-off events in Florida Bay: evidence based on shoot meristem O2 and H2S dynamics. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 504: 47–52.
Keim, B.D., R.A. Muller, and G.W. Stone. 2007. Spatiotemporal patterns and return periods of tropical storm and hurricane strikes from Texas to Maine. Journal of Climate 20: 3498–3509.
Kelble, C.R., E.M. Johns, W.K. Nuttle, T.N. Lee, R.H. Smith, and P.B. Ortner. 2007. Salinity patterns of Florida Bay. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 71: 318–334.
Kelble, C.R., P.B. Ortner, G.L. Hitchcock, M.J. Dagg, and J.N. Boyer. 2010. Temporal and spatial variability of mesozooplankton in a shallow sub-tropical bay: influence of top-down control. Estuaries and Coasts 33: 723–737.
Killick, R., and I.A. Eckley. 2014. Changepoint: an R package for changepoint analysis. Journal of Statistical Software 58 (3): 1–19.
Knott, D.M., and R.M. Martore. 1989. The short-term effects of Hurricane Hugo on fishes and decapods crustaceans in the Ashley River and adjacent marsh creeks, South Carolina. Journal of Coastal Research SI8: 335–356.
Knutson, T.R., and R.E. Tuleya. 2004. Impact of CO2-induced warming on simulated hurricane intensity and precipitation: sensitivity to the choice of climate model and convective parameterization. Journal of Climate 17 (18): 3477–3495.
Koch, M.S., S.A. Schopmeyer, O.I. Nielsen, C. Kyhn-Hansen, and C.J. Madden. 2007. Conceptual model of seagrass die-off in Florida Bay: links to biogeochemical processes. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 350: 73–88.
Lavielle, M. 2005. Using penalized contrasts for the change-point problem. Signal Processing 85: 1501–1510.
Lawrence, D., M.J. Dagg, H. Liu, S.R. Cummings, P.B. Ortner, and C. Kelble. 2004. Wind events and benthic-pelagic coupling in a shallow subtropical bay in Florida. Marine Ecology Progress Series 266: 1–13.
Lee, T.N., E. Johns, N. Melo, R.H. Smith, P. Ortner, and D. Smith. 2006. On Florida Bay hypersalinity and water exchange. Bulletin of Marine Science 79 (2): 301–327.
Lee, T.N., N. Melo, E. Johns, C. Kelble, R.H. Smith, and P. Ortner. 2008. On water renewal and salinity variability in the northeast subregion of Florida Bay. Bulletin of Marine Science 82: 83–105.
Lee, T.N., N. Melo, N. Smith, E.M. Johns, C.R. Kelble, R.H. Smith, and Peter B. Ortner. 2016. Circulation and water renewal of Florida Bay, USA. Bulletin of Marine Science 92 (2): 153–180.
Lugo, A.E. 2008. Visible and invisible effects of hurricanes on forest ecosystems: an international review. Austral Ecology 33 (4): 368–398.
Lugo, A.E., C.S. Rogers, and S.W. Nixon. 2000. Hurricanes, coral reefs and rainforests: Resistance, ruin and recovery in the Caribbean. Ambio: A Journal of the Human Environment 29 (2): 106–115.
Massie, J.A., B.A. Strickland, R.O. Santos, J. Hernandez, N. Viadero, R.E. Boucek, H. Willoughby, M.R. Heithaus, and J.S. Rehage. 2019. Going downriver: Patterns and cues in hurricane-driven movements of common snoo in a subtropical coastal river. Estuaries and Coasts. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-019-00617-y.
Matheson, R.E., K. Camp Jr., S.M. Sogard, and K. Bjorgo. 1999. Changes in seagrass- associated fish and crustacean communities on Florida Bay mud banks: the effects of recent ecosystem changes? Estuaries 22: 534–551.
McArdle, B.H., and M.J. Anderson. 2001. Fitting multivariate models to community data: a comment on distance-based redundancy analysis. Ecology 82 (1): 290–297.
McEachran, J.D., and J.D. Fechhelm. 1998. Fishes of the Gulf of Mexico, volume 1: Myxiniformes to Gasterosteiformes. Austin: University of Texas Press.
