Abstract
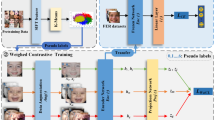
Deep learning based facial expression recognition becomes more successful in many applications. However, the lack of labeled data is still a bottleneck for better recognition performance. Thus, it is of practical significance to exploit the rich unlabeled data for training deep neural networks (DNNs). In this paper, we propose a novel discriminative deep association learning (DDAL) framework. The unlabeled data is provided to train the DNNs with the labeled data simultaneously, in a multi-loss deep network based on association learning. Moreover, the discrimination loss is also utilized to ensure intra-class clustering and inter-class centers separating. Furthermore, a large synthetic facial expression dataset is generated and used as unlabeled data. By exploiting association learning mechanism on two facial expression datasets, competitive results are obtained. By utilizing synthetic data, the performance is increased clearly.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wan M, Yang G, Gai S, Yang Z (2017) Two-dimensional discriminant locality preserving projections (2ddlpp) and its application to feature extraction via fuzzy set. Multimedia Tools Appl 76(1):355–371
Wan M, Li M, Yang G, Gai S, Jin Z (2014) Feature extraction using two-dimensional maximum embedding difference. Inf Sci 274:55–69
Wan M, Lai Z, Yang G, Yang Z, Zhang F, Zheng H (2017) Local graph embedding based on maximum margin criterion via fuzzy set. Fuzzy Sets Syst 318:120–131
Lai Z, Wong WK, Xu Y, Yang J, Zhang D (2015) Approximate orthogonal sparse embedding for dimensionality reduction. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 27(4):723–735
Lai Z, Xu Y, Chen Q, Yang J, Zhang D (2014) Multilinear sparse principal component analysis. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 25(10):1942–1950
Kahou SE, Pal C, Bouthillier X, Froumenty P, Gülçehre Ç, Memisevic R, Vincent P, Courville A, Bengio Y, Ferrari RC, et al. (2013) Combining modality specific deep neural networks for emotion recognition in video. In: Proceedings of the 15th ACM on International Conference on Multimodal Interaction ACM, pp 543–550
Levi G, Hassner T (2015) Emotion recognition in the wild via convolutional neural networks and mapped binary patterns. In: Proceedings of the 2015 ACM on International Conference on Multimodal Interaction ACM, pp 503–510
Zeng N, Zhang H, Song B, Liu W, Li Y, Dobaie AM (2018) Facial expression recognition via learning deep sparse autoencoders. Neurocomputing 273:643–649
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2012) Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp 1097–1105
Simonyan, K, Zisserman A (2014) Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556
Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y, Sermanet P, Reed S, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Vanhoucke V, Rabinovich A (2015) Going deeper with convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 1–9
Bazrafkan S, Nedelcu T, Filipczuk P, Corcoran P (2017) Deep learning for facial expression recognition: a step closer to a smartphone that knows your moods. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics (ICCE), pp 217–220
Kaya H, Gürpınar F, Salah AA (2017) Video-based emotion recognition in the wild using deep transfer learning and score fusion. Image Vision Comput 65:66–75
Knyazev B, Shvetsov R, Efremova N, Kuharenko A (2017) Convolutional neural networks pretrained on large face recognition datasets for emotion classification from video. arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.04598
Ding H, Zhou SK, Chellappa R (2017) Facenet2expnet: Regularizing a deep face recognition net for expression recognition. In: 2017 12th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2017), pp 118–126
Salimans T, Goodfellow I, Zaremba W, Cheung V, Radford A, Chen X (2016) Improved techniques for training gans. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 2234–2242
Radford A, Metz L, Chintala S (2015) Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1511.06434
Chang X, Nie F, Yang Y, Huang H (2014) A convex formulation for semi-supervised multi-label feature selection. In: AAAI, pp 1171–1177
Gao Y, Ma J, Yuille AL (2017) Semi-supervised sparse representation based classification for face recognition with insufficient labeled samples. IEEE Trans Image Process 26(5):2545–2560
Goodfellow I, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, Xu B, Warde-Farley D, Ozair S, Courville A, Bengio Y (2014) Generative adversarial nets. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 2672–2680
Lee DH (2013) Pseudo-label: The simple and efficient semi-supervised learning method for deep neural networks. In: Workshop on Challenges in Representation Learning, ICML, vol. 3, p 2
Wen J, Xu Y, Li Z, Ma Z, Xu Y (2018) Inter-class sparsity based discriminative least square regression. Neural Netw 102:36–47
Wen J, Fang X, Cui J, Fei L, Yan K, Chen Y, Xu Y (2018) Robust sparse linear discriminant analysis. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 29(2):390–403
Roesch EB, Tamarit L, Reveret L, Grandjean D, Sander D, Scherer KR (2011) Facsgen: a tool to synthesize emotional facial expressions through systematic manipulation of facial action units. J Nonverbal Behav 35(1):1–16
Ekman P, Rosenberg EL (1997) What the face reveals: basic and applied studies of spontaneous expression using the Facial Action Coding System (FACS). Oxford University Press, Oxford
