Abstract
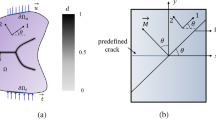
This study presents a crack phase-field approach for anisotropic continua to model, in particular, fracture of fiber-reinforced matrix composites. Starting with the variational formulation of the multi-field problem of fracture in terms of the deformation and the crack phase fields, the governing equations feature the evolution of the anisotropic crack phase-field and the balance of linear momentum, presented for finite and small strains. A recently proposed energy-based anisotropic failure criterion is incorporated into the model with a constitutive threshold function regulating the crack initiation in regard to the matrix and the fibers in a superposed framework. Representative numerical examples are shown for the crack initiation and propagation in unidirectional fiber-reinforced polymer composites under Mode-I, Mode-II and mixed-mode bending. Model parameters are obtained by fitting to sets of experimental data. The associated finite element results are able to capture anisotropic crack initiation and growth in unidirectional fiber-reinforced composite laminates.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
ASTM International (2001) ASTM D6671-01 standards test method for mixed mode I-mode II interlaminar fracture toughness of unidirectional fiber reinforced polymer matrix composites. ASTM International, West Conshohocken
Alessi R, Freddi F (2017) Phase-field modelling of failure in hybrid laminates. Compos Struct 181:9–25
Ambati M, Gerasimov T, De Lorenzis L (2015) Phase-field modeling of ductile fracture. Comput Mech 55:1017–1040
Arteiro A, Catalanotti G, Reinoso J, Linde P, Camanho PP (2019) Simulation of the mechanical response of thin-ply composites: from computational micro-mechanics to structural analysis. Arch Comput Methods Eng 26:1445–1487
Argon AS (1972) Fracture of composites. Treatise Mater Sci Technol 1:79–114
Azzi VD, Tsai SW (1965) Anisotropic strength of composites. Exp Mech 5:283–288
Betten J (1987) Formulation of anisotropic constitutive equations. In: Boehler JP (ed) Applications of tensor functions in solid mechanics. Springer, Wien, pp 228–250 CISM Courses and Lectures no. 292
Borden MJ, Hughes TJR, Landis CM, Anvari A (2016) A phase-field formulation for fracture in ductile materials: Finite deformation balance law derivation, plastic degradation, and stress triaxiality effects. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 312:130–166
Boehler JP (1979) A simple derivation of representations for non-polynomial constitutive equations in some cases of anisotropy. ZAMM Z Angew Math Mech 59:157–167
Cahn JW, Hilliard JE (1958) Free energy of a nonuniform system. I. Interfacial free energy. J Chem Phys 28:258–267
Clayton JD, Knap J (2015) Phase field modeling of directional fracture in anisotropic polycrystals. Comput Mater Sci 98:158–169
Crews JH Jr, Reeder JR (1988) A mixed-mode bending apparatus for delamination testing. NASA TM, 100662. Technical Report
Cuntze RG (2006) Efficient 3D and 2D failure conditions for UD laminae and their application within the verification of the laminate design. Compos Sci Technol 66:1081–1096
Dal H, Gültekin O, Denli FA, Holzapfel GA (2017) Phase-field models for the failure of anisotropic continua. Proc Appl Math Mech 17:91–94
Francfort GA, Marigo J-J (1998) Revisiting brittle fracture as an energy minimization problem. J Mech Phys Solids 46:1319–1342
Griffith AA (1921) The phenomena of rupture and flow in solids. Philos Trans R Soc A 221:163–197
Grogan DM, Leen SB, Brádaigh CMÓ (2014) An XFEM-based methodology for fatigue delamination and permeability of composites. Compos Struct 107:205–218
Gültekin O, Dal H, Holzapfel GA (2016) A phase-field approach to model fracture of arterial walls: Theory and finite element analysis. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 312:542–566
Gültekin O, Dal H, Holzapfel GA (2018) Numerical aspects of failure in soft biological tissues favor energy-based criteria: a rate-dependent anisotropic crack phase-field model. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 331:23–52
Hashin Z (1980) Failure criteria for unidirectional fiber composites. J Appl Mech 47:329–334
Hashin Z (1996) Finite thermoelastic fracture criterion with application to laminate cracking analysis. J Mech Phys Solids 44:1129–1145
Hill R (1998) The mathematical theory of plasticity. Oxford University Press, New York
Holzapfel GA (2000) Nonlinear solid mechanics. A continuum approach for engineering. Wiley, Chichester
Holzapfel GA, Gasser TC, Ogden RW (2000) A new constitutive framework for arterial wall mechanics and a comparative study of material models. J Elast 61:1–48
Li B, Peco C, Millán D, Arias I, Arroyo M (2015) Phase-field modeling and simulation of fracture in brittle materials with strongly anisotropic surface energy. Int J Numer Methods Eng 102:711–727
Marsden JE, Hughes TJR (1994) Mathematical foundations of elasticity. Dover, New York
Miehe C, Welschinger F, Hofacker M (2010) Thermodynamically consistent phase-field models of fracture: variational principles and multi-field FE implementations. Int J Numer Methods Eng 83:1273–1311
