Abstract
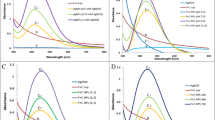
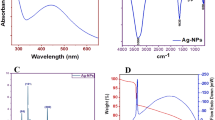
Enterococcus faecalis (E. faecalis) is a Gram-positive bacterium closely related to many refractory infections of human and shows the resistant ability against the antibacterial effects of silver. Simvastatin is a semisynthetic compound derived from lovastatin and a hydroxymethyl glutaryl coenzyme A(HMG-COA) reductase inhibitor showing certain inhibitive effects on bacteria. The main purpose of this study was to establish and characterize the Ag+/silver nanoparticles (AgNPs)-resistant E. faecalis, and further evaluate the function of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in the silver resistance and the effect of simvastatin on the silver-resistance of E. faecalis. The results showed that the established silver-resistant E. faecalis had strong resistance against both Ag+ and AgNPs and simvastatin could decrease the silver-resistance of both original and Ag+/AgNPs-resistant E. faecalis. The Transmission electron microscopy (TEM), High-angle annular dark-field (HAADF) and mapping images showed that the silver ions or particles aggregated and confined in the EPS on surface areas of the cell membrane when the silver-resistant E. faecalis were incubated with Ag+ or AgNPs. When the simvastatin was added, the silver element was not confined in the EPS and entered the bacteria. These findings may indicate that the silver resistance of E. faecalis was derived from the entrapping function of EPS, but simvastatin could compromise the function of EPS to decrease the silver resistant ability of E. faecalis.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Aldilla VR, Chen R, Martin AD, Marjo CE, Rich AM, Black DS, Thordarson P, Kumar N (2020) Anthranilamide-based short peptides self-assembled hydrogels as antibacterial agents. Sci Rep 10:770. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-57342-6
Alla VM, Agrawal V, DeNazareth A, Mohiuddin S, Ravilla S, Rendell M (2013) A reappraisal of the risks and benefits of treating to target with cholesterol lowering drugs. Drugs 73:1025–1054. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-013-0072-9
Allon I, Anavi Y, Allon DM (2014) Topical simvastatin improves the pro-angiogenic and pro-osteogenic properties of bioglass putty in the rat calvaria critical-size model. J Oral Implantol 40:251–258. https://doi.org/10.1563/AAID-JOI-D-11-00222
Almog Y, Shefer A, Novack V, Maimon N, Barski L, Eizinger M, Friger M, Zeller L, Danon A (2004) Prior statin therapy is associated with a decreased rate of severe sepsis. Circulation 110:880–885
Anand K, Sketris I, Zhang Y, Levy A, Gamble JM (2017) The impact of US FDA and health canada warnings related to the safety of high-dose simvastatin. Drugs Real World Outcomes 4:215–223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40801-017-0116-7
Andersson DI, Balaban NQ, Baquero F, Courvalin P, Glaser P, Gophna U, Kishony R, Molin S, Tønjum T (2020) Antibiotic resistance: turning evolutionary principles into clinical reality. FEMS Microbiol Rev. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsre/fuaa001
Balaei-Gajan E, Shirmohammadi A, Abashov R, Agazadeh M, Faramarzie M (2010) Detection of Enterococcus Faecalis in subgingival biofilm of patients with chronic refractory periodontitis. Med Oral Patol Oral 15:e667–670
Bergman P, Linde C, Pütsep K, Pohanka A, Normark S, Henriques-Normark B, Andersson J, Björkhem-Bergman L (2011) Studies on the antibacterial effects of statins–in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 6:e2439. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0024394
Bhaskar PV, Bhosle NB (2006) Bacterial extracellular polymeric substance (EPS): a carrier of heavy metals in the marine food-chain. Environ Int 32:191–198
Björkhem-Bergman L, Bergman P, Andersson J, Lindh JD (2010) Statin treatment and mortality in bacterial infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 5:e10702. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0010702
Blanco Massani M, Klumpp J, Widmer M, Speck C, Nisple M, Lehmann R, Schuppler M (2018) Chromosomal Sil system contributes to silver resistance in E. coli ATCC 8739. Biometals 31:1101–1114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-018-0143-1