Li J, Zhang D, Zhang J, Zhang J, Li T, Xia Y, Yan Q, Xun L (2017) Facial expression recognition with faster R-CNN. Procedia Comput Sci 107:135–140
Ren S, He K, Girshick R, Sun J (2015) Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In: Advances in neural information processing systems, pp 91–99
Hu P, Cai D, Wang S, Yao A, Chen Y (2017) Learning supervised scoring ensemble for emotion recognition in the wild. In: Proceedings of the 19th ACM International Conference on Multimodal Interaction, pp 553–560
Ji S, Xu W, Yang M, Yu K (2013) 3D convolutional neural networks for human action recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(1):221–231
Tran D, Bourdev L, Fergus R, Torresani L, Paluri M (2015) Learning spatiotemporal features with 3d convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 4489–4497
Pons G, Masip D (2018) Multi-task, multi-label and multi-domain learning with residual convolutional networks for emotion recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1802.06664
Cohen I, Sebe N, Cozman FG, Huang TS (2003) Semi-supervised learning for facial expression recognition. In: Proceedings of the 5th ACM SIGMM International Workshop on Multimedia Information Retrieval, pp 17–22
Zhang Z, Ringeval F, Dong B, Coutinho E, Marchi E, Schüller B (2016) Enhanced semi-supervised learning for multimodal emotion recognition. In: 2016 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp 5185–5189
Du C, Du C, Li J, Zheng Wl, Lu Bl, He H (2017) Semi-supervised bayesian deep multi-modal emotion recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1704.07548
Haeusser P, Mordvintsev A, Cremers D (2017) Learning by association–a versatile semi-supervised training method for neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 89–98
Haeusser P, Frerix T, Mordvintsev A, Cremers D (2017) Associative domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp 2765–2773
Cai J, Meng Z, Khan AS, Li Z, O’Reilly J, Tong Y (2018) Island loss for learning discriminative features in facial expression recognition. In: 2018 13th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition, pp 302–309
Langner O, Dotsch R, Bijlstra G, Wigboldus DH, Hawk ST, Van Knippenberg A (2010) Presentation and validation of the radboud faces database. Cognit Emotion 24(8):1377–1388
Zhao G, Huang X, Taini M, Li SZ, PietikäInen M (2011) Facial expression recognition from near-infrared videos. Image Vis Comput 29(9):607–619
Krinidis S, Pitas I (2006) Facial expression synthesis through facial expressions statistical analysis. In: 2006 14th European Signal Processing Conference, pp 1–5
Abbasnejad I, Sridharan S, Nguyen D, Denman S, Fookes C, Lucey S (2017) Using synthetic data to improve facial expression analysis with 3d convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 1609–1618
Zhou Y, Shi BE (2017) Photorealistic facial expression synthesis by the conditional difference adversarial autoencoder. In: 2017 Seventh International Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction (ACII), pp 370–376
Kulkarni TD, Whitney WF, Kohli P, Tenenbaum J (2015) Deep convolutional inverse graphics network. In: Advances in Neural information processing systems, pp 2539–2547
Dosovitskiy A, Tobias Springenberg J, Brox T (2015) Learning to generate chairs with convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 1538–1546
King DE (2009) Dlib-ml: a machine learning toolkit. J Mach Learn Res 10(Jul):1755–1758
Sagonas C, Antonakos E, Tzimiropoulos G, Zafeiriou S, Pantic M (2016) 300 faces in-the-wild challenge: database and results. Image Vis Comput 47:3–18
Liu W, Zhang H, Tao D, Wang Y, Lu K (2016) Large-scale paralleled sparse principal component analysis. Multimedia Tools Appl 75(3):1481–1493
Sun W, Zhao H, Jin Z (2017) An efficient unconstrained facial expression recognition algorithm based on stack binarized auto-encoders and binarized neural networks. Neurocomputing 267:385–395
Moeini A, Moeini H (2015) Multimodal facial expression recognition based on 3D face reconstruction from 2D images. In: Face and facial expression recognition from real world videos, Springer, pp 46–57
Sun W, Zhao H, Jin Z (2018) A visual attention based roi detection method for facial expression recognition. Neurocomputing 296:12–22
Scovanner P, Ali S, Shah M (2007) A 3-dimensional sift descriptor and its application to action recognition. In: Proceedings of the 15th ACM international conference on Multimedia, pp 357–360
Cugu I, Sener E, AkbaS E (2017) Microexpnet: An extremely small and fast model for expression recognition from frontal face images. arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.07011
Klaser A, Marszałek M, Schmid C (2008) A spatio-temporal descriptor based on 3d-gradients. In: BMVC 2008-19th British Machine Vision Conference. British Machine Vision Association, p 275-1
Jung H, Lee S, Yim J, Park S, Kim J (2015) Joint fine-tuning in deep neural networks for facial expression recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 2983–2991
Acknowledgements
This work is partially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 61872188, U1713208, 61602244, 61672287, 61702262, 61773215. Meanwhile, this work is partially supported by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation under Grant No.2018M643183.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, X., Sun, W. & Jin, Z. A discriminative deep association learning for facial expression recognition. Int. J. Mach. Learn. & Cyber. 11, 779–793 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-019-01024-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-019-01024-2