Miehe C, Hofacker M, Welschinger F (2010) A phase field model for rate-independent crack propagation: robust algorithmic implementation based on operator splits. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 199:2765–2778
Miehe C, Schänzel LM, Ulmer H (2015) Phase field modeling of fracture in multi-physics problems. Part I. Balance of crack surface and failure criteria for brittle crack propagation in thermo-elastic solid. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 294:449–485
Miehe C, Hofacker M, Schänzel LM, Aldakheel F (2015) Phase field modeling of fracture in multi-physics problems. Part II. Coupled brittle-to-ductile failure criteria and crack propagation in thermo-elastic-plastic solids. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 294:486–522
Miehe C, Dal H, Schänzel LM, Raina A (2016) A phase-field model for chemo-mechanical induced fracture in lithium-ion battery electrode particles. Int J Numer Methods Eng 106:683–711
Nairn JA (1989) The strain-energy release rate of composite microcracking-a variational approach. J Compos Mater 23:1106–1129
Naghipour P, Bartsh M, Voggenreiter H (2011) Simulation and experimental validation of mixed mode delamination in multidirectional CF/PEEK laminates under fatigue loading. Int J Solids Struct 48:1070–1081
Naghipour P (2011) Numerical simulations and experimental investigations on quasi-static and cyclic mixed mode delamination of multidirectional CFRP laminates. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Stuttgart
Naghipour P, Schneider J, Bartsch M, Hausmann J, Voggenreiter H (2009) Fracture simulation of CFRP laminates in mixed mode bending. Eng Fract Mech 76:2821–2833
Nguyen T-T, Réthéro J, Yvonnet J, Baietto M-C (2017) Multi-phase-field modeling of anisotropic crack propagation for polycrystalline materials. Comput Mech 60:289–314
Puck A, Schürmann H (1998) Failure analysis of FRP laminates by means of physically based phenomenological models. Compos Sci Technol 58:1045–1067
Qiu G, Pence T (1997) Remarks on the behavior of simple directionally reinforced incompressible nonlinearly elastic solids. J Elast 49:1–30
Reinoso J, Arteiro A, Paggi M, Camanho PP (2017) Strength prediction of notched thin ply laminates using finite fracture mechanics and the phase field approach. Compos Sci Technol 58:205–216
Schreiber C, Kuhn C, Müller R (2018) Phase field modeling of brittle fracture in materials with anisotropic fracture resistance. PAMM 18:e201800113
Schröder J, Neff P (2003) Invariant formulation of hyperelastic transverse isotropy based on polyconvex free energy functions. Int J Solids Struct 40:401–445
Soden PD, Hinton MJ, Kaddour AS (2004) Lamina properties, lay-up configurations and loading conditions for a range of fibre reinforced composite laminates. In: Hinton M, Soden PD, Kaddour A-S (eds) Failure criteria in fibre-reinforced polymer composites. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 30–51
Spencer A (1972) Deformations of fibre-reinforced materials. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Teichtmeister S, Kienle D, Aldakheel F, Keip M-A (2017) Phase-field modeling of fracture in anisotropic brittle solids. Int J Non-Linear Mech 97:1–21
Talreja R, Singh CV (2012) Damage and failure of composite materials. Cambridge University Press, New York
Talreja R (2014) Assessment of the fundamentals of failure theories for composite materials. Compos Sci Technol 105:190–201
Tsai SW, Wu EM (1971) General theory of strength for anisotropic materials. J Compos Mater 5:58–80
Turon A, Dávila CG, Camanho PP, Costa J (2007) An engineering solution for mesh size effects in the simulation of delamination using cohesive zone models. Eng Fract Mech 74:1665–1682
von Mises R (1913) Mechanik der festen Körper im plastisch deformablen Zustand. Göttin Nachr Math Phys 1:582–592
Wang Y, Waisman H (2015) Progressive delamination analysis of composite materials using XFEM and a discrete damage zone mode. Comput Mech 55:1–26
Wolfe WE, Butalia TS (1998) A strain-energy based failure criterion for non-linear analysis of composite laminates subjected to biaxial loading. Compos Sci Technol 58:1107–1124
Yang Q, Cox B (2005) Cohesive models for damage evolution in laminated composites. Int J Fract 133:107–137
Yazdani S, Rust WJH, Wriggers P (2016) An XFEM approach for modelling delamination in composite laminates. Compos Struct 135:353–364
Zhao L, Gong Y, Zhang J, Chen Y, Fei B (2016) Simulation of delamination growth in multidirectional laminates under mode I and mixed mode I/II loadings using cohesive elements. Compos Struct 116:509–522
Acknowledgements
H.D. gratefully acknowledges the financial support from Tübitak grant scheme Bideb 2232 under Grant Number 114C073.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Denli, F.A., Gültekin, O., Holzapfel, G.A. et al. A phase-field model for fracture of unidirectional fiber-reinforced polymer matrix composites. Comput Mech 65, 1149–1166 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-019-01812-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00466-019-01812-1