Bo T, Shao S, Wu D, Niu S, Zhao J, Gao L (2017) Relative variations of gut microbiota in disordered cholesterol metabolism caused by high-cholesterol diet and host genetics. Microbiologyopen. https://doi.org/10.1002/mbo3.491
Cereda R, Sader H, Sejas L, Machado A, Zanatta Y, Rego S, Medeiros E (2001) Enterococcus faecalis resistant to vancomycin and teicoplanin (VanA phenotype) isolated from a bone marrow transplanted patient in Brazil. Braz J Infect Dis 5:40–46
Chabert V, Hologne M, Sénèque O, Crochet A, Walker O, Fromm KM (2017) Model peptide studies of Ag(+) binding sites from the silver resistance protein SilE. Chem Commun (Camb) 53:6105–6108. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7cc02630g
Comte S, Guibaud G, Baudu M (2006) Biosorption properties of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) resulting from activated sludge according to their type: soluble or bound. Process Biochem 41:815–823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2005.10.014
Dimkpa CO, Calder A, Britt DW, McLean JE, Anderson AJ (2011a) Responses of a soil bacterium, Pseudomonas chlororaphis O6 to commercial metal oxide nanoparticles compared with responses to metal ions. Environ Pollut 159:1749–1756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.04.020
Dimkpa CO, Calder A, Gajjar P, Merugu S, Huang W, Britt DW, McLean JE, Johnson WP, Anderson AJ (2011b) Interaction of silver nanoparticles with an environmentally beneficial bacterium, Pseudomonas chlororaphis. J Hazard Mater 188:428–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.01.118
Elkrewi E, Randall CP, Ooi N, Cottell JL, O'Neill AJ (2017) Cryptic silver resistance is prevalent and readily activated in certain Gram-negative pathogens. J Antimicrob Chemother 72:3043–3046. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkx258
Fan W, Li Y, Sun Q, Ma T, Fan B (2016) Calcium-silicate mesoporous nanoparticles loaded with chlorhexidine for both anti-Enterococcus Faecalis and mineralization properties. J Nanobiotechnol 14:72
Fan W, Sun Q, Li Y, Tay FR, Fan B (2018) Synergistic mechanism of Ag(+)-Zn(2+) in anti-bacterial activity against Enterococcus Faecalis and its application against dentin infection. J Nanobiotechnology 16:10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-018-0336-3
Flemming HC, Wingender J (2010) The biofilm matrix. Nat Rev Microbiol 8:623–633. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2415
Graves JL Jr, Tajkarimi M, Cunningham Q, Campbell A, Nonga H, Harrison SH, Barrick JE (2015) Rapid evolution of silver nanoparticle resistance in Escherichia coli. Front Genet 6:42. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2015.00042
Graziano TS, Cuzzullin MC, Franco GC, Schwartz-Filho HO, de Andrade ED, Groppo FC, Cogo-Müller K (2015) Statins and antimicrobial effects: simvastatin as a potential drug against Staphylococcus aureus biofilm. PLoS ONE 10:e0128098. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0128098
George S, Tay I, Phue WH, Gardner H, Sukumaran B (2019) Enhancing the bioavailability of silver through nanotechnology approaches could overcome efflux pump mediated silver resistance in methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Biomed Nanotechnol 15:2216–2228. https://doi.org/10.1166/jbn.2019.2858
Gupta M, Sharma R, Kumar A (2019) Comparative potential of simvastatin, rosuvastatin and fluvastatin against bacterial infection: an in silico and in vitro study. Orient Pharm Exp Med 19:259–275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13596-019-00359-z
Ha J, Gélabert A, Spormann AM, BrownJr GE (2010) Role of extracellular polymeric substances in metal ion complexation on Shewanella oneidensis: Batch uptake, thermodynamic modeling, ATR-FTIR, and EXAFS study. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 74:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2009.06.031
Hall Snyder A, Werth BJ, Barber KE, Sakoulas G, Rybak MJ (2014) Evaluation of the novel combination of daptomycin plus ceftriaxone against vancomycin-resistant enterococci in an in vitro pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic simulated endocardial vegetation model. J Antimicrob Chemother 69:2148–2154. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dku113
