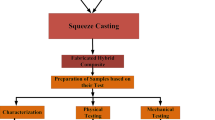
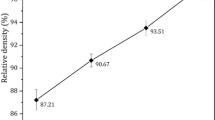
Aluminum matrix composites reinforced with boron carbide are a kind of materials that are widely used because of high strength, low density, and improved tribological properties. In this study, mechanical properties of Al 6061–B4C composites reinforced with B4C of three different particle sizes were investigated. In the Al 6061–B4C composite materials, produced by the powder metallurgy methods (extrusion of billets obtained by sintering at temperature of 550°C under pressure of 450 MPa), the change of mechanical properties such as hardness, compressive strength, and fatigue life, related to B4C particle size and the applied heat treatment mode (aging at 180°C for 5 h), were investigated. The hardness of the materials is increased with B4C grain size and the heat treatment. After the heat treatment, the fatigue life of Al 6061–B4C (3 μm) material increases slightly, while that of the composite materials decreases with larger size of B4C reinforcement. The fatigue life of the composite materials reinforced with a larger grain size B4C is reduced by heat treatment. While the compression test data of untreated composite materials were similar to each other, the heat treatment increased these values in all samples. The highest increase in the compression strength was observed in the composite reinforced with 17 μm sized B4C. The addition of graphite reduces the deformation ability of the composites.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.M. Mohanty, K. Balasubramian, and S.K. Seshadri, “Boron carbide-reinforced alumnium 1100 matrix composites: Fabrication and properties,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 498, No. 1, 42–52 (2008).
K. Shirvanimoghaddam, H. Khayyam, H. Abdizadeh, M.K. Akbari, A.H. Pakseresht, E. Ghasali, and M. Naebe, “Boron carbide reinforced aluminium matrix composite: Physical, mechanical characterization and mathematical modelling,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 658, 135–149 (2016).
P. Liu, A. Wang, J. Xie, and S. Hao, “Characterization and evaluation of interface in SiCp/2024 Al composite,” Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 25, No. 5, 1410–1418 (2015).
B. Li, B.H. Luo, K. He, L. Zeng, W. Fan, and Z.H. Bai, “Effect of aging on interface characteristics of Al– Mg–Si/SiC composites,” J. Alloy Compd., 649, 495–499 (2015).
S. Spigarelli, M. Cabibbo, E. Evangelista, and T.G. Langdon, “Creep properties of an Al-2024 composite reinforced with SiC particulates,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 328, Nos. 1–2, 39–47 (2002).
A. Pakdel, A. Witecka, G. Rydzek, D.N.A. Shri, and V. Nicolassi, “A comprehensive analysis of extrusion behavior, microstructural evolution, and mechanical properties of 6063 Al–B4C composites produced by semisolid stir casting,” Mater. Sci. Eng. A., 721, 28–37 (2018).
A. Nieto, H. Yang, L. Jiang, and J.M. Schoenung, “Reinforcement size effects on the abrasive wear of boron carbide reinforced aluminum composites,” Wear, 390–391, 228–235 (2017).
Z. Zhou, G. Wu, L. Jiang, R. Li, and Z. Xu, “Analysis of morphology and microstructure of B4C/2024Al composites after 7.62 mm ballistic impact,” Mater. Des.63, 658–663 (2014).
I. Sudhakar, G.M. Reddy, and K.S. Rao, “Ballistic behavior of boron carbide reinforced AA7075 aluminium alloy using friction stir processing—An experimental study and analytical approach,” Def. Technol., 12, No. 1, 25–31 (2016).
R. Gunes, and K. Arslan, “Experimental damage evaluation of honeycomb sandwich structures with Al/B4C FGM face plates under high velocity impact loads,” Compos. Struct., 202, 304–312 (2018).
I. Topcu, H.O. Gulsoy, N. Kadioglu, and A.N. Gulluoglu, “Processing and mechanical properties of B4C reinforced Al matrix composites,” J. Alloys Compd., 482, 516–521 (2009).
A. Baradeswaran, S.C. Vettivel, A.E. Perumal, N. Selvakumar, and R.F. Issac, “Experimental investigation on mechanical behaviour, modelling and optimization of wear parameters of B4C and graphite reinforced aluminium hybrid composites,” Mater. Des.,63, 620–632 (2014).
K. Shirvanimoghaddam, H. Khayyam, H. Abdizadeh, M. K. Akbari, A. H. Pakseresht, F. Abdi, A. Abbasi, and M. Naebe, “Effect of B4C, TiB2 and ZrSiO4 ceramic particles on mechanical properties of aluminium matrix composites: Experimental investigation and predictive modeling,” Ceram. Int., 42, No. 5, 6206– 6220 (2016).
Y. Li, Q. Li, D. Li, W Liu, and G. Shu, “Fabrication and characterization of stir casting AA6061–31% B4C composite”, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 26, No. 9, 2304–2312 (2016).
H. Alihosseini, K. Dehghani, and J. Kamali, “Microstructure characterization, mechanical properties, compressibility and sintering behavior of Al–B4C nanocomposite powders”, Adv. Powder Technol., 28, No. 9, 2126–2134 (2017).
A. Alizadeh, A. Abdollahi, and M.J. Radfar, “Processing, characterization, room temperature mechanical properties and fracture behavior of hot extruded multi-scale B4C reinforced 5083 aluminum alloy based composites,” Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 27, No. 6, 1233–1247 (2017). 558
A.V. Pozdniakov, V.S. Zolotorevskiy, R.Yu. Barkov, A. Lotfy, and A.I. Bazlov, “Microstructure and material characterization of 6063/B4C and 1545K/B4C composites produced by two stir casting techniques for ≤nuclear applications,” J. Alloys Compd., 664, 317–320 (2016).
N. Panwar and A. Chauhan, “Fabrication methods of particulate reinforced aluminium metal matrix composite-A review”, Mater. Today, 5, No. 2, 5933–5939 (2018).
P.R. Jadhav, B.R. Sridhar, M. Nagaral, and J.I. Harti, “Evaluation of mechanical properties of B4C and graphite particulates reinforced A356 alloy hybrid composites,” Mater. Today, 4, No. 9, 9972-9976 (2017).
I. Aatthisugan, A.R. Rose, and D.S. Jebadurai, “Mechanical and wear behaviour of AZ91D magnesium matrix hybrid composite reinforced with boron carbide and graphite,” J. Magnes. Alloy, 5, No. 1, 20–25 (2017).
T. Haskel, G.O. Verran, and R. Barbieri, “Rotating and bending fatigue behavior of A356 aluminum alloy: Effects of strontium addition and T6 heat treatment,” Int. J. Fatigue, 114, 1–10 (2018).
L. Tang, H. Sang, J. Song, Z. Luo, and Y. Sun, “Mechanical model for failure modes of rock and soil under compression,” Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 26, No. 10, 2711–2723 (2016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Poroshkova Metallurgiya, Vol. 58, Nos. 9–10 (529), pp. 69–78, 2019.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goçer, A., Karamiş, M.B. Fatigue and Compression Characteristics of Al 6061–B4c Composite Materials. Powder Metall Met Ceram 58, 550–558 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-020-00109-w
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-020-00109-w