McEachran, J.D., and J.D. Fechhelm. 2005. Fishes of the Gulf of Mexico, volume 2: Scorpaeniformes to Tetraodontiformes. Austin: University of Texas Press.
Mukherjee, S., A. Chaudhuri, S. Sen, and S. Homechaudhuri. 2012. Effect of Cyclone Aila on estuarine fish assemblages in the Matla River of the Indian Sundarbans. Journal of Tropical Ecology 28: 405–415.
Nuttle, W.K., J.W. Fourqurean, J. Coby, J.C. Zieman, and M.B. Robblee. 2000. Influence of net freshwater supply on salinity in Florida Bay. Water Resources Research 36: 1805–1822.
Oouchi, K., J. Yosuimura, H. Yoshimura, R. Mizuta, S. Kusunoki, and A. Noda. 2006. Tropical cyclone climatology in a global-warming climate as simulated in a 20 km-mesh global atmospheric model: frequency and wind intensity analyses. Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan 84 (2): 259–276.
Orr, D.W., and J.C. Ogden. 1992. The impact of Hurricane Andrew on the on the ecosystems of south Florida. Conservation Biology 6 (4): 488–490.
Paerl, H.W., L.M. Valdes, A.R. Joyner, B.L. Peierls, M.F. Piehler, S.R. Riggs, R.R. Christian, L.A. Eby, L.B. Crowder, J.S. Ramus, E.J. Clesceri, C.P. Buzzelli, and R.A. Luettich Jr. 2006. Ecological response to hurricane events in the Pamlico Sound system, North Carolina, and implications for assessment and management in a regime of increased frequency. Estuaries and Coasts 29 (6A): 1033–1045.
Paerl, H.W., J.R. Crosswell, B. Van Dam, N.S. Hall, K.L. Rossignol, C.L. Osburn, A.G. Hounshell, R.S. Sloup, and L.W. Harding Jr. 2018. Two decades of tropical cyclone impacts on North Carolina’s estuarine carbon, nutrient and phytoplankton dynamics: implications for biogeochemical cycling and water quality in a stormier world. Biogeochemistry 141: 307–332.
Paperno, R., D.M. Tremain, D.H. Adams, A.P. Sebastian, J.T. Sauer, and J. Dutka-Gianelli. 2006. The disruption and recovery of fish communities in the Indian River lagoon, Florida, following two hurricanes in 2004. Estuaries and Coasts 29 (6A): 1004–1010.
Peierls, B.L., R.R. Christian, and H.W. Paerl. 2003. Water quality and phytoplankton as indicators of hurricane impacts on a large estuarine ecosystem. Estuaries 26 (5): 1329–1343.
Powell, A.B., D.E. Hoss, W.F. Hettler, D.S. Peters, and S. Wagner. 1989. Abundance and distribution of ichthyoplankton in Florida Bay and adjacent waters. Bulletin of Marine Science 44 (1): 35–48.
Powell, A. B., G. Thayer, M. Lacroix, and R. Cheshire. 2007. Juvenile and small resident fishes of Florida Bay, a critical habitat in the Everglades National Park, Florida. NOAA Professional Paper NMFS 6. 210 pp.
Price, R.M., W.K. Nuttle, B.J. Cosby, and P.K. Swart. 2007. Variation and uncertainty in evaporation from a subtropical estuary: Florida Bay. Estuaries and Coasts 30: 497–506.
R Core Team. 2016. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. In R Foundation for statistical computing. Vienna: Available online at https://www.R-project.org/. Accessed 9 Oct 2019.
Ray, C., and C.R. Robins. 2016. A field guide to Atlantic coast fishes: North America. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt.
Report: Hurricane Irma (AL112017). National Hurricane Center, Miami, FL. 111 pp. Available from: https://www.nhc.noaa.gov/data/tcr/AL112017_Irma.pdf
Robblee, M.B., T.R. Barber, P.R. Carlon Jr., M.J. Durako, J.W. Fourqurean, L.K. Muehlstein, D. Porter, L.A. Yarbro, R.T. Zieman, and J.C. Zieman. 1991. Mass mortality of the tropical seagrass Thalassia testudinum in Florida Bay (USA). Marine Ecology Progress Series 71: 297–299.
Robins, C.R. 1957. Effects of storms on the shallow-water fish fauna of southern Florida with new records of fishes from Florida. Bulletin of Marine Science of the Gulf and Caribbean 7 (3): 266–275.