Hanczvikkel A, Füzi M, Ungvári E, Tóth Á (2018) Transmissible silver resistance readily evolves in high-risk clone isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung 65:387–403. https://doi.org/10.1556/030.65.2018.031
Harish R, Samuel J, Mishra R, Chandrasekaran N, Mukherjee A (2012) Bio-reduction of Cr(VI) by exopolysaccharides (EPS) from indigenous bacterial species of Sukinda chromite mine, India. Biodegradation 23:487–496. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-011-9527-4
Henriques LC, de Brito LC, Tavares WL, Teles RP, Vieira LQ, Teles FR, Sobrinho AP (2016) Microbial ecosystem analysis in root canal infections refractory to endodontic treatment. J Endod 42:1239–1245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2016.05.014
Horn MP, Knecht SM, Rushing FL, Birdsong J, Siddall CP, Johnson CM, Abraham TN, Brown A, Volk CB, Gammon K, Bishop DL, McKillip JL, McDowell SA (2008) Simvastatin inhibits Staphylococcus aureus host cell invasion through modulation of isoprenoid intermediates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 326:135–143. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.108.137927
Hosny AEM, Rasmy SA, Aboul-Magd DS, Kashef MT, El-Bazza ZE (2019) The increasing threat of silver-resistance in clinical isolates from wounds and burns. Infect Drug Resist 12:1985–2001. https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S209881
Janda S, Young A, Fitzgerald JM, Etminan M, Swiston J (2010) The effect of statins on mortality from severe infections and sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Crit Care 25:656.e7–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrc
Javidi M, Afkhami F, Zarei M, Ghazvini K, Rajabi O (2014) Efficacy of a combined nanoparticulate/calcium hydroxide root canal medication on elimination of Enterococcus Faecalis. Aust Endod J 40:61–65. https://doi.org/10.1111/aej.12028
Kang F, Alvarez PJ, Zhu D (2014) Microbial extracellular polymeric substances reduce Ag+ to silver nanoparticles and antagonize bactericidal activity. Environ Sci Technol 48:316–322. https://doi.org/10.1021/es403796x
Ketikidis I, Banti CN, Kourkoumelis N, Tsiafoulis CG, Papachristodoulou C, Kalampounias AG, Hadjikakou SK (2020) Conjugation of penicillin-G with silver (I) ions expands its antimicrobial activity against gram negative bacteria. Antibiotics (Basel) 9(1):E25. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9010025
Khan AR, Riaz M, Bin Abdulhak AA, Al-Tannir MA, Garbati MA, Erwin PJ, Baddour LM, Tleyjeh IM (2013) The role of statins in prevention and treatment of community acquired pneumonia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 8:e52929. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0052929
Kim TH, Yun YP, Shim KS, Kim HJ, Kim SE, Park K, Song HR (2018) In vitro anti-inflammation and chondrogenic differentiation effects of inclusion nanocomplexesof hyaluronic acid-beta cyclodextrin and simvastatin. Tissue Eng Regen Med 15:263–274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13770-018-0119-9
Li XZ, Nikaido H, Williams KE (1997) Silver-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli display active efflux of Ag+ and are deficient in porins. J Bacteriol 179:6127–6132
Liu H, Fang HH (2002) Characterization of electrostatic binding sites of extracellular polymers by linear programming analysis of titration data. Biotechnol Bioeng 80:806–811
Liu Y, Li J, Xiao FQ, Clemens B (2007) Bactericidal activity of nitrogen-doped metal oxide nanocatalysts and the influence of bacterial extracellular polymeric substances (EPS). J Photochem Photobiol A 190:94–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2007.03.017
López-Cortés LE, Gálvez-Acebal J, Del Toro MD, Velasco C, de Cueto M, Caballero FJ, Muniain MA, Pascual A, Rodríguez-Baño J (2013) Effect of statin therapy in the outcome of bloodstream infections due to Staphylococcus aureus: a prospective cohort study. PLoS ONE 8:e82958. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0082958
Masadeh M, Mhaidat N, Alzoubi K, Al-Azzam S, Alnasser Z (2012) Antibacterial activity of statins: a comparative study of atorvastatin, simvastatin, and rosuvastatin. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob 11:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-0711-11-13
Mei L, Zhu S, Yin W, Chen C, Nie G, Gu Z, Zhao Y (2020) Two-dimensional nanomaterials beyond graphene for antibacterial applications: current progress and future perspectives. Theranostics 10:757–781. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.39701
Mijnendonckx K, Leys N, Mahillon J, Silver S, Van Houdt R (2013) Antimicrobial silver: uses, toxicity and potential for resistance. Biometals 26:609–621. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-013-9645-z
Moraschini V, Almeida DCF, Calasans-Maia JA, Diuana Calasans-Maia M (2018) The ability of topical and systemic statins to increase osteogenesis around dental implants: a systematic review of histomorphometric outcomes in animal studies. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 47:1070–1078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2017.12.009
Moreau JW, Weber PK, Martin MC, Gilbert B, Hutcheon ID, Banfield JF (2007) Extracellular proteins limit the dispersal of biogenic nanoparticles. Science 316:1600–1603
Muller M, Merrett ND (2014) Pyocyanin production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa confers resistance to ionic silver. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58:5492–5499. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.03069-14
Munita JM, Arias CA (2016) Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Microbiol Spectr. https://doi.org/10.1128/microbiolspec.VMBF-0016-2015
Muzondiwa D, Mutshembele A, Pierneef RE, Reva ON (2020) Resistance sniffer: an online tool for prediction of drug resistance patterns of mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates using next generation sequencing data. Int J Med Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmm.2020.151399
Kaur P, Vadehra DV (1986) Mechanism of resistance to silver ions in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 29:165–167
Panáček A, Kvítek L, Smékalová M, Večeřová R, Kolář M, Röderová M, Dyčka F, Šebela M, Prucek R, Tomanec O, Zbořil R (2018) Bacterial resistance to silver nanoparticles and how to overcome it. Nat Nanotechnol 13:65–71. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-017-0013-y
Piekarska K, Kochman M, Lawrynowicz-Paciorek M (2005) Characteristic of clinical fluoroquinolone resistant isolates E. faecalis. Med Dosw Mikrobiol 57:345–353
Plotkin BJ, Konakieva MI (2017) Attenuation of antimicrobial activity by the human steroid hormones. Steroids 128:120–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.steroids.2017.09.007
Randall CP, Gupta A, Jackson N, Busse D, O'Neill AJ (2015) Silver resistance in Gram-negative bacteria: a dissection of endogenous and exogenous mechanisms. J Antimicrob Chemother 70:1037–1046. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dku523
Randall CP, Oyama LB, Bostock JM, Chopra I, O'Neill AJ (2013) The silver cation (Ag+): antistaphylococcal activity, mode of action and resistance studies. J Antimicrob Chemother 68:131–138. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dks372
Rodrigues CT, de Andrade FB, de Vasconcelos LRSM, Midena RZ, Pereira TC, Kuga MC, Duarte MAH, Bernardineli N (2018) Antibacterial properties of silver nanoparticles as a root canal irrigant against Enterococcus Faecalis biofilm and infected dentinal tubules. Int Endod J 51:901–911. https://doi.org/10.1111/iej.12904
Shitara Y, Sugiyama Y (2006) Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic alterations of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase inhibitors: drug–drug interactions and interindividual differences in transporter and metabolic enzyme functions. Pharmacol Ther 112:71–105
Silver S (2003) Bacterial silver resistance: molecular biology and uses and misuses of silver compounds. FEMS Microbiol Rev 27:341–353
Środa-Pomianek K, Michalak K, Palko-Łabuz A, Uryga A, Szczęśniak-Sięga B, Wesołowska O (2019) Simvastatin strongly augments proapoptotic, anti-inflammatory and cytotoxic activity of oxicam derivatives in doxorubicin-resistant colon cancer cells. Anticancer Res 39:727–734. https://doi.org/10.21873/anticanres.13169