Rogers, C.S. 1993. Hurricanes and coral reefs: the intermediate disturbance hypothesis revisited. Coral Reefs 12: 127–137.
Rudnick, D.T., Z. Chen, D.L. Childers, J.N. Boyer, and T.D. Fontaine III. 1999. Phosphorous and nitrogen inputs to Florida Bay: the importance of the Everglades watershed. Estuaries 22 (2B): 398–416.
Schmidt, T.W. 1979. 1979 Ecological study of fishes and the water quality characteristics of Florida Bay, Everglades National Park, Florida. Final Project Report# RSP-EVER N-36. 99 pp.
Sheridan, P.F. 1992. Comparative habitat utilization by estuarine macrofauna within the mangrove ecosystem of Rookery Bay, Florida. Bulletin of Marine Science 50 (1): 21–39.
Smith, N.P. 1997. An introduction to the tides of Florida Bay. Florida Scientist 60 (1): 53–57.
Smith, N.P. 1998. Tidal and long-term exchanges through channels in the middle and upper Florida Keys. Bulletin of Marine Science 62 (1): 199–211.
Smith, N.P., and T.N. Lee. 2003. Volume transport through tidal channels in the middle Florida Keys. Journal of Coastal Research 19 (2): 254–260.
South Florida Natural Resources Center (SFNRC) (2018) DataForEVER Dataset, Everglades National Park, Homestead, FL, Generated by Ian Zink, using Appaserver software (http://www.appaserver.com), Sacramento, CA. Public URL not currently available, please send data requests to EVER_data_request@nps.gov. Retrieved 11/19/18.
Stabenau, E., and K. Kotun. 2012. Salinity and hydrology of Florida Bay: status and trends 1990-2009. National Park Service, Everglades National Park, South Florida Natural Resources Center, Homestead, FL. Status and Trends Report. SFNRC Technical Series 2012:1. 39 pp.
Stevens, P.W., D.A. Blewett, and J.P. Casey. 2006. Short-term effects of a low dissolved oxygen event on estuarine fish assemblages following the passage of Hurricane Charley. Estuaries and Coasts 29 (6A): 997–1003.
Strickland, B.A., J.A. Massie, N. Viadero, R. Santos, K.R. Gastrich, V. Paz, P. O'Donnell, A.M. Kroetz, D.T. Ho, J.S. Rehage, and M.R. Heithaus. 2019. Movements of juvenile bull sharks in response to a major hurricane within a tropical estuarine nursery system. Estuaries and Coasts. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-019-00600-7.
Stumpf, R.P., M.L. Frayer, M.J. Durako, and J.C. Brock. 1999. Variations in water clarity and bottom albedo in Florida Bay from 1985 to 1997. Estuaries 22 (2B): 431–444.
Switzer, T.S., B.L. Winner, N.M. Dunham, J.A. Whittington, and M. Thomas. 2006. Influence of sequential hurricanes on nekton communities in a southeast Florida estuary: short-term effects in the context of historical variations in freshwater inflow. Estuaries and Coasts 29 (6A): 1011–1018.
Tabb, Durbin C., and Albert C. Jones. 1962. Effect of Hurricane Donna on the aquatic fauna of north Florida Bay. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 91 (4): 375–378.
Thayer, G.W., and A.J. Chester. 1989. Distribution and abundance of fishes among basin and channel habitats in Florida Bay. Bulletin of Marine Science 44 (1): 200–219.
Thayer, G.W., A.B. Powell, and D.E. Hoss. 1999. Composition of larval, juvenile, and small adult fishes relative to changes in environmental conditions in Florida Bay. Estuaries 22 (2B): 518–533.
Thomas, L.P., D.R. Moore, and R.C. Work. 1961. Effects of Hurricane Donna on the turtle grass beds of Biscayne Bay, Florida. Bulletin of Marine Science of the Gulf and Caribbean 11 (2): 191–197.
Tilmant, J.T., R.W. Curry, R. Jones, A. Szmant, J.C. Zieman, M. Flora, M.B. Robblee, D. Smith, R.W. Snow, and H. Wanlass. 1994. Hurricane Andrew’s effects on marine resources. BioScience 44 (4): 230–237.