Sun X, Li S, Wang S, Luo C, Hou B (2018) The evaluation of E. faecalis colonies dissolution ability of sodium hypochlorite in microenvironment by a novel device. Biomed Microdevices 20:36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-018-0279-3
Teitzel GM, Parsek MR (2003) Heavy metal resistance of biofilm and planktonic Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:2313–2320
Thangamani S, Mohammad H, Abushahba MF, Hamed MI, Sobreira TJ, Hedrick VE, Paul LN, Seleem MN (2015) Exploring simvastatin, an antihyperlipidemic drug, as a potential topical antibacterial agent. Sci Rep 5:16407. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep16407
Tulbah AS, Pisano E, Landh E, Scalia S, Young PM, Traini D, Ong HX (2019) Simvastatin nanoparticles reduce inflammation in LPS-stimulated alveolar macrophages. J Pharm Sci 108:3890–3897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xphs.2019.08.029
Van Acker H, Van Dijck P, Coenye T (2014) Molecular mechanisms of antimicrobial tolerance and resistance in bacterial and fungal biofilms. Trends Microbiol 22:326–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2014.02.001
Vidana R, Sullivan A, Billström H, Ahlquist M, Lund B (2011) Enterococcus Faecalis infection in root canals - host-derived or exogenous source? Lett Appl Microbiol 52:109–115. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-765X.2010.02972.x
Vu B, Chen M, Crawford RJ, Ivanova EP (2009) Bacterial extracellular polysaccharides involved in biofilm formation. Molecules 14:2535–2554. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules14072535
Wang Z, Liu X, Teng Da, Mao R, Hao Y, Yang N, Wang X, Li Z, Wang X, Wang J (2020) Development of chimeric peptides to facilitate the neutralisation of lipopolysaccharides during bactericidal targeting of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli. Commun Biol 3:41. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-020-0761-3
Werth BJ, Steed ME, Ireland CE, Tran TT, Nonejuie P, Murray BE, Rose WE, Sakoulas G, Pogliano J, Arias CA, Rybak MJ (2014) Defining daptomycin resistance prevention exposures in vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium and E. faecalis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58(9):5253–5261. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.00098-14
Wilt TJ, Bloomfield HE, MacDonald R, Nelson D, Rutks I, Ho M, Larsen G, McCall A, Pineros S, Sales A (2004) Effectiveness of statin therapy in adults with coronary heart disease. Arch Intern Med 164:1427–1436
Wu D, Fan W, Kishen A, Gutmann JL, Fan B (2014) Evaluation of the antibacterial efficacy of silver nanoparticles against Enterococcus Faecalis biofilm. J Endod 40:285–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2013.08.022
Xu Y, Shi Y, Lei F, Dai L (2020) A novel and green cellulose-based Schiff base-Cu (II) complex and its excellent antibacterial activity. Carbohydr Polym 230:115671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115671
Zeng M, Xu J, Luo Q, Hou C, Qiao S, Fu S, Fan X, Liu J (2020) Constructing antibacterial polymer nanocapsules based on pyridine quaternary ammonium salt. Mater Sci Eng C 108:110383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.110383
Funding
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81570969). The Funding body had no role in study design, collected data, analysis, or manuscript writing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JC and MD performed the experiments, acquisition of data and manuscript writing. QS helped collect and analyze data. WF is the corresponding author who designed the study, reviewed the manuscript and provided funding support. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, J., Duan, M., Sun, Q. et al. Simvastatin decreases the silver resistance of E. faecalis through compromising the entrapping function of extracellular polymeric substances against silver. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 36, 54 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-020-02830-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-020-02830-5