Wachnicka, A., J. Browder, T. Jackson, W. Louda, C. Kelble, O. Abdelrahman, E. Stabenau, and C. Avila. 2019. Hurriane Irma’s impact on water quality and phytoplankton communities in Biscyane Bay (Florida, USA). Estuaries and Coasts. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-019-00592-4.
Wang, J.C., and E.C. Raney. 1971. Distribution and fluctuations in the fish fauna of the Charlotte Harbor Estuary, Florida. Sarasota: Mote Mar. Lab 56 pp.
Wang, J.D., J. van de Kreeke, N. Krishnan, and D. Smith. 1994. Wind and tide response in Florida Bay. Bulletin of Marine Science 54 (3): 579–601.
Warton, D.I., S.T. Wright, and Y. Wang. 2012. Distance-based multivariate analyses confound location and dispersion effects. Methods in Ecology and Evolution 3: 89–101.
Webster, P.J., G.J. Holland, J.A. Curry, and H.-R. Chang. 2005. Changes in tropical cyclone number, duration, and intensity in a warming environment. Science 309 (5742): 1844–1846.
Williams, A.B. 1984. Shrimps, lobsters, and crabs of the Atlantic coast of the eastern United States, Maine to Florida. Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington, D.C.
Wilson, S.S., B.T. Furman, M.O. Hall, and J.W. Fourqurean. 2019. Assessment of Hurricane Irma imapcts on south Florida seagrass communities using long-term monitoring programs. Estuaries and Coasts. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-019-00623-0.
Wingard, G.L., S.E. Bergstresser, B.L. Stackhouse, M.C. Jones, M.E. Marot, K. Hoefke, A. Daniels, and K. Keller. 2019. Impacts of Hurricane Irma on Florida Bay islands, Everglades National Park. USA. Estuaries and Coasts. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-019-00638-7.
Woodley, J.D., E.A. Chornesky, P.A. Clifford, J.B.C. Jackson, K.S. Kaufman, N. Knowlton, J.C. Lang, M.P. Pearson, J.W. Porter, M.C. Rooney, K.W. Rylaarsdam, V.J. Tunnicliffe, C.M. Wahle, J.L. Wulff, A.S.G. Curtis, M.D. Dallmeyer, B.P. Jupp, M.A.R. Koehl, J. Neigel, and E.M. Sides. 1981. Hurricane Allen’s impact on Jamaican coral reefs. Science 214 (4522): 749–755.
Zhao, M., I.M. Held, S.-J. Lin, and G.A. Vecchi. 2009. Simulations of global hurricane climatology, interannual variability, and response to global warming using a 50-km resolution GCM. Journal of Climate 22: 6653–6678.
Zieman, J.C., J.W. Fourqurean, and T.A. Frankovich. 1999. Seagrass die-off in Florida Bay: long-term trends in abundance and growth of turtle grass, Thalassia testudinum. Estuaries 22 (2B): 460–470.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Joseph Serafy (SEFSC NMFS NOAA) and three anonymous reviewers for discussions that improved the presentation of this study and provided insight of the ecological impacts observed after the passage of Hurricane Irma. We also thank the guest editors of this issue for their comments on the draft manuscript. A number of technicians located at the AOML OAR NOAA and SEFSC NMFS NOAA offices in Miami, FL, assisted with field collections and laboratory species identifications that yielded the fish and macroinvertebrate community dataset; we are indebted to their assistance. This research was carried out [in part] under the auspices of the Cooperative Institute for Marine and Atmospheric Studies (CIMAS), a Cooperative Institute of the University of Miami and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, cooperative agreement #NA10OAR4320143.
Funding
This study was funded by US Army Corps of Engineers RECOVER (REstroation COodination and VERification) as part of the Comprehensive Everglades Restoration Plan Monitoring and Assessment Plan (MAP). Fish and macroinvertebrate community sampling was conducted under NPS Permit no. EVER-2018-SCI-0059.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Melisa C. Wong
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(DOCX 25 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zink, I.C., Browder, J.A., Kelble, C.R. et al. Hurricane-Mediated Shifts in a Subtropical Seagrass Associated Fish and Macroinvertebrate Community. Estuaries and Coasts 43, 1174–1193 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-020-00715-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12237-020-00715-2